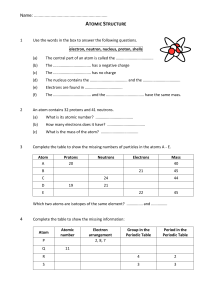
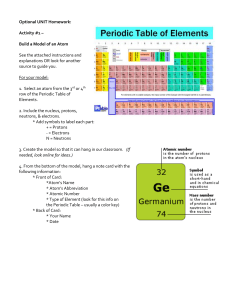
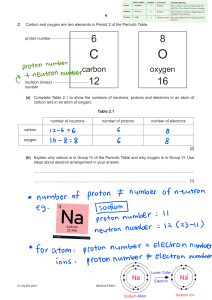
Students’ copy Chapter 8: Atoms & Molecules Theme: Models Duration: Express~12 periods, NA~9 periods Students’ copy Learning objectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: 1. compare the size of an atom with the sizes of everyday objects [POS] 2. *show an appreciation of how, in practice, models are constructed, justified and continuously revised as they are used to probe new phenomena and collect additional data (e.g., the various atomic models) [VEA] 3. describe an atom as an entity that is electrically neutral and is made up of a positively charged nucleus (protons and neutrons) with negatively charged electrons moving around the nucleus [CI] 4. *recognise that atoms have mass that is mainly contributed by the mass of the nucleus [CI] 5. show an awareness that the atoms of an element have a unique number of protons [CI] * Optional for N(A) Science Students’ copy Learning objectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: 6. compare atoms and molecules [POS] 7. show an understanding that a molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are chemically combined [CI] 8. state the numbers and types of atoms, given the chemical symbol of an element or the chemical formula of a compound, e.g., carbon dioxide (Note: Writing of chemical formulae is not required. Giant molecular compounds are also not required.) [CI] 9. show an awareness that technologies resulting from the knowledge of atoms have created social and ethical issues, risks and costs (e.g., atomic bombs) [VEA] 8.1 What is the simplest unit of an element and how do we represent its structure? AB 8.1.1: How small is an Atom? AB Page: 91, 93 *Not doing the practical, Watch video on the next slide and attempt Q2 on page 93 Go through in class: 15 min 8.1 What is the simplest unit of an element and how do we represent its structure? AB 8.1.3: Why is an Atom Electrically Neutral? AB Page: 101 - 103 Duration: 60 min (2 periods) Teachers’ Notes: The SLS package is titled “Why Is an Atom Electrically Neutral? [LSS (Exp/NA)]”. 8.1 What is the simplest unit of an element and how do we represent its structure? AB 8.1.4: What makes up the Mass of an Atom? AB Page: 105 (*Optional for NA) Go through in Class: 15 min 8.1 What is the simplest unit of an element and how do we represent its structure? Read textbook page 64 – 71 8.1 What is the simplest unit of an element and how do we represent its structure? Duration: 15 mins (1)Introduction to atom • All matter is made up of tiny invisible particles called atoms Definition of an atom • An atom is defined as the smallest particle of an element characterizing the element that can exist All elements in the Periodic Table are made up of atoms E.g. Gold is an element which is made up of gold atoms (the smallest particles in gold). It is these particles that determines the properties of gold. How small are atoms? Most part of an atom is empty space. If the size of an atom were the size of a football field, the size of nucleus would be like the size of a pea! pea Atoms are made of sub-atomic particles called electrons neutrons and ___________. protons __________ ___________, (2) Nature of the Sub-atomic particles in an atom The Three Main Sub-atomic Particles • Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus • Electrons are found in electron shells found away from the nucleus. 16 Sub-atomic Particle Relative Mass Relative Charge Location in the Atom proton 1 +1 nucleus neutron 1 0 nucleus electron 1 1840 –1 around the nucleus on electron shell (3) Atoms are Electrically Neutral • Atoms are electrically neutral. • Number of protons = number of electrons 17 (4) Number of Neutrons in an Atom • Unless the number of electrons, the number of neutrons in an atom is not always equal to the number of protons in the atom. 18 © 2023 Marshall Cavendish Education Pte Ltd (5) Mass of an Atom • Mass of an atom is mainly contributed by the mass of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus. • Electrons have mass, but they are much lighter compared to protons and neutrons. Thus, mass of electrons is considered negligible and does not add up to the mass of the atom. 19 Type of Atom Number of Protons Number of Electrons Number of Neutrons Atomic Mass (mass of Protons + Neutrons) Hydrogen 1 1 0 1 Helium 2 2 2 4 Lithium 3 3 4 7 Potassium 19 19 20 39 © 2023 Marshall Cavendish Education Pte Ltd 8.2 How can the number of Protons in an Atom be used to identify an Element? Read textbook page 72 - 74 & notes in the subsequent slides Classifying Elements – The Periodic Table • At present, there are 118 known elements. • They are represented by chemical symbols and grouped in a table called the Periodic Table of elements. Classifying Elements – The Periodic Table The elements are arranged in increasing proton number Across the Periodic Table, from left to right, the proton number increases by 1. Classifying Elements – The Periodic Table Dividing line separates the metals non-metals and non-metals metals Elements such as silicon and germanium, found close to the dividing line are known as metalloids. Metalloids exhibit some properties of metal and nonmetals. Classifying Elements – The Periodic Table Vertical columns are called Groups. Total = 18 groups Labelled as Group 1,2,3,…,18 Classifying Elements – The Periodic Table Horizontal rows are called Periods. Total = 7 Periods. Labelled as 1, 2, 3.. Classifying Elements – The Periodic Table Representing Elements Each element in the Periodic Table are represented in the following format: 11 proton (atomic)number 6 Na C sodium atomic symbol element name 23 relative atomic mass carbon 12 • Each element is given a proton number which is unique to the element (just like your NRIC number). • For elements represented by more than 1 letter, the 1st letter of the atomic symbol must be a capital letter and the subsequent letters are small letters 8.2 How can the number of Protons in an Atom be used to identify an Element? AB 8.2.1: Are they from the same Element? AB Page: 107 - 108 Go through in class: 30 min (1 period) 8.3 How do we represent the Simplest Units of Elements and some Compounds? AB 8.3.1: What are Elements & Compounds made up of? AB Page: 109 ñ 111 Go through in class: 60 min (2 periods) 8.3 How do we represent the Simplest Units of Elements and some Compounds? Duration: 15 mins Molecules #wO A molecule is made up of …………………………….. or more ……………………………..atoms of the same …………………………….. element or different …………………………….. elements …………………………….. combined together. chemically element A molecule of an ………………. consists of only ………………. type of atoms that are chemically ove combined. Oxygen – O2 O Nitrogen – N2 Ozone– O3 O N O N O O A molecule of a ………………… consists of two more ………………….. types of atoms that are chemically combined. O Nitrogen dioxide – NO2 Water– H2O H N O O H Chemical Formula The chemical formula is another way to represent molecules. A chemical formula provides two information of a substance: type (a)The …………………. of elements in the compound. number (b)The …………………. of atoms in each element in the compound. Chemical Formula • Examples: Name Formula Element present Number of each element Carbon dioxide CO2 Carbon Oxygen 1C 2O O C O Molecules of compound Zinc InS SUIfUr aluminum flOUrde aluminium scouvire ↑ AI I 3 sodium oxide sodium Na 2 oxygen 0 I magnesium hitrogen oxygen Mig N 0 I I car ~ sulfuric acid bun E hydrogen H oxygen 0 hydrogen sulfur uxygen 2 ↳ 2 1 S O 2 I 4 w 8.4 What are some Applications of Atomic Technologies and the possible issues that can arise from them? Read TB 79 ñ 82 8.4 What are some Applications of Atomic Technologies and the possible issues that can arise from them? AB 8.4.1: Issues related to the Applications of Atomic Technologies AB Page: 113 ñ 115 Go through in class: 60 min (2 periods) Practice Questions AB Page 117 ñ 118 Go through in class: 30 min (1 period) (20 marks) Duration: 25 min (1 period) (Optional for NA) 7 Model of Matter – The Particulate Nature of Matter Sprint Test Check & Review Paper Duration: 30 min (1 period) (Optional for NA) 7 Model of Matter – The Particulate Nature of Matter Sprint Test Answers