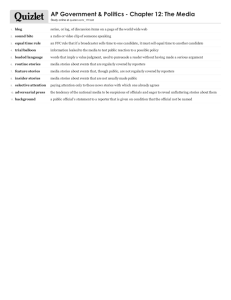
Pain Management Fundamentals of Nursing Contraindication Pain is very personal - both physical & emotional. While everyone experiences pain, not everyone experiences it in the same way. Something that may feel very painful to one person may not feel painful to another Factors affecting how pain is perceived Ethnic and cultural variables Developmental Stage Environment and support people Previous pain experience Meaning of the Pain It's working! Some people see pain as a good thing like, “If the chemo hurts me, it means it’s working.” Types & Sources of Pain Acute Pain Chronic Pain 0 No Pain 1 2 Mild Pain 3 4 Moderate Pain 5 6 Severe Pain 7 8 9 Very Severe Pain 5% of pain 10 Worst Pain Possible reporters exaggrate Sudden, severe, short-term pain Example: New bump or bruise Long-term pain “recurring, over an extended time” Example: Back pain (long-term) Referred Pain The feeling of pain in one part of body is caused by pain or injury in another part of the body Example: Chest pain from a heart attack could trigger pain in the jaw Phantom Pain Pain that feels like it is coming from a body part that is no longer there Test Tips Real pain! Example: Amputations Pain Management Strategies Formulate a plan • Educate the client to make a REALISTIC pain goals • Keep client involved in strategies to manage pain Acknowledge the pain • Only about 5% of pain reporters are found to be exaggerating • Reduce anxiety about pain Pharmacologic treatment • Non opioid pain meds: NSAIDS, Acetaminophen • Opioids • Co therapy Non-Pharmacologic treatment • Breathing techniques • Distraction: TV, reading, games • Heat or cold application • Rest • Meditation • Massage NSAIDS OPIOIDS