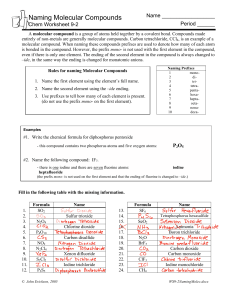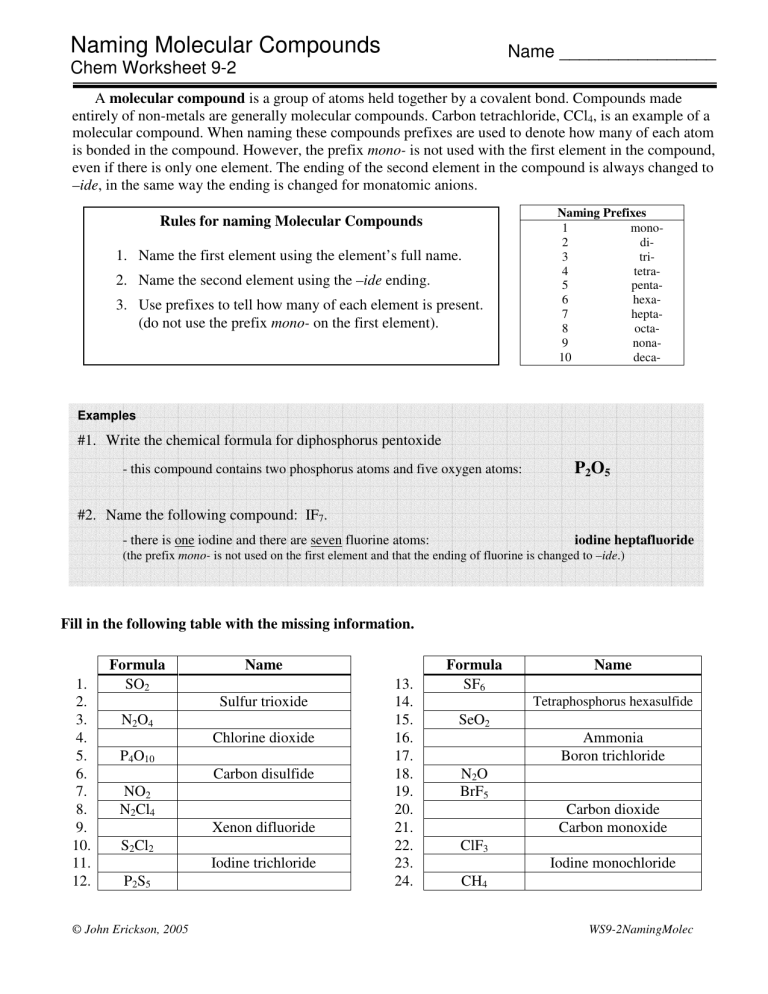
Naming Molecular Compounds Name ________________ Chem Worksheet 9-2 A molecular compound is a group of atoms held together by a covalent bond. Compounds made entirely of non-metals are generally molecular compounds. Carbon tetrachloride, CCl4, is an example of a molecular compound. When naming these compounds prefixes are used to denote how many of each atom is bonded in the compound. However, the prefix mono- is not used with the first element in the compound, even if there is only one element. The ending of the second element in the compound is always changed to –ide, in the same way the ending is changed for monatomic anions. Rules for naming Molecular Compounds 1. Name the first element using the element’s full name. 2. Name the second element using the –ide ending. 3. Use prefixes to tell how many of each element is present. (do not use the prefix mono- on the first element). Naming Prefixes 1 mono2 di3 tri4 tetra5 penta6 hexa7 hepta8 octa9 nona10 deca- Examples #1. Write the chemical formula for diphosphorus pentoxide - this compound contains two phosphorus atoms and five oxygen atoms: P2O5 #2. Name the following compound: IF7. iodine heptafluoride - there is one iodine and there are seven fluorine atoms: (the prefix mono- is not used on the first element and that the ending of fluorine is changed to –ide.) Fill in the following table with the missing information. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Formula SO2 N2O4 P4O10 NO2 N2Cl4 S2Cl2 P2S5 © John Erickson, 2005 Name Sulfur trioxide Chlorine dioxide Carbon disulfide Xenon difluoride Iodine trichloride 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. Formula SF6 SeO2 N2O BrF5 ClF3 CH4 Name Tetraphosphorus hexasulfide Ammonia Boron trichloride Carbon dioxide Carbon monoxide Iodine monochloride WS9-2NamingMolec