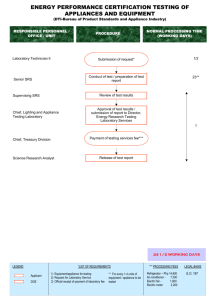
Connect GNS3 to the Internet (GNS3 VM) 1. The topology created in this document looks as follows: The topology created in this document looks as follows: DOWNLOAD THE INTERNET APPLIANCE FROM THE GNS3 WEBSITE 1. Using a web browser, browse to https://gns3.com and click the MARKETPLACE menu item: 2. Click Appliances: 3. Select the Internet for GNS3 VM appliance: 4. An appliance description is displayed. Confirm details of the appliance and then click Download Template: 5. The appliance is downloaded to your local PC: IMPORT GNS3 APPLIANCE 1. Create a new GNS3 topology: 2. Name the project and click OK:. In this example, the name GNS3-VM-Internet is used: 3. In the GNS3 user interface, click File and then Import appliance: 4. Navigate to your Downloads folder, select the internet.gns3a appliance and then click Open: 5. The Internet window displays. Review the summary information: “This appliance simulates a domestic modem. It provides IP addresses using DHCP and will NAT all connections to the Internet without you having to use a cloud interface in your GNS3 topologies. The IP subnets used are in the 172.16.0.0/16 range. Multiple internets can be configured and will have different IP address ranges from 172.16.1.0/24 to 172.16.2.0/24” Click Next >: 6. Select the Run the appliance on the GNS VM (recommend) Server type because the GNS3 VM is required for this server type. Click Next >: 7. An operating system is bundled with the Internet new appliance. Click Next >: 8. A confirmation prompt is displayed. Click Yes to install the appliance: 9. A Summary of settings are displayed. Click Next > to continue: 10. A Usage screen is displayed. Click Finish to complete the appliance addition 11. The appliance is added to GNS3 and a success message displayed. Click OK: 12. Click the Browse all Devices menu option to view the newly imported GNS3 appliance: 13. OptionalYou can view the appliance settings by clicking Edit and then Preferences: 14. Optional Click on the appliance type (will vary) to view the appliance details: 15. Once you have imported the new appliance into GNS3, you can create topologies which include the new appliance. Drag and drop the Internet 0.1 appliance from the GNS3 Toolbar to the GNS3 Workspace. You may be prompted to upload the appliance operating system to the GNS3 VM. Click Yes to upload the appliance operating system. 16. The appliance operating system is uploaded to the GNS3 VM 17.To add a router to the GNS3 topology, clickn the Routers button on the Devices_Toolbar 18. The routers available will depend on your GNS3 configuration. In this example both a local router and GNS3 VM router are available. 19. Drag and drop a GNS3 VM router to the GNS3 Workspace. An instance of the node becomes available in the Workspace: 20. Drag and drop another local router to the GNS3 Workspace: 21. Click the Toolbar Device button again to collapse the group: 22. Click the Add a Link button to start adding links to your topology. The mouse cursor will change to indicate that links can be added: 23. Click on the first router topology to display available interfaces (this is device dependant): 24. Click the interface and then select the cloud in the topology to connect the interface to. In this example FastEthernet 0/0 on R1 was selected and the link was joined to the cloud Internet_0.1-1 25. Select an interface on the cloud to complete the connection. In this example, Ethernet0 on cloud Internet 0.1-1 was selected: 26. Add another link between R2 and R1: 27. Click the Add a Link button to stop adding links. The mouse cursor will change back to normal to indicate that you have stopped adding links: 28. If not already done, click the Show/Hide interface labels button on the GNS3 Toolbar to display interface labels in your topology: 29. You are now ready to power on your network devices. Click the Start/Resume button on the GNS3 Toolbar to start up your network devices: 30. Click the Console connect to all devices button on the GNS3 Toolbar to open a connection to every device in the topology: 31. A console connection is opened to each router in the topology: CONFIGURE THE GNS3 NETWORK: 1. Login to the GNS3 Internet appliance: Username: gns3 Password: gns3 username 'gns3', password 'gns3' Run filetool.sh -b if you want to save your changes box login: gns3 Password: ( '>') /) TC (\ Core is distributed with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY. (/-_--_-\) www.tinycorelinux.net gns3@box:~$ 2. Ping google.com: gns3@box:~$ ping google.com PING google.com (216.58.201.46): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 216.58.201.46: seq=0 ttl=127 time=14.306 ms 64 bytes from 216.58.201.46: seq=1 ttl=127 time=13.987 ms ^C --- google.com ping statistics --2 packets transmitted, 2 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 13.987/14.146/14.306 ms gns3@box:~$ Result The GNS3 Internet appliance is able to ping Internet devices. 3. Configure the IP address of R1 (connected to the cloud): R1# configure terminal R1(config)# interface FastEthernet 0/0 R1(config-if)# ip address dhcp R1(config-if)# no shutdown R1(config-if)# end R1# Result An IP address is allocated to the router by the Cloud DHCP server: R1# *Mar 1 00:02:14.619: %DHCP-6-ADDRESS_ASSIGN: Interface FastEthernet0/0 assigned DHCP address 172.16.48.202, mask 255.255.255.0, hostname R1 R1# 4. Ensure that the router is configured to use the correct DNS server: R1# configure terminal R1(config)# ip domain-lookup R1(config)# ip name-server 8.8.8.8 R1(config)# end R1# 5. Ping google.com: R1# ping google.com Translating "google.com"...domain server (172.16.48.1) [OK] Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 216.58.201.46, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 12/21/32 ms R1# Result Pings succeed. 6. Configure IP addressing on the Internal GNS3 network: Configuration on the routers: R1 R1# configure terminal R1(config)# interface FastEthernet 0/1 R1(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)# no shutdown R1(config-if)# exit R1(config)# R2R2# configure terminal R2(config)# interface FastEthernet 0/0 R2(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 R2(config-if)# no shutdown R2(config-if)# exit R2(config)# 7. Configure OSPF on R1 and R2 and advertise a default route: R1R1(config)# router ospf 1 R1(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0 R1(config-router)# default-information originate R1(config-router)# end R1# R2R2(config)# router ospf 1 R2(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0 R2(config-router)# end R2# Result OSPF neighbor relationships are established: R1*Mar 1 00:10:30.275: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 10.1.1.2 on FastEthernet0/1 from LOADING to FULL, Loading Done R2*Mar 1 00:10:30.307: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 172.16.48.202 on FastEthernet0/0 from LOADING to FULL, Loading Done 8. Configure DNS settings on R2: R2# configure terminal R2(config)# ip domain-lookup R2(config)# ip name-server 8.8.8.8 R2(config)# end R2# 9. R2 will not be able to ping Internet devices until you configure NAT on R1. In this example, the Internet gateway does not support routing, so NAT will be configured on R1: R1# configure terminal R1(config)# interface FastEthernet 0/0 R1(config-if)# ip nat outside R1(config-if)# interface FastEthernet 0/1 R1(config-if)# ip nat inside R1(config)# ip nat inside source list 1 interface FastEthernet 0/0 overload R1(config)# access-list 1 permit 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 R1(config)# end R1# wr 10. Test R2 connectivity to the Internet: R2# ping google.com Translating "google.com"...domain server (8.8.8.8) [OK] Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 74.125.140.138, timeout is 2 seconds: .!!!! Success rate is 80 percent (4/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 36/40/44 ms R2# wr Result R2 is able to ping devices on the Internet. 11.Congratulations! You have configured Internet connectivity from GNS3 VM devices.