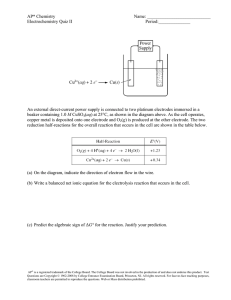
IB Topics 9 & 19 Multiple Choice Practice 1. What are the oxidation states of chromium in (NH4)2Cr2O7 (s) and Cr2O3 (s)? 2. Which of the following is a redox reaction? A. 3Mg (s) + 2AlCl3 (aq) → 2Al (s) + 3MgCl2 (aq) B. SiO2 (s) + 2NaOH (aq) → Na2SiO3 (aq) + H2O (l) C. KCl (aq) + AgNO3 (aq) → AgCl (s) + KNO3 (aq) D. 2NaHCO3 (aq) → Na2CO3 (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l) 3. What is the reaction type and major product at the anode (positive electrode) when molten sodium chloride is electrolysed using platinum electrodes? 4. What is the order of decreasing reactivity of the metals (most reactive first)? Zn(s) + Sn2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Sn(s) Cu(s) + Zn2+(aq) → No Reaction Sn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Sn2+(aq) + Cu(s) Ag(s) + Cu2+(aq) → No Reaction A. Zn > Cu > Sn > Ag B. Sn > Zn > Ag > Cu C. Ag > Cu > Zn > Sn D. Zn > Sn > Cu > Ag 5. What is the oxidation half-equation in the redox reaction? 2S2O32–(aq) + I2(aq) → S4O62–(aq) + 2I–(aq) A. I2(aq) + 2e– → 2I–(aq) B. 2I–(aq) → I2(aq) + 2e– C. 2S2O32–(aq) → S4O62–(aq) + 2e– D. S4O62–(aq) + 2e– → 2S2O32–(aq) 1 6. Which statements are correct for a voltaic cell? A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 7. Which of the following does not react with dilute HCl(aq)? A. Na2CO3 B. Cu C. Zn D. CuO 8. Which element is reduced in the following decomposition? (NH4)2Cr2O7(s) → N2(g) + Cr2O3(s) + 4H2O(g) A. N B. H C. Cr D. O 9. Which of the following is not a redox reaction? A. CH4(g) + Cl2(g) → CH3Cl(g) + HCl(g) B. C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) C. 2CO(g) → CO2(g) + C(s) D. CH3COOH(aq) + NaOH(aq) → CH3COONa(aq) + H2O(l) 10. What occurs at the anode (positive electrode) during the electrolysis of molten strontium bromide? A. Formation of bromine and oxidation B. Formation of bromine and reduction C. Formation of strontium and oxidation D. Formation of strontium and reduction 11. Consider the following half-equations: I2 (s) + 2e– 2I– (aq) Eθ = +0.54 V (brown) (colourless) MnO4– (aq) + 8H+ (aq) + 5e– Mn2+ (aq) + 4H2O (l) Eθ = +1.51 V (purple) (colourless) Which statement is correct for the reaction between KMnO4 (aq) and KI (aq) in acidic conditions? A. MnO4– reduces I– to I2. B. I– reduces MnO4– to Mn2+. C. The colour changes from brown to purple. D. MnO4– is oxidized to Mn2+. 2 12. What are the products when an aqueous solution of copper(II) sulfate is electrolysed using inert graphite electrodes? 13. Which change represents oxidation? A. HClO4 to HClO3 B. N2 to NH3 C. N2O to NO D. SO42− to SO32− 14. A reaction takes place when a rechargeable battery is used: Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2SO42−(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l) Which statements are correct? I. H+ is reduced II. The oxidation state of Pb metal changes from 0 to +2 III. PbO2 is the oxidising agent A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 15. Which statement is correct for the overall reaction in a voltaic cell? 2AgNO3(aq) + Ni(s) → 2Ag(s) + Ni(NO3)2(aq) E θ= +1.06 V A. Electrons flow from Ag electrode to Ni electrode. B. Ni is oxidized to Ni2+ at the cathode (negative electrode). C. Ag+ is reduced to Ag at the anode (positive electrode). D. Ag has a more positive standard electrode potential value than Ni. 16. In the electrolysis of aqueous potassium nitrate, KNO3(aq), using inert electrodes, 0.1 mol of a gas was formed at the cathode (negative electrode). Which is correct? 17. Which element is reduced in the following decomposition? (NH4)2Cr2O7(s) → N2(g) + Cr2O3(s) + 4H2O(g) A. N B. H C. Cr D. O 3 18. What is the standard half-cell potential of copper if the “zero potential reference electrode” is changed from the standard hydrogen electrode to a standard zinc electrode? A. –1.1 B. –0.34 C. +0.34 D. +1.1 19. What are the relative volumes of gas given off at E and F during electrolysis of the two cells in series? Assume all electrodes are inert. A. 1:1 B. 1:2 C. 2:1 D. 5:2 20. Which compounds can be reduced? I. C2H4 II. CH3COOH III. CH3CHO A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 21. Which experimental methods could be used to observe the progress of the following reaction? Cr2O72-(aq) + 6I-(aq) + 14H+(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 3I2(aq) + 7H2O(l) I. Change in colour II. Change in mass III. Change in electrical conductivity A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 22. Which is a correct statement for the reaction below? 2MnO4-(aq) + 6H+(aq) + 5NO2-(aq) → 2Mn2+(aq) + 5NO3-(aq) + 3H2O(l) A. MnO4- is the reducing agent and the oxidation number of Mn increases. B. MnO4- is the oxidizing agent and the oxidation number of Mn decreases. C. NO2- is the reducing agent and the oxidation number of N decreases. D. NO2- is the oxidizing agent and the oxidation number of N increases. 4 23. Applying IUPAC rules, what is the name of MnO2? A. Magnesium(II) oxide B. Manganese(II) oxide C. Magnesium(IV) oxide D. Manganese(IV) oxide 24. Which statement is correct for a voltaic but not for an electrolytic cell? A. An electrolyte is required. B. The anode is where oxidation occurs. C. Ions move in the electrolyte. D. Electrons flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode. 25. A voltaic cell is constructed from zinc and copper half-cells. Zinc is more reactive than copper. Which statement is correct when this cell produces electricity? A. Electrons flow from the copper half-cell to the zinc half-cell. B. The concentration of Cu2+ (aq) increases. C. Electrons flow through the salt bridge. D. Negative ions flow through the salt bridge from the copper half-cell to the zinc half-cell. 26. Which are necessary conditions for the standard hydrogen electrode to have an EΘ of exactly zero? I. Temperature = 298 K II. [H+]=1 moldm−3 III. A. B. C. D. [H2]=1 moldm−3 I and II only I and III only II and III only I, II and III 27. Which statement is correct for a voltaic but not for an electrolytic cell? A. An electrolyte is required. B. The anode is where oxidation occurs. C. Ions move in the electrolyte. D. Electrons flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode. 28. Which compound forms both hydrogen and oxygen at the electrodes when a concentrated aqueous solution is electrolyzed? A. KI B. NaCl C. H2SO4 D. AgNO3 5 29. Which signs for both Eθcell and ΔGθresult in a spontaneous redox reaction occurring under standard conditions? 30. z mol of copper is deposited from CuSO4 (aq) by a current, I, in time t. What is the amount of silver, in mol, deposited by electrolysis from AgNO3 (aq) by a current, , in time 2t? A. B. C. z D. 2z 31. An iron rod is electroplated with silver. Which is a correct condition for this process? A. The silver electrode is the positive electrode. B. The iron rod is the positive electrode. C. The electrolyte is iron(II) sulfate. D. Oxidation occurs at the negative electrode. 32. Which represents a redox reaction? A. B. C. D. 33. Which species can oxidize ethanol to ethanoic acid? A. B. Fe C. D. Acidified 34. Two half-cells are connected via a salt bridge to make a voltaic cell. Which statement about this cell is correct? A. Oxidation occurs at the positive electrode (cathode). B. It is also known as an electrolytic cell. C. Ions flow through the salt bridge. D. It requires a power supply to operate. 6 35. What are the oxidation states of each element in ? 36. What is the coefficient for I– when the following equation is balanced using the smallest possible whole numbers? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 5 ___ ___ ___ ___ 37. A voltaic cell is made by connecting a copper half-cell, , to an iron half-cell . Which combination correctly identifies the positive electrode and the species being oxidized? 38. Which represents a redox reaction? A. B. C. D. 7 39. Two half-cells are connected via a salt bridge to make a voltaic cell. Which statement about this cell is correct? A. Oxidation occurs at the positive electrode (cathode). B. It is also known as an electrolytic cell. C. Ions flow through the salt bridge. D. It requires a power supply to operate. 40. Which signs are correct for a spontaneous redox reaction? 41. Consider the standard electrode potentials: What is the standard cell potential, in V, for the reaction? A. B. C. D. 42. Which is a redox reaction? A. B. C. D. 43. The standard electrode potentials for three reactions involving copper and copper ions are: Which statement is correct? A. ions are a better oxidizing agent than ions. B. Copper metal is a better reducing agent than ions. C. ions will spontaneously form copper metal and ions in solution. D. Copper metal can be spontaneously oxidized by ions to form ions. 8 44. The same quantity of electricity is passed through separate dilute aqueous solutions of sulfuric acid and copper(II) sulfate using platinum electrodes under the same conditions. Which statement is correct? A. The same volume of oxygen is obtained in both cases. B. The same volume of hydrogen is obtained in both cases. C. The amount of copper deposited at the negative electrode in the copper(II) sulfate solution is half the amount of hydrogen gas formed at the negative electrode in the sulfuric acid solution. D. The pH of both solutions increases as the electrolysis proceeds. 45. Which species of vanadium has a different oxidation number from the rest? A. B. C. D. 46. Which statement is correct for the following reaction? A. is the oxidizing agent and it undergoes reduction. B. C. D. is the reducing agent and it undergoes oxidation. is the oxidizing agent and it undergoes oxidation. is the reducing agent and it undergoes reduction. 47. Which statement about an electrolytic cell is correct? A. Chemical energy is converted to electrical energy. B. Electrons move through the electrolyte. C. The cathode is the negative electrode. D. The negative ions move towards the negative electrode. 48. At which side of the equation are electrons, ions and needed to complete the half-equation? 49. What are the correct names for and , using oxidation numbers? A. Potassium permanganate and potassium dichromate B. Potassium manganate(IV) and potassium chromate(VII) C. Potassium permanganate(IV) and potassium dichromate(VII) D. Potassium manganate(VII) and potassium dichromate(VI) 9 50. At which electrodes does oxidation occur in a voltaic cell and in an electrolytic cell? 51. What are the correct oxidation numbers of chromium in and manganese in ? 52. Zinc is more reactive than copper. In this voltaic cell, which species is reduced and in which direction do negative ions flow in the salt bridge? 53. Which process occurs when a molten salt is electrolysed? A. The metal ion is oxidized and deposited on the negative electrode (cathode). B. The metal ion is reduced and deposited on the negative electrode (cathode). C. The metal ion is oxidized and deposited on the positive electrode (anode). D. The metal ion is reduced and deposited on the positive electrode (anode). 10 54. Which species are produced at each electrode during the electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide, ? 55. Consider the following standard electrode potentials. Which species will reduce H (aq) to H (g) under standard conditions? A. Fe (aq) B. Sn (aq) C. Sn(s) D. Fe (aq) 56. A number of molten metal chlorides are electrolysed, using the same current for the same length of time. Which metal will be produced in the greatest amount, in mol? A. Mg B. Al C. K D. Ca 57. The overall equation of a voltaic cell is: The standard electrode potential for , is electrode potential for the silver half-cell, A. B. C. D. . What is the standard , in V? 58. Which species are the oxidizing and reducing agents in the following reaction? 11 59. Which components are used to make the standard hydrogen electrode? A. B. C. D. 60. What is the cell potential, in V, of the reaction below? A. B. C. D. 61. What is the name of A. Cobalt(II) phosphite B. Cobalt(II) phosphate C. Cobalt(III) phosphite D. Cobalt(III) phosphate ? 62. Consider the following reaction. Which statement is correct? A. is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes oxidation. B. is the reducing agent because the oxidation number of nitrogen changes from C. Sn is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes reduction. D. Sn is the reducing agent because the oxidation number of tin changes from 0 to . 63. Which statements are correct for the electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide, I. is reduced at the negative electrode (cathode). II. is oxidized at the positive electrode (anode). III. Bubbles of a brown gas are observed at the negative electrode (cathode). A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 64. Which statement is correct about a reducing agent? A. It is reduced by gaining electrons. B. It is oxidized by gaining electrons. C. It is oxidized by losing electrons. D. It is reduced by losing electrons. 12 ? to . 65. What is the correct increasing order of reactivity of the metals X, Y and Z based on the following information? A. B. C. D. 66. Which statement describes a reducing agent? A. It is reduced and gains electrons. B. It is reduced and loses electrons. C. It is oxidized and gains electrons. D. It is oxidized and loses electrons. 67. Which is the oxidizing agent in the following reaction? A. B. C. D. 68. The overall reaction in the voltaic cell below is: Which statement is correct for the nickel half-cell? A. Nickel is the positive electrode (cathode) and is reduced. B. Nickel is the negative electrode (anode) and is reduced. C. Nickel is the positive electrode (cathode) and is oxidized. D. Nickel is the negative electrode (anode) and is oxidized. 13 69. In the electrolytic cell shown, at which electrode will chlorine form, and what is process taking place there? the 70. Consider the following reaction. Which statement is correct? A. B. C. D. is the oxidizing agent and the oxidation number of chromium changes from +3 to +6. is the reducing agent and undergoes reduction. is the oxidizing agent and the oxidation number of chlorine changes from +1 to 0. is the reducing agent and the oxidation number of chlorine changes from –1 to 0. 71. Consider the following two standard electrode potentials at 298 K. What is the equation and cell potential for the spontaneous reaction that occurs? A. B. C. D. 72. What happens during the electrolysis of concentrated aqueous potassium chloride? I. Reduction takes place at the negative electrode (cathode). II. Hydrogen gas is evolved at the negative electrode (cathode). III. The pH of the electrolyte increases. A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 73. An aqueous solution of a metal salt is electrolysed. Which factor will have no effect on the mass of the metal deposited on the negative electrode (cathode), if all other variables remain constant? A. Size of metal ion B. Relative atomic mass of metal C. Current D. Charge on metal ion 14 74. Which are correct statements about a voltaic cell? I. A spontaneous redox reaction occurs which converts chemical energy to electrical energy. II. Oxidation occurs at the negative electrode (anode). III. Electricity is conducted by the movement of electrons through the salt bridge. A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 75. The standard electrode potentials of some half-reactions are given below. Which of the following reactions will occur spontaneously? A. Iodine reduces to B. Iodine reduces to C. Iodine oxidizes to D. Iodine oxidizes to 76. Which statement is correct for electroplating an object with gold? A. The object must be the negative electrode (cathode). B. The negative electrode (cathode) must be gold. C. The object must be the positive electrode (anode). D. The gold electrode must be pure. 77. Which compound contains nitrogen with an oxidation number of +3? A. NH4Cl B. HNO3 C. N2O4 D. KNO2 78. A voltaic cell is made by connecting zinc and lead half-cells. The overall equation for the reaction occurring in the cell is shown below. Which statements are correct when the cell produces electricity? I. The zinc is oxidized. II. Electrons move from zinc to lead in the external circuit. III. The mass of the lead electrode increases. A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 79. Which process occurs during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride? A. Oxidation occurs at the positive electrode (anode). B. Electrons move through the electrolyte. C. Sodium ions move through the electrolyte to the positive electrode (anode). D. Chloride ions move through the electrolyte and are reduced at the negative electrode (cathode). 15 80. What is the name of A. Copper(I) sulfide B. Copper(I) sulfate C. Copper(II) sulfide D. Copper(II) sulfate ? 81. Consider the following reaction: Which statement is correct? A. is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes oxidation. B. is the reducing agent because it undergoes oxidation. C. is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes oxidation. D. is the reducing agent because it undergoes oxidation. 82. What occurs during the operation of a voltaic cell based on the following overall reaction? 83. Consider the following standard electrode potentials: What is the value of the cell potential, in V, for the spontaneous reaction that occurs when the two halfcells are connected together? A. B. 0.00 C. D. 84. Two electrolytic cells are connected in series and the same current passes through each cell. The first cell contains silver electrodes in silver nitrate solution. The second cell contains copper electrodes in copper(II) sulfate solution. In one experiment 1.00 g of silver is deposited in the first cell. What mass of copper, in g, is deposited in the second cell? A. B. C. D. 16 85. What is the correct decreasing order of reactivity of the metals X, Y and Z based on the following equations? A. X B. Y C. Z D. Y Y Z Y X Z X X Z 86. What is produced at the positive electrode (anode) and negative electrode (cathode) during the electrolysis of molten lithium chloride and molten lead bromide? 87. Which of the following redox reactions take place? I. II. III. A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 88. Which species could be reduced to form A. ? B. C. D. NO 89. Consider the overall reaction taking place in a voltaic cell. What is the role of zinc in the cell? A. The positive electrode and the oxidizing agent. B. The positive electrode and the reducing agent. C. The negative electrode and the oxidizing agent. D. The negative electrode and the reducing agent. 17 90. What happens to the manganese in the following reaction? A. It is oxidized and its oxidation number increases. B. It is oxidized and its oxidation number decreases. C. It is reduced and its oxidation number increases. D. It is reduced and its oxidation number decreases. 1. B 2. A 3. B 4. D 5. C 6. B 7. B 8. C 9. D 10. A 11. B 12. C 13. C 14. C 15. D 16. B 17. C 18. D 19. B 20. D 21. B 22. B 23. D 24. D 25. D 26. A 27. D 28. C 29. D 30. D 31. A 32. A 33. D 34. C 35. A 36. D 37. A 38. A 39. C 40. A 41. B 42. C 43. C 44. A 45. D 46. A 47. C 48. A 49. D 50. C 51. B 52. A 53. B 54. D 55. C 56. C 57. C 58. D 59. A 60. B 61. B 62. D 63. A 64. C 65. A 66. D 67. B 68. D 69. D 70. C 71. B 72. D 73. A 74. A 75. D 76. A 77. D 78. D 79. A 80. A 81. B 82. C 83. D 84. C 85. D 86. D 87. A 88. B 89. D 90. D 18