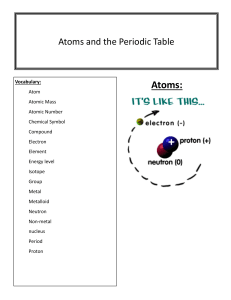
Name__________________________________________ Atoms Worksheet #1 Average Atomic Mass Problems Average atomic mass: the weighted average of the masses of all the isotopes of that element. A weighted average reflects both the mass and the abundance of the isotopes as they occur in nature. Isotope Atomic mass abundance (%) H-1 1.0078amu 99.985% H-2 2.0141amu 0.015% H-3 3.0160amu negligible The average atomic mass of hydrogen is 1.0079amu. Multiply each atomic mass by the percent abundance and add them up. (1.0078amu)(.99985) + (2.0141amu)(0.00015) = 1.0079amu Fill in the missing information. Calculate the average atomic mass of each element (show work). 1. Carbon Nuclear Symbol-Mass # % Abundance Mass of Atom # protons # electrons # neutrons Symbol 12 C-12 98.93% 12.00amu C 6 C-13 1.07% 13.00amu negligible 14.00amu 6 8 Average Atomic Mass of Carbon=____________ 2. Potassium Symbol-Mass # % Abundance Mass of Atom K-39 93.26% 38.96amu # protons # electrons # neutrons Nuclear Symbol 39 K 19 K-40 0.01% 39.96amu 6.73% 40.96amu Average Atomic Mass of Potassium=____________ 19 22 3. Nitrogen Symbol-Mass # % Abundance Mass of Atom N-14 99.632% 14.00amu 0.0368% 15.00amu # protons # electrons 7 # neutrons Nuclear Symbol 8 Average Atomic Mass of Nitrogen=____________ 4. Chlorine Symbol-Mass # % Abundance Mass of Atom Cl-35 75.78% 34.97amu 24.22% 36.97amu # protons # electrons 17 # neutrons Nuclear Symbol 20 Average Atomic Mass of Chlorine=____________ 5. Oxygen Symbol-Mass # % Abundance Mass of Atom O-16 99.757% 15.99amu O-17 0.038% 16.99amu O-18 0.205% 18.00amu Average Atomic Mass of Oxygen=____________ # protons # electrons # neutrons Nuclear Symbol 6. Silver Symbol-Mass # % Abundance Mass of Atom Ag-107 51.839% 106.91amu 48.161% 108.90amu # protons # electrons # neutrons 47 Nuclear Symbol 62 Average Atomic Mass of Silver=____________ 7. Copper Symbol-Mass # % Abundance Mass of Atom Cu-63 69.17% 62.93amu Cu-65 30.83% 64.93amu # protons # electrons # neutrons Nuclear Symbol Average Atomic Mass of Copper=____________ 8. Counting Atoms – How many atoms are in the following compounds? a) CaCl2_______ b) NH4OH_______ c) NaCl_______ d) N2O7_______ e) P2O5_______ f) Zn(NO3)2_______ g) Al2(CO3)3_______ h) 4 Na3PO4_______ i) 3 Mg(NO3)2_______ j) 6 C6H12O6_______ k) 8 (NH4)2Cr2O7_______ 9. Element Z has 2 natural isotopes. One isotope has a of 15.0amu and has a relative abundance of 30%. The other isotope has a mass of 16.0amu and has a relative abundance of 70%. Estimate the average atomic mass for this element to one decimal place. 10. Three isotopes of argon occur in nature – Ar-36, Ar-38, Ar-40. Calculate the average atomic mass of argon to two decimal places, given the following relative atomic masses and abundances of each of the isotopes: Ar36 (35.97amu; 0.337%), Ar-38 (37.96amu; 0.063%), and Ar-40 (39.96amu; 99.600%). 11. Naturally occurring boron is 80.20% boron-11 (atomic mass = 11.01amu) and 19.80% of some other isotopic form of boron. What must the atomic mass of this second isotope be in order to account for the 10.81amu average atomic mass of boron? (Write the answer to two decimal places.) Atoms Worksheet #2 (The Mole) 1. Counting Atoms – How many atoms are in the following compounds? a) CaCl2_______ b) NH4OH_______ c) NaCl_______ d) N2O7_______ f) Zn(NO3)2_______ g) Al2(CO3)3_______ h) 4 Na3PO4_____ e) P2O5_______ i) 3 Mg(NO3)2_______ 2. Calculate the molar mass of the following compounds: a) Na3PO4____________________ b) Fe2O3____________________ d) (NH4)2SO4____________________ e) Ca3(PO4)2____________________ c) Mg(OH)2____________________ 3. Mole-to-Gram/Gram-to-Mole Conversions (One Step Problems) a) How many grams of CaI2 are present in 3.28 moles? b) How many grams of SO2 are present in 5.39 moles? c) How many moles of AgCl are there in 4.98 gram? d) How many moles of MgS are present in 3.03 x 10-2 grams? 4. Conversions using Avogadro’s number (One Step Problems) a) How many atoms are present in 34.69 moles of Mg? b) How many atoms are present in 0.529 moles of Li? c) How many moles of Mn3P2 are present in 4.09 x 1024 particles of Mn3P2? d) How many moles of NiS are present in 5.88 x 1019 particles? ↔ ↔ 5. Grams Moles Particles OR Atoms OR Molecules (Two Step Problems) a) Calculate the number of molecules in 8.33 grams of O2 b.) Calculate the number of atoms in 43.33 grams of iron, Fe? c) Calculate the number of particles in 32.8 grams of Cu2S. e) Calculate the number of grams of Li2NO3 in 5.44 x 1021 particles of lithium nitrate. f) Calculate the number of grams of SO3 in 3.92 x 1025 molecules of sulfur trioxide. Atoms Worksheet #3 (More Practice Problems) SHOW ALL WORK USING DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS!!!!! l. Calculate the following: a. molecules in 5.00 moles of nitrogen gas, N2 b. molecules in 8.78 moles of oxygen gas, O2 c. particles in 4.89 moles of calcium chloride, CaCl2 d. atoms in 6.0 moles of nitrogen gas, N2 e. ions of chlorine in 3.0 moles of magnesium chloride, MgCl2 2. Calculate the number of grams represented by the following: a. 3.0l X l023 particles of sodium hydroxide, NaOH b. l.20 X l024 atoms of sulfur c. 3.99 X l0l8 particles of ammonium carbonate (NH4)2CO3 d. l.44 X l026 molecules of carbon dioxide CO2 3. How many particles are there in 2.73 X l0-2 moles of magnesium iodide, MgI2? 4. How many moles of SO3 are in 2.4 X l024 molecules of SO3? 5. The chemical formula for aspirin is C9H8O4. What is the mass in grams of 0.40 moles of aspirin? 6. How many particles are there in 2.4 pounds of calcium acetate, Ca(C2H3O2)2? (1 pound = 454 grams) 7. How much would l.00 X l026 atoms of aluminum weigh in pounds? (1 pound = 454 grams) 8. 65.3 grams of lithium oxide, Li2O, would contain how many lithium ions? 9. A sample of potassium sulfide, K2S, contains 7.00X1026 ions of potassium. What is the mass in grams of this sample? Atoms Test Review Read (and understand) notes and be able to complete all mole problems from the Atoms Worksheets. 1._____How many neutrons in an atom with an atomic number of 42 and mass number of 96. 2._____How many electrons are present in an atom of mercury-201? 3._____Calculate the number of protons in an atom with a mass number of 19 and 10 neutrons. 4._____How many electrons are in an atom with a mass number of 75 and 42 neutrons. 5. How did the results of the gold foil experiment lead Rutherford to recognize the existence of the atomic nuclei? 6. Explain why atoms are neutral. 7._____Which has less mass: an electron or a proton? 8. What information about an atom is provided by the atoms atomic number? The atoms mass number? 9. Write the complete nuclear symbols for isotopes of uranium that have 142 neutrons, 143 neutrons, and 146 neutrons. 10. _____Write the nuclear symbol and hyphen notation for two isotopes of carbon. Both isotopes have six protons. One isotope has six neutrons, while the other has seven neutrons. 11._____All barium atoms have 56 protons. One isotope of barium has 74 neutrons, and another isotope has 81 neutrons. Write the nuclear symbols for these two isotopes of barium. 12._____Precidt which isotope of nitrogen is more commonly found, nitrogen-14 or nitrogen-15. 13._____Write the nuclear symbol for the following ion: 25 protons, 28 electrons, and 30 neutrons. 14. Explain why different atoms of the same element always have the same atomic number but can have different mass numbers. 15. What is an ion? 16. What are the charges of an electron, a proton, and a neutron? 17. State the law of conservation of mass, law of determine proportions, and law of multiple proportions. 18. Calculate the average atomic mass for each of the following elements assuming that each consists of the isotopic mixture shown. (A) 99.76% Oxygen-16, 0.04% Oxygen-17, 0.20% Oxygen-18 (B) 96.941% Calcium-40, 0.647% Calcium-42, 0.135%Calcium-43, 2.086% Calcium-44, 0.004% Calcium-46, 0.187% Calcium-48 (C) 51.83% Silver-107, 48.175 Silver-109 19. Understand the modern atomic theory including Daltons’ Postulates, Thomson’s discovery of electron properties, Rutherford’s nuclear atom, and Bohr’s nuclear atom.