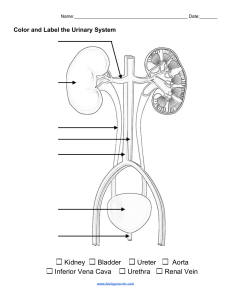
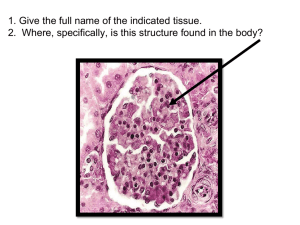
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: System Disorder STUDENT NAME _____________________________________ Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia DISORDER/DISEASE PROCESS __________________________________________________________ Alterations in Health (Diagnosis) Pathophysiology Related to Client Problem Enlargement of the gland that begins to cause urinary dysfunction Urinary retention related to obstruction in the bladder neck or urethra as evidneced by urinary hesitancy REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER___________ Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Exercise on a regular basis to prevent BPH or reduce the growth of it, is to exercise regularly; try to exercise at least 30-minutes per day ASSESSMENT Risk Factors Expected Findings - Increased age - Smoking, chronic alcohol use - Sedentary lifestyle - Western Diet (high-fat, -protein, -carbohydrate; low-fiber) - Diabetes, Heart Disease Laboratory Tests - International Prostate Symptom Score - Urinary frequency, urgency, hesitancy, or incontinence - Incomplete emptying of bladder - Urinary stasis & persistent urinary retention Diagnostic Procedures - Urinalysis - CBC - BUN & Creatinine - Prostate - specific antigen - Culture & sensitivity of prostatic fluid - Monitor vital signs & urinary output - Admister/provide increased fluid - Assist the client to ambulate as soon as possible - Monitor for bleeding - Patient is at high risk for urinary tract infection becuae they are having an obstruction that is not allowing them to urinate - Digital rectal exam - Transrectal ultrasound w/ needle aspiration biopsy - Early prostate cancer antigen PATIENT-CENTERED CARE Nursing Care SAFETY CONSIDERATION S Complications Medications - Finasteride (Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) - lowering medications) - Tamsulosin (Alpha - blocking agents) Client Education - Frequent ejaculation releases - Avoid drinking large amount fluids at one time - Avoid bladder stimulants - Avoid medications that cause decreased bladder tone - Urinary tract infections (UTIs) - Bladder stone - Bladder damage - Kidney damage r Therapeutic Procedures - Prostatic stent - Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) - Transurethral needle ablation - Surgical resection ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES Interprofessional Care - Urology - Regrowth of prostate tissue - Reoccurence of bladder neck obstruction In Text Citation: Holman, H. C., Williams, D., Sommer, S., Johnson, J., Ball, B. S., Wheless, L., Leehy, P., & Lemon, T. (2022). Content Mastery Series: RN Adult Medical Surgical Nursing (11th ed., pp. 233-237). ATI.