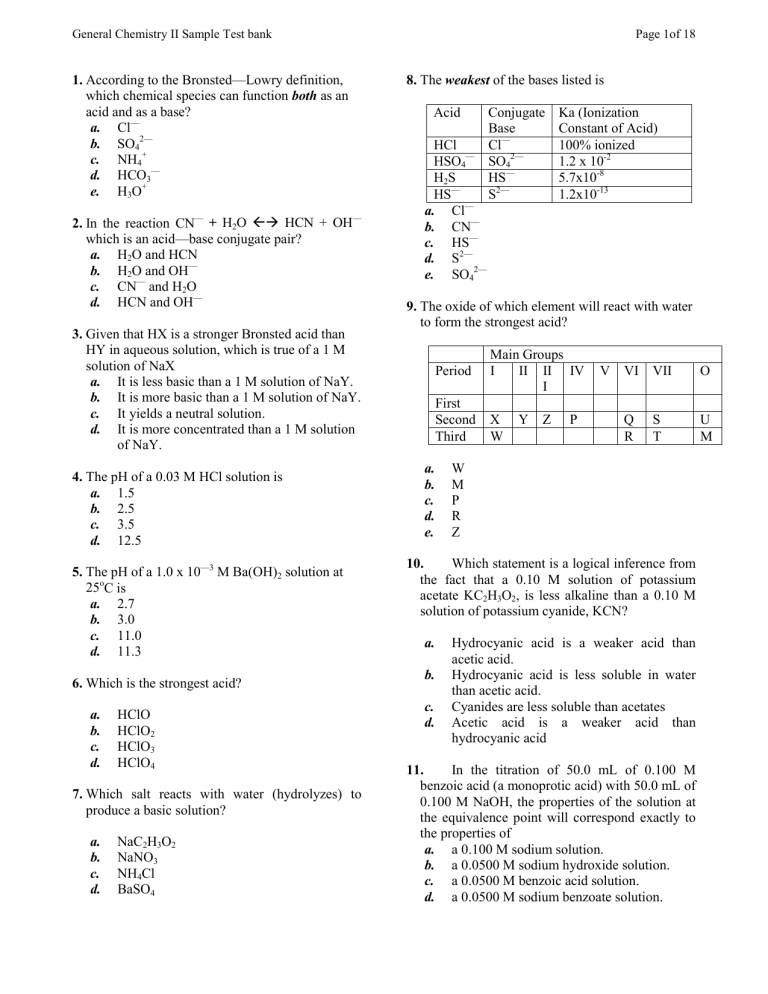
General Chemistry II Sample Test bank 1. According to the Bronsted—Lowry definition, which chemical species can function both as an acid and as a base? a. Cl— b. SO42— c. NH4+ d. HCO3— e. H3O+ 2. In the reaction CN— + H2O !" HCN + OH— which is an acid—base conjugate pair? a. H2O and HCN b. H2O and OH— c. CN— and H2O d. HCN and OH— 3. Given that HX is a stronger Bronsted acid than HY in aqueous solution, which is true of a 1 M solution of NaX a. It is less basic than a 1 M solution of NaY. b. It is more basic than a 1 M solution of NaY. c. It yields a neutral solution. d. It is more concentrated than a 1 M solution of NaY. 4. The pH of a 0.03 M HCl solution is a. 1.5 b. 2.5 c. 3.5 d. 12.5 5. The pH of a 1.0 x 10—3 M Ba(OH)2 solution at 25oC is a. 2.7 b. 3.0 c. 11.0 d. 11.3 6. Which is the strongest acid? a. b. c. d. HClO HClO2 HClO3 HClO4 7. Which salt reacts with water (hydrolyzes) to produce a basic solution? a. b. c. d. NaC2H3O2 NaNO3 NH4Cl BaSO4 Page 1of 18 8. The weakest of the bases listed is Acid HCl HSO4— H2S HS— a. Cl— b. CN— c. HS— d. S2— e. SO42— Conjugate Base Cl— SO42— HS— S2— Ka (Ionization Constant of Acid) 100% ionized 1.2 x 10-2 5.7x10-8 1.2x10-13 9. The oxide of which element will react with water to form the strongest acid? Period First Second Third a. b. c. d. e. Main Groups I II II IV I X W Y Z P V VI VII O Q R S T U M W M P R Z 10. Which statement is a logical inference from the fact that a 0.10 M solution of potassium acetate KC2H3O2, is less alkaline than a 0.10 M solution of potassium cyanide, KCN? a. b. c. d. Hydrocyanic acid is a weaker acid than acetic acid. Hydrocyanic acid is less soluble in water than acetic acid. Cyanides are less soluble than acetates Acetic acid is a weaker acid than hydrocyanic acid 11. In the titration of 50.0 mL of 0.100 M benzoic acid (a monoprotic acid) with 50.0 mL of 0.100 M NaOH, the properties of the solution at the equivalence point will correspond exactly to the properties of a. a 0.100 M sodium solution. b. a 0.0500 M sodium hydroxide solution. c. a 0.0500 M benzoic acid solution. d. a 0.0500 M sodium benzoate solution. General Chemistry II Sample Test bank Page 2of 18 12. A mixture of which pair of 0.1 M aqueous solutions would constitute a buffer? a. NaOH and NaCl b. HCl and NaOH c. HCl and NaCl d. NH3 and NH4NO3 13. What do these have in common? 24 Ne 19F1Mg2+ 20 a. b. c. d. the same number of protons the same number of neutrons the same number of electrons the same size 14. The number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom of 1327Al is a. 40 b. 13 c. 27 d. 14 e. 9 15. The orbitals of 2p electrons are often represented as being a. elliptical. b. Pyramidal c. Tetrahedral d. dumbbell shaped e. spherical. 16. The element in Period 5, Group 3A, has the outer electron configuration a. 5s25p1 b. 3s23p5 c. 3s23p3 d. 5s25p3 17. Which electron impossible? a. 1s22s22p63s2 b. 1s22s22p63s23p6 c. 1s22s22p62d2 d. 1s22s22p53s1 configuration is 18. The element X occurs naturally to the extent of 20.0% 12X and 80.0% 13X. The atomic mass of X is nearest a. b. c. d. 12.2 12.5 12.8 13.0 19. Which electron transition is associated with the largest emission of energy? a. b. c. d. n=2 to n=1 n=2 to n=4 n=2 to n=3 n=3 to n=2 20. If an electron moves from one energy level in an atom to another energy level more remote from the nucleus of the same atom a. energy is absorbed. b. energy is liberated. c. there is no energy change. d. the atom must assume a different ionic valence e. light of a definite wave length is emitted. 21. A photon of light of 450 nm, when compared to light of wavelength 300 nm, has (1nm = 10-9 m) a. b. c. d. a higher frequency. lower energy. a greater velocity. a shorter wavelength 22. Which set of quantum numbers is possible for an electron in an atom? a. b. c. d. n=3, l=0, ml=1, ms = -½ n=2, l=2,ml= -2, ms = -½ n=5, l=2, ml=2, ms =+½ n=4, l=3, ml= -4, ms= -½ 23. A compound consisting of an element having a low ionization potential and a second element having a high electron affinity is likely to have a. b. c. d. covalent bonds metallic bonds coordinate covalent bonds ionic bonds. 24. According to modern bonding theory the number of sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds in the ethylene molecule H2C=CH2 is a. l π and 4 σ b. l π and 1 σ c. l π and 5 σ d. 2 π and 4 σ e. l π and 6 σ General Chemistry II Sample Test bank 25. a. b. c. d. The number of σ bonds in N=N is 1 2 3 4 26. The elements in an ionic compound are held together by a. b. c. d. e. electrostatic forces of attraction. van der Waals forces the spin of paired electrons. the formation of hybrid orbitals. an electron pair. 27. In every electrolytic and galvanic (voltaic) cell the anode is that electrode a. b. c. d. at which oxidation occurs. which attracts cations. at which electrons are supplied to the solution. at which reduction occurs. 28. Metal X was plated from a solution containing cations of X. The passage of 48.25 C deposited 31 mg of X on the cathode. What is the mass of X (in grams) per mole of electrons? a. 47 b. 62 c. 93 d. 186 29. In a galvanic (voltaic) cell in which the reaction is Cd + Cu2+ " Cu + Cd2+ and the ions are at unit concentration (activity), the cell potential is Cd " Cd2++ 2eCu " Cu2+ + 2ea. 0.1383 V b. 0.4021 V c. 0.344 V d. 0.7461 V e. 0.3677 V 0.4021 V - 0.344 V 30. In which reaction will an increase in total pressure at constant temperature favor formation of the products? a. CaCO3(s) !" CaO(s) + CO2(g) b. H2(g) + Cl2(g) !" " 2HCl(g) c. 2NO(g) + O2(g) !" 2NO2(g) d. COCl2(g) !" CO(g) + Cl2(g) Page 3of 18 Standard Potentials Eo Mg" Mg2++2e 2.37V Al " Al3++3e 1.66V Zn " Zn2++2e 0.76V 2+ Fe"Fe +2e 0.44V Cu " Cu2++2e 0.34V Ag" Ag++ e -0.80V 31. Using only the metals Mg, Al, Zn, Fe, Cu and Ag, together with their 1 M salt solutions, a voltaic cell of the highest possible voltage would be constructed using electrodes of these metals. a. Mg and Ag b. Mg and Fe c. Zn and Cu d. Al and Ag e. Mg and Al 32. E = Eo - 0.059/n log Q (Nernst equation) + [H ] = 1.0 M initially, P02 = 1.0 atm 4e + O2(g)+4H+(aq)!" 2H2O(l) Eo=1.23V Based on the information above, which statement is correct? a. b. c. d. n = 1, since one mole of oxygen is being considered. Addition of base should result in an E value, which is less than 1.23 V. E is independent of the pH of the solution. Q = [H2O]2 [O2] [H+] 33. The equilibrium constant for the gaseous reaction C + D !" E + 2F is 3.0 at 50 oC. In a 2.0 L flask at 50 oC are placed 1.0 mol of C, 1.0 mol of D, 1.0 mol of E, and 3.0 mol of F. Initially, the reaction will a. proceed at equal rates in both directions. b. proceed more rapidly to form E and F. c. proceed more rapidly to form C and D. d. not occur in either direction. Compound ∆Gof kJ/mol H2O(l) —237 H2O(g) —229 34. At 298 K the equilibrium constant for H2(g) + ½ O2(g)!" H2O(l) a. b. c. is larger than the Keq for H2(g) + ½ O2(g)!" H2O(g) will have a value of 1 0 at equilibrium. cannot be computed since data on O2 and General Chemistry II Sample Test bank d. H2 are not provided. will have the same value as the Keq for 2 H2(g) + O2(g)!" 2 H2O(l) 35. Consider the reversible system at equilibrium: 2CO + O2 !" 2CO2 + heat When the temperature is increased at constant pressure a. b. c. d. e. the CO2 concentration will be increased. the CO2 concentration will be decreased. the amount of each substance will be unchanged. the amount of each substance will be increased. the result cannot be predicted from the information given. 36. The numerical value of the equilibrium constant for any chemical change is affected by changing a. the catalyst. b. the concentration of the products. c. the concentration of reacting substances. d. the pressure. e. the temperature 37. What is the equilibrium constant expression for the gas phase oxidation of CO to CO2 by O2? a. K = [CO2]2 [CO][O2] b. K= [CO]2 [O2] [CO2] c. K= [CO2]2 [CO]2 [O2] d. K= [CO] [O2] [CO2] 38. Into an empty vessel COCl2(g) is introduced at 1.0 atm pressure whereupon it dissociates until equilibrium is established: 2COCl2(g) !" C(graphite) +CO2(g) + 2Cl2(g) a. If x represents the partial pressure of CO2(g) at equilibrium, what is the value of the equilibrium constant, Kp? x.2x2 (1.0-2x)2 Page 4of 18 b. c. d. x x 2x2 (1.0-2x2) x (2x)2 (1.0- 2x)2 x (2x)2 (1.0—x)2 39. At a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant for the reaction 2HI(g) !" " H2(g) + I2(g) is 0.49. Calculate the number of moles of hydrogen produced when one mole of HI is placed in a 1 L vessel at this temperature. a. 0.41 b. 0.25 c. 0.29 d. 3.45 40. What is the [OH-] of a solution which is 0.18 M in ammonium ion and 0.10 M in ammonia? Kb = 1.8 x 10-5 a. 1.3x10-3 b. 1.0x10-3 c. 1.3x10-5 d. 1.0x10-5 41. What is the pH of a 0.10 M solution of a monoprotic acid, HA, with a Ka = 1.0 x 10-6? a. 1.6 b. 3.5 c. 5.0 d. 6.0 42. When 0.10 mol of a weak acid HA was diluted to one liter, experiment showed the acid to be 1% dissociated. HA + H2O !" H3O+ + AWhat is the acid dissociation constant, Ka? a. 1 x10-6 b. 1 x10-5 c. l x10-3 d. 1 x105 43. Which solution has a pH less than 7.0? a. 1 M NH4Cl b. 1 M K2CO3 c. 1 M NaOCl d. 1 M NaOH 44. What is the pH of a 0.1 M NaF solution? Ionization constant for HF, Ka = 7 x 10-4 a. 2.1 b. 5.9 c. 8.1 d. 9.1 General Chemistry II Sample Test bank 45. What is the hydrogen ion concentration of a buffer solution containing 0.10 M NO21- and 0.20 M HNO2? Ionization constant for Nitrous Acid, Ka = 4.5x 10-4 a. b. c. d. 2.2x10-4M 9.0 x 10-4 M 4.5 x 10-4 M 9.5 x 10-3M 46. The solubility of BaCO3 is 7.9 x 10-3 g/L. Calculate the solubility product, Ksp ignoring hydrolysis. MW of BaCO3 197 g/mol a. b. c. d. 1.6x10-2 1.6x10-9 4.0x10-5 6.2x10-5 47. The addition of solid Na2SO4 to an aqueous solution in equilibrium with solid BaSO4 will cause a. b. c. d. no change in [Ba2+] in solution. more BaSO4 to dissolve. precipitation of more BaSO4. an increase in the Ksp of BaSO4. 48. Assume that standardized aqueous solutions of each of these are available. Substance Ionization Constant NaOAc Kb = 5.6 x 10-10 RNH3+Cl- Ka = 5.6 x 10-10 RNH2 Kb=1.8x10-5 HOAc Ka=1.8x10-5 A buffer with a desired pH is 5.0 would be conveniently prepared by appropriate mixtures of a. NaOAc and HOAc b. HOAc and water c. NaOAc and RNH2 d. HOAc and RNH2 49. a. b. c. d. Which substance is most soluble in water? C6H6 CaCO3 C2H5OH CO2 50. The solubility of BaCrO4 in water is 2.8 x -3 10 g/L what is the Ksp of the salt? MW of Page 5of 18 BaCrO4 253 g/mol a. 1.2x10-10 b. 2.2x10-5 c. 2.8x10-3 d. 7.8 xl0-6 51. Which is the correct expression for the solubility product constant for Ag2CrO4? a. Ksp = [Ag+]2 [CrO42-] b. Ksp = [2Ag+]2 [CrO42-] c. Ksp = [Ag+] [CrO42-] d. Ksp = [Ag+] [CrO42-]2 e. Ksp = [2Ag+] [CrO42-] 52. a. b. c. d. The correct IUPAC name of N2O3 is nitrogen oxide. nitrogen(II) oxide. nitrous oxide dinitrogen trioxide. 53. In which case is the substance with the given formula followed by its correct name? a. KNO2 — potassium nitrate b. FeCl3 — iron(III) chloride c. FeS — iron(II) sulfite d. Mg3N2 — magnesium nitrite e. HClO — hydrochloric oxide 54. Balance the equation for the following reaction, using no fractional coefficients. ? C +? HNO3 " ? CO2 +? NO2 +? H2O The sum of the coefficients in the balanced equation is a. 5 b. 7 c. 9 d. 12 e. 16 55. Complete and balance the equation for the reaction, where the reactants are in aqueous solution. Use no fractional coefficients. ? Na3PO4 + ? Ba(NO3)2 " ? + ? The number of moles and formula of the product containing Ba are a. 3NaNO3 b. BaPO4 c. Ba(PO4)2 d. Ba2P3 e. Ba3(PO4)2 General Chemistry II Sample Test bank 56. According to the kinetic molecular theory, a. b. c. d. e. gaseous molecules are continuously in random motion and collisions are perfectly elastic. the absolute temperature of a gas depends on its molar mass. the pressure exerted on a gas affects the speed of its molecules. gaseous molecules can travel in straight or curved paths. all gaseous molecules are diatomic. 57. The volume of a given mass of gas varies inversely with pressure, provided that the temperature remains constant because a. b. c. d. e. attractive forces between gas molecules are negligible. attractive forces between gas molecules are appreciable. the average kinetic energy of the molecules of a gas is proportional to the absolute temperature. increasing the molecular concentration, at constant temperature, means increasing the number of collisions between molecules and container. collisions between gas molecules are perfectly elastic. 58. The Kelvin temperature of one liter of gas is doubled and its pressure is tripled, volume will then be l /6 L /3 L 3 /2 L 6L 59. Which gas, present in the same closed system, has the greatest average kinetic energy at a given temperature? a. b. c. d. a. b. c. d. 2 Page 6of 18 60. A sample of neon occupies a volume of 27.3 L at STP. What would be the neon volume at 177 oC and 0.100 atm pressure? a. b. c. d. 177 L 350 L 422 L 450 L 61. Under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, the gas whose molecules possess the highest average speed is a. H2O b. O2 c. F2 d. Ne 62. What is the volume of 2.00 mol of helium gas at 27 oC and 3.00 atm? a. b. c. d. 63. 6.1x10-2L 1.48L 16.4L 44.8 L Real gases are most like ideal gases at a. b. c. d. high pressure and high temperature. low pressure and low temperature. high pressure and low temperature. low pressure and high temperature. 64. 500 mL of a gaseous compound has a mass of 0.9825 g at 0oC and 760 mmHg. What is the approximate molar mass of the compound? a. 19.7 b. 38.7 c. 44.0 d. 58.9 65. The partial pressures of a gaseous mixture are given in the table. What is the mole percent of hydrogen? Hydrogen neon carbon dioxide None; the average kinetic energy is the same for each gas. a. b. c. d. hydrogen carbon dioxide methane ethylene 20.0 25.8 38.8 41.7 Partial Pressures 200 mmHg 150 mmHg 320 mmHg 105 mmHg General Chemistry II Sample Test bank 66. It is desired to collect enough oxygen over water at 25 oC and 750 mmHg barometric pressure to be equivalent to 1 L of pure oxygen at 0 oC and 760 mmHg. The vapor pressure of water at 25 oC is 23.5 mm. The volume collected is a. 1 L (298/273)(750/760) b. 1 L (273/298)((750-23.5)/(760-23.5)) c. 1 L (273/298)((750-23.5)/760) d. 1 L (298/273)(760/(750-23.5)) 67. Methane, CH4, diffuses in a given apparatus at the rate of 30 mL/min. At what rate would a gas with a molar mass of 100 diffuse under the same conditions? MW of CH4 = 16 g/mol a. 0.77 mL/min b. 30 mL/min c. 6.7 mL/min d. 75 mL/min e. 12.0 mL/min 68. The Arrhenius equation, k= Ae-E/RT expresses the relationship between the reaction rate constant, k, and the energy of activation, E. The probability that colliding molecules will react a. increases with increasing energy of activation. b. depends only on the empirical constant, A. c. increases with decreasing temperature. d. decreases with increasing energy of activation. 69. The rate law for the reaction A+B"C+D is first order in [A] and second order in [B]. If [A] is halved and [B] is doubled, the rate of the reaction will a. b. c. d. remain the same be increased by a factor of 2. be increased by a factor of 4. be increased by a factor of 8. 70. The addition of a catalyst in a chemical reaction a. increases the concentration of products at equilibrium. b. increases the fraction of reactant molecules with a given kinetic energy. c. provides an alternate path with a different activation energy. d. lowers the enthalpy change in the overall reaction. Page 7of 18 71. The following mechanism has been proposed for the formation of ethylbenzene: CH3CH2Br + AlBr3 " AlBr4- + CH3CH2+ CH3CH2+ + C6H6 " C6H6CH2CH3+ C6H6CH2CH3+ + AlBr4- "AlBr3 + HBr + C6H5CH2CH3 Which substance serves as the catalyst? a. b. c. d. AlBr3 CH3CH2+ AlBr4C6H6CH2CH3+ 72. Which substance has the highest boiling point? a. b. c. d. CH4 He HF Cl2 73. The table presents data for the reaction: The temperature of the reaction is constant. The initial rate is in arbitrary units. 2H2(g) + 2NO(g) " 2H2O(g) + N2(g) Exp. I II III IV Initial Concentration (mol/L) [NO] x 10-3 [H2] x 10-3 Initial Rate 6.0 1.0 18 6.0 2.0 36 1.0 6.0 3 2.0 6.0 12 What is the rate law for this reaction? a. rate = k1 [H2][NO] b. rate = k1 [H2]2 [NO]2 c. rate = k1 [H2]2 [NO] d. rate = k1 [H2] [NO]2 74. The reaction 2A + 2B " C +D proceeds by this mechanism: 2A !" A2 (equilibrium) A2 + B " X + C (rate determining) X+B"D (rapid) The rate equation for the reaction is a. b. c. d. rate = k[A] [B] rate = k[A]2 [B]2/[C][D] rate = k[A]2 [B]2[D] rate = k[A]2 [B] General Chemistry II Sample Test bank Page 8of 18 75. What is the correctly reported mass of water based on this data? a. Mass of beaker and water 29.62 g Mass of beaker only 28.3220 g a. b. c. d. 1.3g 1.30g 1.298g 1.2980g 76. When a small single piece of magnesium ribbon is dropped into a test tube half filled with dilute sulfuric acid, the metal soon floats to the surface of the liquid. The best explanation for this is that, (Densities, Mg, 1.79 g/cm3; H2SO4(dilute) 1.2 g/cm3) a. b. c. d. e. the metal is less dense than the acid. the metal gets hot and expands and decreases its density markedly as it reacts with the acid the magnesium sulfate formed increases the density of the solution. gas bubbles attached to the metal buoy the metal to the top. convection currents set up in the acid carry the metal to the top. 77. The equilibrium vapor pressure of a few liters of a liquid is dependent on a. b. c. d. c. d. e. 80. The stronger the intermolecular forces in a substance a. b. c. d. 65.4 92.0 184 238 79. When a hypothetical ionic crystal M+X- is heated, it vaporizes to form separate M+(g) and X-(g) ions. The energy required for this vaporization (the lattice energy) will be greatest when the higher the boiling point. the lower the boiling point. the higher the vapor pressure. the smaller the deviation from ideal gas behavior. 81. Which group of substances is correctly arranged in order from the highest to the lowest melting point? a. b. c. d. HF>H2>NaF NaF>H2>HF HF>NaF>H2 NaF>HF>H2 82. The fact that H2O has a dipole moment suggests that the water molecule is the mass of the liquid. the surface area of the liquid the temperature only the volume of the liquid 78. The edge of a unit cube of an element Y, containing two atoms per unit cube, was found (by X- ray diffraction) to be 3.16 x 10-8 cm. The density of the metal is 19.35 g/cm3. What is the approximate atomic molar mass of Y? a. b. c. d. b. the electron affinity of X is small in magnitude and the ionization potential of M is large in magnitude. the heat of vaporization of crystalline M is small. the heat of vaporization of crystalline M is large. the effective radii of M+ and X- are large. the effective radii of M+ and X- are small. a. b. c. d. 83. dimeric symmetrical. bent. nonpolar. Which pair is geometrically similar? a. b. c. d. SO2 and CO2 CO2 and OF2 PH3 and BF3 SO2 and O3 84. The bond type and molecular polarity of SiCl4 are a. b. c. d. Bond Type polar polar nonpolar nonpolar Polarity of Molecule nonpolar polar polar nonpolar General Chemistry II Sample Test bank 85. The fact that BCl3 is a planar molecule while NCl3 is pyramidal can be explained several different ways. Which is the best rationalization? a. b. c. d. 86. a. b. c. d. Nitrogen is more electronegative than boron. The nitrogen atom in NCl3 has a lone pair of electrons whereas the boron atom in BCl3 does not. The nitrogen atom is smaller than the boron atom The boron atom in BCl3 is sp3 hybridized, while the nitrogen atom in NCl3 is sp2 hybridizes Page 9of 18 isotope? a. b. c. d. 91. Which of these molecules is the most polar? (X and Y are two different elements, Y being the more electronegative.) a. b. c. d. X2 Y2 X—Y—X X—Y X X e. Y—X X The geometry for SeF3+ is trigonal pyramidal. tetrahedral. square planar. rectangular planar. 92. The Lewis structure of BrF5 is F F F Br F F 87. 4 days 8 days 12 days 16 days 14 6C a. b. c. d. In the beta emission of a species such as the process may be considered as the change of a proton into a neutron. the change of a neutron into a proton. the same mode of decay as electron capture. neutrino absorption by the nucleus. The molecular structure of BrF5 is a. b. c. d. 88. square pyramidal. trigonal pyramidal. trigonal bipyramidal. octahedral. 93. Which compound is a paraffin (methane series) hydrocarbon? a. b. c. d. e. Which is planar? a. b. c. d. e. PCl3 ClO3CO32NH3 PH3 89. A molecule of the type ML4 consists of four bonding pairs of electrons and no lone pairs. Which structure would it be expected to assume? a. square planar b. tetrahedral c. linear d. square pyramidal 90. A sample of a radioactive isotope initially contains 20 x 1010 atoms. After 16 days, 5 x 1010 atoms remain. What is the half-life of the C5H12 C5H11OH (C2H5)2O C6H6 C6H5Cl 94. lsobutane differs from butane in that the former a. b. c. d. e. 95. has a higher molecular weight. has a different percentage composition. is not a saturated hydrocarbon. has a different empirical formula. has a different structural formula. Which has the highest boiling point? a. b. c. d. n-butane C4H10 n-heptane C7H16 n-hexane C6H14 n-pentane C5H12 General Chemistry II Sample Test bank 96. The reaction between acetic acid and ethyl alcohol is classified as Page 10of 18 the magnesium acts as a reducing agent. How many electrons does each magnesium atom lose? CH3COOH + C2H5OH " CH3COOC2H5 + H2O a. b. c. d. 97. in a. b. c. d. a. b. c. d. e. saponification addition esterification hydrolysis Manganese has the oxidation number of +5 [MnF6]3Mn2O7 [MnO4]2[Mn(CN)6]1- a. b. c. d. e. a. b. c. d. 100. Cu2+ is oxidized. Cu2+ gains in oxidation state. Cu2+ is reduced. Fe(s) is reduced. a. b. c. d. 101. a. b. c. d. Standard Potentials Na " Na+ +e Zn " Zn2++2e Fe " Fe2+ + 2e Pb " Pb2++2e H2 " 2H++ 2e Cu " Cu2++2e Hg " Hg2++2e Ag " Ag+ +e Eo 2.71 V 0.40 V 0.00 V -0.80 V Na+ H2 Cd0 Ag+ In this reaction 3Mg + 2HNO3(dilute) + 6H" 3Mg2+ + 2NO + 4H2O Standard Potentials Na" Na+ + e Al " Al3++3e Sn2+"Sn4++2e 21— " l2+2e 2F—"F2 + 2e Na+ Al Sn4+ F2 Eo 2.714 V 1.67 V -0.14 V -0.535 V -2.85 V 104. Which metal will reduce copper(ll) ions but not zinc ions? Which is the strongest oxidizing agent? Standard Potentials Na " Na+ + e Cd " Cd2+ + 2e H2 " 2H+ + 2e Ag "Ag+ + e Na+ O2FMg2+ 103. The greatest oxidizing power (tendency to gain electrons) is shown by VO2+ VBr4 NH4VO3 V2(SO4)3 V(CN)63— Fe(s) + Cu2+ (aq) " Cu(s) + Fe2+ (aq) Which statement is true for the reaction? 99. 102. Which of these isoelectronic ions is the most polarizable? a. b. c. d. 98. The highest oxidation number of vanadium is exhibited in 1 2 3 4 6 a. b. c. d. Na Hg Pb Ag Eo 2.71 V 0.76 V 0.4 V 0.13 V 0.00 V -0.34.V -0.85 V -0.80 V General Chemistry II Sample Test bank 105. A metal, M, forms an oxide of formula M2O3. The ground state valence shell electron configuration of the M atom is a. b. c. d. 2 ns np np6 4s13d10 4f7 GaSe GaSe2 Ga2Se Ga2Se3 107. Use this section of a periodic table. A E Q R If atoms of R have one “d” type electron, what is the formula for a nitride of element A? a. b. c. d. A3N A3N2 AN AN2 108. In which pair of particles is the first member larger than the second member? a. b. c. d. + 2+ Li ; Be Li+ ; Na+ Li+ ; Li Be ; Mg 109. Which would be expected to be the most electronegative? a. b. c. d. 111. In which reaction is the energy term referred to as the ionization energy? a. b. c. d. 1 106. From your knowledge of the periodic nature of the elements, what formula would be anticipated for gallium selenide? a. b. c. d. Page 11of 18 P As Si Al 112. Based on their positions in the periodic table, which is most likely to replace selenium, Se, in a biological system? a. Te b. Br c. As d. I 113. Which conditions favor the high solubility of a gas in a liquid? a. high pressure, high temperature b. high pressure, low temperature c. low pressure, high temperature d. low pressure, low temperature 114. Ionic compounds in the solid state at room temperature are generally characterized by their a. ability to conduct an electric current. b. high vapor pressures. c. solubility in polar solvents. d. solubility in nonpolar solvents. e. low melting points. 115. Which precipitate will not dissolve in aqueous HCl solution? a. AgBr b. BaCO3 c. CaSO3 d. Fe(OH)3 e. ZnS 116. A cellophane bag, which acts as a membrane permeable only to water, contains a 2 M sugar solution. The bag is immersed in a 1 M sugar solution. What will happen? a. 110. Predict which element would have the largest difference between its first and second ionization energies. a. Sodium b. Phosphorus c. Silicon d. magnesium NaCl(crystal) + energy " Na+(g) + Cl—(g) Cl(g) + energy "Cl+ + e Cl(g) + e " Cl—(g) + energy Cl— g) + H+(g) " HCl(g) + energy b. c. d. e. The bag will soon contain more solution that will be are concentrated than 2 M. The bag will soon contain more solution that will be less concentrated than 2 M. The bag will lose sugar and the solution in it will become less concentrated. The bag will lose water and the solution in it will become more concentrated. There will be no change. General Chemistry II Sample Test bank 117. If 0.400 g of a substance R (MW = 80.0 g/mol) is dissolved in 100 g of liquid Q, what is the molality of the solution? a. b. c. d. 4.00x10–3 m 5.00x10–2 m 5.00 x 10–3 m 4.00 x 10–1 m 118. What is the mole fraction of water in 200. g of 95% (by mass) ethanol, C2H5OH (mw = 46.0 g/mol)? a. b. c. d. 0.050 0.12 0.56 0.88 119. A 0.10 m aqueous solution of HF shows a freezing point of - 0.198 oC. What is the percent dissociation of HF? Molal freezing point constant, Kf for water = 1 .86 oC/m a. b. c. d. 6.4% 10% 20% 98% 120. A 0.10 m solution of MgSO4 freezes at -0.245oC instead of 2 x (- 0.186 oC) as predicted for ideal behavior. This deviation from ideality can best be explained on the basis of a. b. c. d. interionic attraction. hydrogen bonding. the Le Chatelier principle. the solubility product constant 121. Which aqueous solution has the smallest freezing point depression? a. b. c. d. 0.2 m Ca(NO3)2 0.2 m MgSO4 0.2 m CH3OH 0.2 m K3PO4 122. When one mole of naphthalene is dissolved in 1000 g of benzene, the freezing point changes from 5.51 oC to 0.41 oC. When 20 g of an unknown organic compound is dissolved in 500 g of benzene, the freezing point of this solution is 5.00 oC. What is the molar mass of the unknown organic compound? Page 12of 18 a. b. c. d. e. 40 g./mol 200 g/mol 100 g./mol 400 g/mol 128 g./mol 123. When dilute aqueous solutions of lead(II) nitrate and potassium bromide are mixed, a precipitate is observed. The products of this reaction are a. b. c. d. Pb2+(aq) + Br 1- (aq) + KNO3(s) Br2(aq) + NO2(g) + PbK2(s) PbO(s) + K+(aq) + Br1-(aq) + NO2(g) PbBr2(s) + K+(aq) + NO3 1-(aq) 124. Assuming ideal behavior, what is the vapor pressure of a solution of 16.0 mol of carbon tetrachloride and 4.00 mol of dioxane at 23 oC? Vapor Pressure @ 23 oC Carbon tetrachloride 100. mm Hg Dioxane 38.00 mm Hg a. b. c. d. 50.4 mmHg 62.8 mmHg 74.2 mmHg 87.6 mmHg 125. What is the empirical formula for the substance with this analysis: Na=54.0%, B=8.50%, O=37.5% a. b. c. d. Na3BO3 Na4BO4 Na2B2O3 NaB2O2 126. A hydrocarbon undergoes complete combustion to give 0.44g of CO2 and 0.27 g of H2O. What is the simplest (empirical) formula of the hydrocarbon? a. b. c. d. C44H27 CH4 C2H3 CH3 General Chemistry II Sample Test bank 127. A 6.80 g coin was dissolved in nitric acid and 6.21 g of AgCl was precipitated by the addition of excess sodium chloride, Calculate the percentage silver in the coin. Ag+(aq) + Cl1-(aq)" AgCl(s) a. 24.7% b. 68.7% c. 75.3% d. 91.3% 128. A 40- mL portion of a 0.1 M MgSO4 solution contains how many grams of MgSO4? a. 120 g b. 24 g c. 0.96 g d. 0.6 g e. 0.48 g 129. An aqueous solution containing 49 g of sulfuric acid per liter has a concentration of a. 0.50 M b. 1.0M c. 4.9% by mass d. 4.9M 130. One hundred milliliters of a solution of oxalic acid, (COOH)2, is neutralized with 50.0 mL of 0.750 M KOH solution. What is the molarity of the oxalic acid solution? a. 0.099 M b. 0.375 M c. 0.188 M d. 0.750 M e. 0.333 M 131. How many L of CO2 gas at STP can be obtained by burning one mole of C3H8? C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) "3 CO2(g) + 4H2O(g) a. 11.2 b. 44.8 c. 67.2 d. 112 132. What volume of ammonia gas, NH3, measured at STP, will be produced by the decomposition of two moles of ammonium carbonate? (NH4)2CO3(s) " 2NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(g) a. 22.4 L b. 33.6 L c. 44.8 L d. 89.6 L e. 112 L Page 13of 18 133. Which change is likely to be accompanied by the greatest increase in entropy? a. b. c. d. N2(g) + 3H2(g) " 2NH3(g) (at 25 oC) Ag+(aq) + Cl1-(aq) " AgCl(s) (at 25 oC) CO2(s) " CO2(g) (at - 70 oC) H2O(g) " H2O(l) (at 100 oC) 134. When 45.0 g of an alloy at 100.0 oC is dropped into 100.0 g of water at 25.0 oC the final temperature is 37.0 oC. What is the specific heat of the alloy? (for water, specific heat = 4.184 J g1 o -1 C ) a. 0.423 J g-1 oC-1 b. 1.77 J g-1 oC-1 c. 9.88 J g-1 oC-1 d. 48.8 J g-1 oC-1 135. What is the standard enthalpy of combustion of C2H6 in kJ mol-1? Reaction H2(g) + ½ O2(g) " H2O(l) C2H4(g) + H2(g) " C2H6(g) C2H4(g) + 3 O2(g)" 2 CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g) a. b. c. d. ∆Ho -286 kJ -137 kJ -1412 kJ –1275 kJ –31561 kJ –1558 kJ +1834 kJ 136. Given these equations ∆Ho = +300 kJ SO2(g) " O2(g) + S(s) 2SO2(g) + O2(g) " 2SO3(g) ∆Ho = - 200 kJ calculate the heat of formation of SO3(g). a. –500 kJ.mol-1 b. +100 kJ.mol-1 c. –400 kJ.mol-1 d. +200 kJ.mol-1 137. More heat is derived from cooling one gram of steam at 100 oC to water at 50 oC than from cooling one gram of liquid water at 100 oC to 50 oC because a. b. c. d. e. water is a poor thermal conductor. the steam is hotter than the water. the steam occupies a greater volume than the water. the density of water is greater than that of steam. the heat of condensation is evolved. General Chemistry II Sample Test bank 138. Calculate the value of (in kJmol-1) for the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g) "2NH3(g) Bond Energies H—H N=N N—H a. b. c. d. (kJ. mol-1) 435 946 (in N2) 389 Page 14of 18 142. Which nuclear equation is properly balanced? a. 4He + 9Be " 12C + 1H b. 4He + 14N " 17O + 1H c. 4He + 24Mg " 27Si + 1H d. 14N + 0-1e " 14O 143. What is the correct reading for the buret? 32 2340 kJ of heat absorbed 213 kJ of heat absorbed 2340 kJ of heat evolved 83 kJ of heat evolved 33 139. When Al2O3(s) is formed from the elements at standard conditions, the values of ∆Ηo and ∆Go at 298 K are -1617 kJ.mol-1 and -1577 kJ.mol-1, respectively. The standard entropy of formation per mole, in joules per degree, will be a. -315 b. -134 c. - 93.3 d. 0.0933 e. +15.7 a. b. c. d. 144. A particular chemical reaction has a negative ∆H and negative ∆S. Which statement is correct? a. b. 140. Vaporization of a liquid is an example of a process for which a. ∆H, ∆S, and ∆G are positive at all temperatures. b. ∆H and ∆S are positive. c. ∆G is negative at low temperatures, positive at high temperatures. d. ∆H=∆S 141. Consider the boiling point of a series of hydrogen compounds. The abnormally high boiling point for water is due to BP 32 mL 32.2 mL 32.26 mL 33.74 mL c. d. The reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures. The reaction is nonspontaneous at all temperatures. The reaction becomes spontaneous as temperature increases. The reaction becomes spontaneous as temperature decreases. 145. Which line in the diagram represents the activation energy for a forward reaction? a. b. c. d. A B C D A D E B C Reaction Coordinate H2O a. b. c. d. H2S H2Se H H2Te extensive hydrogen bonding its low dipole moment. the extreme stability of the compound. the high electronegativity of hydrogen. 146. a. b. c. d. e. The group —C=O is characteristic of aldehydes. ketones. alcohols esters acids General Chemistry II Sample Test bank 147. Uranium—234 undergoes spontaneous radioactive decay to give an alpha particle and a new nucleus, X. U " 4He + X a. 23090U b. 23090Th c. 23894U d. 23894Pu 234 148. Page 15of 18 150. Consider the phase diagram of a pure compound. Which statement applies? What is X? A C P Which is classified as an alkene? O B Temperature a. b. c. CH3—CH2—C—H CH3CH2CH3 CH3—C = C H d. HC HC 149. a. b. CH2 CH2 c. CH2 CH2 d. An example of an organic acid is O 151. The path A " C represents sublimation. Following the path A " B "C the compound would first liquefy and then vaporize. If the compound is in state A, continued reduction of the pressure (at constant temperature) will cause it to melt. None of these statements is correct. Which is the formula of an alcohol? a. b. CH3CH2CH2 —O—CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2 – O H O a. CH3CH2COCH3 O b. CH3CH2COH O c. CH3 CH2 —C—CH3 O c. CH3CH2CNH2 O d. CH3CH2CH2C—H d. CH3 CH2CH 152. Which choice best indicates the degree of correctness of this statement? “The boiling point of normal propanol is lower than the boiling point of turpentine.” Temperature n-propanol Water Turpentine a. b. c. d. e. 0oC 3.4 4.6 2.1 Vapor Pressure of Substances in mmHg 20oC 50oC 80oC 95oC 100oC 14.5 87.2 376 697 836 17.6 92.0 354.9 760 4.4 17.0 61.3 131.1 The statement is true. The statement is probably true; additional data would be needed for a final decision. It is impossible to judge the statement because the data are insufficient. The statement is probably false; additional data would be needed for a final decision. The statement is false. General Chemistry II Sample Test bank Page 16of 18 153. For the reaction 2H2O2 "2H2O +O2 Which plot confirms that the rate is first order with respect to H2O2? a. b. c. [H2O2] 1/[H2O2] [H2O2]2 time 154. time d. log[H2O2] time time Sulfur dioxide can be described by the structures: S O S O O O This implies that a. b. c. d. the two bonds in SO2 are of equal length, and the electronic distribution in the two SO bonds is identical. the single bond is longer than the double bond and the electronic distribution in the two SO bonds is different. an electron pair in the SO2 molecule alternates back and forth between the two sulfur— oxygen electron pairs so that the two different bonds seem to exchange positions. the SO2 molecule revolves so that the two different bonds seem to exchange positions. Vapor pressure mm Hg 155. The graph shows how the vapor pressure of liquid A and of liquid B changes with the temperature. Select the choice that best indicates the degree of correctness of this statement: “The normal boiling point of liquid B is 78 0C.” 1000 900 800 A 600 B 400 300 200 100 0 a. b. c. d. e. 20 40 60 80 Temperature oC 100 120 The statement is true. The statement is probably true; additional data would be needed for a final decision. It is impossible to judge the statement because data are insufficient. The statement is probably false; additional data would be needed for a final decision. The statement is false. General Chemistry II Sample Test bank 156. Page 17of 18 The isomerism represented by H H H H H H H— C—C—C—O—H and H—C—C—O—C—H H H H a. b. c. d. 157. a. b. c. d. H H H cis—trans. optical. positional. geometric. In a sample of a nearly ideal gas, this graph could represent a plot of V vs. T at a given constant P. P vs. T at a given constant V. P vs. V at a given constant T PV vs. P at a given constant T 158. A mixture of 100 g of K2Cr2O7 and 200 g of water is stirred at 60 oC until no more of this salt dissolves. The resulting solution is decanted (poured off) and cooled to 20 oC. What mass of K2Cr2O7 crystallizes from the solution during the cooling? 80 60 Solubility (g/100 mL) 40 20 0 a. b. c. d. e. 20 40 60 80 Temperature in oC 100 24 g 31 g 43 g 58 g 86 g 159. The height of the mercury in the right arm open to atmospheric pressure (760 mmHg) is 100 mm and the height in the left arm is 120 mm. gas What is the pressure of the gas in the bulb? a. b. c. d. 20 mmHg 640 mmHg 740 mmHg 780 mmHg 120 mm 100 mm General Chemistry II Sample Test bank Page 18of 18 Key to Answers Q# Ans Q# Ans Q# Ans Q# Ans Q# Ans 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 D B A A D D A A D A D D C D D A C C A A B C D C A A A B D C A B C A B 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 E C C C D B B A C B B C A C A A D B D E A D B D D A C D C B D E D B C 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 A C D D B D C C E A D C D A B A A C B B D B A E B C D C C D B B D C A 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 D B A A A B A B C A B B B A A C D D D A D B E A C C D C B C C E D B B 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 A B C D A A B D B D B A D A A C C D C



