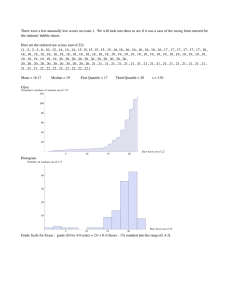
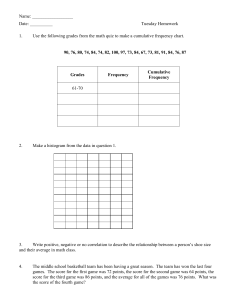
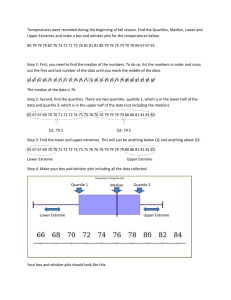
Business Math Reviewer Finals Commission - fee paid to person who makes a sale - usually a percent of the selling price. - the percent is called the Commission Rate. Formula for Commission Commission Rate x Total Amount Sale of the Month Formula for the Gross Pay for the Month Commission + Basic Salary 3 Different Types of Commission 1. Straight Commission - a type of commission where a person is paid a percentage of his/her sales only. 2. Salary Plus Commission - a type of commission where a person gets paid a salary and a percentage of his/her sales. 3. Graduated Commission - a type of commission that the company gives to their sales agent not in once but in gradual. - The commission will increase if the sale of an agent also increases. - This will encourage the agent to sell more so that they can earn a big commission. Commission on Installment Basis - If the sales are on installment basis, they are giving commissions based on the payment made by the buyers. Installment means that the buyers didn’t pay all at once. Down Payment - a type of payment made in cash during the onset of the purchase of an expensive good or service. - The payment represents a percentage of the full purchase price. Book Balance or Gross Balance - the term used by banks to describe the amount of money available before any adjustment is made for deposits in transit, checks that have not been cleared, and reserve requirements and interest received from “float funds”. Current Increased Balance - the term used by banks to describe the amount of money available before any adjustment is made for deposits in transit, checks that have not been cleared, and reserve requirements and interest received from “float funds”. Salary - compensation is usually quoted annually or monthly for an employee. Wage - compensation quoted in an hourly or daily rate for an employee. Income - money that an individual receives in exchange for providing a good/service or investing capital. Benefit - employee compensation given by an employer on top of the basic salary/wage. Business Math Reviewer Finals - may come in the form of cash or in kind. Cash Benefits - 13th month pay, bonuses, rice subsidy, transportation allowance Non-cash benefits - SSS/GSIS, Pag-ibig, Philhealth Gross earning - the amount earned by any person before subtracting the taxes, benefits, loans, and other possible deductions. Net earning - the amount earned by any person from the gross earnings less the total deductions. Deduction - the amount held by any authority as a form of payment for some necessary dues like taxes, loans, etc. Formula E=D+N N=E-D D=E-N Where E is the Total Earnings, D as Deductions, and N as Net Earnings. Overtime Pay - the additional compensation given to the employee who rendered an overtime work. (formulas can be found in the test paper) Presentation of Data - refers to the organization of data into tables, graphs or charts, so that logical and statistical conclusions can be derived from the collected measurements. Data may be presented in three methods o Textual Presentation - the data gathered are presented in paragraph forms. - data are written and read and it is a combination of texts and figures. o Tabular - methods of presenting data using the statistical table. - A systematic organization of data in columns and rows. o Graphical - Presentation using graphs such as: - Bar Graph - Pie or Circle Graph - Line Graph - Pictograph Measures of Central Tendency - A single number that can represent the entire number or set of values. - A single figure which is the representative or summary of the characteristics of a given set of data. Most commonly used measures of central tendency Mean - defined as the sum of all items or terms divided by the total number of items or terms. Median - the middlemost number/term that divides an arranged (either Business Math Reviewer Finals ascending or descending order) distribution into two equal parts. Mode - the number that occurs most frequently more than any other number in a given set of data. Formula in Computing the Mean of variation determine the discrepancy or difference between the data. • Range - the difference between the highest and the lowest entries. • Quartiles - points which divide the set of data into four equal parts. There are three quartiles: Q1 Q2 Q3 Formula in Computing the Median Quartile 1 or Q1 - The first quartile or the lower quartile is the value that separates the lower 25% from the higher 75% of the scores: Q1 = ¼ x N Quartile 2 or Q2 - The second quartile is the median Q2 = Median Quartile 3 or Q3 - The third quartile or the higher quartile is the value that separates the lower 75% from the higher 25% of the scores: Q3 = ¾ x N Interquartile Range (IQR) - the difference between the third quartile and the first quartile. IQR = Q3 – Q1 Note: the quartiles are computed similar to the median. Measures of Variation - a value that is used to describe the spread of a set of data. - If a measure of central tendency gets the typical value, the measures Line Graph - a graphical presentation of data that shows a continuous change or trend. - It may show an ascending or descending trend Business Math Reviewer Finals - Used to track changes over short and long periods of time. - Used to compare changes over the same period of time for more than one group. - Used for quantitative continuous data and is appropriate with frequency data. Bar Graph - Uses bars to compare categories of data. - It may be drawn vertically or horizontally. - Best when comparing means or percentages between distinct categories. - The categories are measured independently and compared with one another. - May contain more than 5 categories. - Is plotted on either the x axis or the y axis. - The categories may be plotted on one axis while the other axis contains the numerical values that represent the data being measured. Histogram - A graphical presentation of a frequency distribution. - It is a representation of tabulated frequencies (Y-axis) using adjacent erected rectangles with their corresponding class intervals (Xaxis). - The rectangles are of equal width since the class mark is used to represent the class intervals. Pie Graph - Also called a circle graph. - A circle with the wedges or sectors to show how much of the whole each part makes up. - Each slice of the pie is written in percentage. - To get the measure of each sector in the chart, we compute the following: (Can’t see the formula, here’s an example instead:) Reviewer by: Dayne Ask permission first if you want to share this with others, mwa. “Linking without permission is stealing. Period, end of story.” ~ Mark Cuban Business Math Reviewer Finals FILL IN THE BLANKS ANSWERS (Welcomes, mwa) PHILIPPINE HOLIDAY PAY RULES For the employee who works during regular (1) holidays he/she shall be paid 200% of his/her regular pay, while work done in excess of eight hours shall be paid (2) 260%. If the said holiday falls on the (3) Scheduled rest day of the employee then he/she shall be paid 200% x 130%, and (4) 260% x 130% in excess of eight hours. On the other hand the pay rules for special (non-working) holiday is daily rate x 130%, and (5) 195% (bonus) in excess of its eight hours. If the special (non-working) holiday falls on the rest day of the employee, he/she shall be paid (6) 150% of his/her regular wage for the first 8 hours and 150% x 130% in excess of the eight hours