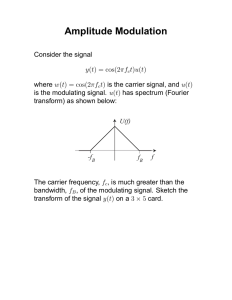
1. Explain the basic concept of Amplitude Modulation (AM). How does it work, and what are its key characteristics? Amplitude Modulation (AM) is a modulation technique employed in electronic communication. It involves the alteration of the amplitude of a carrier wave in proportion to the instantaneous amplitude of a modulating signal. The modulating signal, typically an audio or voice signal, is superimposed onto the carrier wave to create a new signal that conveys the information contained in the modulating signal. In essence, AM encodes information by varying the amplitude of the carrier wave, enabling the transmission of audio signals, such as voice or music, over radio frequencies. 2. Discuss the mathematical representation of an AM signal and its spectrum. How can you calculate the sideband frequencies and their bandwidth? 3. Explain the advantages and disadvantages of Amplitude Modulation as a modulation technique in communication systems. Advantages • • • Relatively simple to implement. Energy efficient throughout long range applications Compatibility towards hardware of receivers Disadvantages • • • Can be affected by noise and interference. Uses bandwidth inefficiently Has limited response towards frequencies of audio signals 4. Describe the concept of modulation index in AM. How does it affect the quality of the modulated signal? The modulation index in Amplitude Modulation (AM) is a dimensionless parameter representing the ratio of the peak amplitude of the modulating signal to the peak amplitude of the carrier signal. It is calculated as the amplitude of the modulating signal divided by the amplitude of the carrier signal. This modulation index plays a crucial role in determining the quality of the modulated signal. Excessive modulation can lead to distortion, while insufficient modulation results in a poor signal-to-noise ratio. 5. Discuss the use of envelope detection in demodulating AM signals. What is the role of a diode in envelope detection, and why is it necessary? Envelope detection is a vital step in demodulating Amplitude Modulation (AM) signals, enabling the recovery of the original modulating signal from the carrier wave. In this process, a diode plays a crucial role by rectifying the AM signal. The diode allows only one half of the signal (positive or negative) to pass through, effectively extracting the envelope that represents the variations in the modulating signal. The diode's necessity lies in its ability to rectify the signal. The diode converts the AM signal into a unidirectional form, simplifying the isolation of the signal's envelope. Additionally, it is able to extract the envelope by selectively allowing part of the signal to pass, the diode extracts the envelope, representing the original modulating signal's variations, and lastly. The diodes simplicity and efficiency enable it to be a cost-effective and efficient method for demodulating AM signals, especially for recovering low-frequency modulating signals like audio or data.