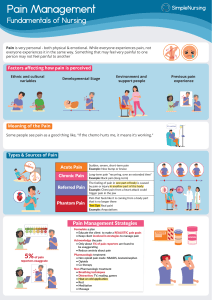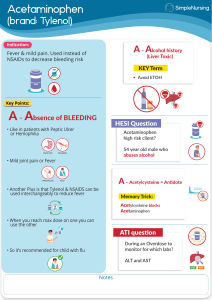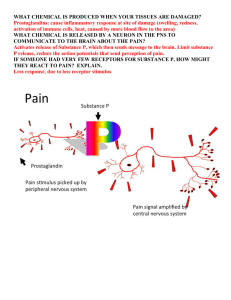
Pain management 5-11 Patho Nociceptors: Pain receptors on nerve endings that respond selectively to painful stimuli. Nociception: The transmission of pain. Chemical substances: some increase pain sensitivity some decrease pain sensitivity. Cox 1: Mediates prostaglandin formation, platelet formation, provides gut protection from ulcers. Cox 2: Present in inflammation, pain and fever. Inhibition will reduce symptoms of fever inflammation and pain. Inhibits substance P. Decrease pain sensation: Endorphins and enkephalins, act as endogenous opioids. Types of pain Chronic : Persistent malignant pain that lasts longer than six months. Factors that influence pain ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ Past experience. Anxiety: decreases pain threshold. Depression: decreases pain threshold. Age. Gender. Culture: different cultures respond to pain differently based on what they were taught to be appropriate. Effects of pain Acute: Increased cardiac output, impaired insulin response, immune supression, increased cortisol production, and increased fluid retention. Chronic: Immune suppression, depression, disability, fatigue, anger, inability to perform ADL’s. Acute pain: Sudden onset of pain, specific to injury. Lasts from seconds to six months. Pharmacologic treatments Non opioids ❖ NSAIDS: Mild pain. Ketorolac, sprix, calador, ibuprofen. ❖ Acetaminophen: Can cause hepatotoxicity can be given with NSAIDs. ❖ Ofirmev: IV acetaminophen, newly approved for short term use IV piggyback. Opioids ❖ Tramadol ❖ Tylenol 3 ❖ Meperidine ❖ Propoxyphene with tylenol ❖ Oxycodone ❖ Fetanyl ❖ Morphine ❖ Dauladid Other ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ PCA pump PRN medications Multi modal: use of one or more drug Routine admin: admin around the clock Topical Local anesthesia Intraspinal Non pharmacologic treatments ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ Cutaneous stimulation: TENS machine Massage Thermal therapies: Heat and cold Distraction Relaxation Guided imagery Hypnosis Music therapy Alternative therapy: Acupuncture Focused pain assessment ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ Scale: 0-10 Timing: When did the pain start, what was happening when it started? Location: Where is the pain? Is it radiating? Duration: How long have you had the pain? Quality: Is it dull, sharp, or stabbing? Aggravating and alleviating factors: What makes it worse? What makes it better? www.Simplenursing.com 5-11