Uploaded by
Baekhyunee Pubby
Human Excretion & Homeostasis: Kidney, Glucose, Temperature
advertisement

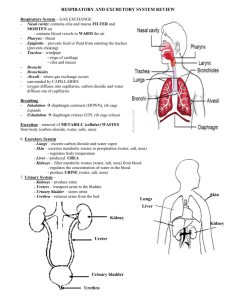
Excretion • The urea is now transported through the bloodstream until it reaches the kidneys. • The kidneys are important filtration organ: helps in regulating water and salts in the body. It also used to remove urea from the blood • The kidney consists of several nephrons, o Structure: close to blood capillaries and are made of tubules. The small tubes loops are around the kidney structure layers and have capillaries around them o Tubules merge into one giant tube known as ureter • • • • • Blood flows into the kidneys through the renal artery. The start of every nephron is a bundle of blood capillaries coiled together called a glomerulus. This bundle of capillaries are squeezed together and the pressure forces out small molecules our of the capillaries into the nephron o Small molecules are allowed to pass through (water, glucose, urea, ions) o Larger structure such as proteins, blood cells are kept flowing in the capillaries The filtrate flows through the tubules and its contents is adjusted depending of the hydration of the individual Reabsorption happens. Water, glucose and ions are reabsorbed by the kidney tissues surrounding the tubules. The reabsorption depends on the concentration of the tissues surrounding the kidney. Almost all glucose is reabsorbed but some water and ions remain along with urea. The resulting filtrate continues to flow and will eventually become urine Reabsorption by the kidney tissues will return these substances back into the blood through the capillaries and eventually the renal vein Health tip • Urine consists of salts and urea. These are water soluble substances that can potentially crystallize given the right conditions. When urine is too concentrated, the salt minerals and urea can form crystal formations and these solids will block the urinary tract • Kidney stones 肾结石: can block urinary tract and damage the tissues resulting to bleeding Homeostasis • Maintenance of a constant internal environment • Control of internal conditions within set limits by negative feedback The control of the glucose concentration of the blood by the liver and the roles of insulin and glucagon from the pancreas • • Both hormones are secreted by the pancreas and are transported to the liver in the bloodstream Insulin control blood glucose level by increasing the uptake of glucose by cells and stimulate cells to convert glucose to glycogen Type 1 diabetes Symptoms • Increased glucose in urine • Blurred vision • Slow wound healing • Treatment • Insulin by injection Regular blood glucose test • Controlled diet The maintenance of a constant internal body temperature in humans in terms of vasodilation and vasoconstriction of arterioles supplying skin surface capillaries When you are cold, body produces and save heat • Shivering: muscles contract and relax -> produce heat • Vasoconstriction: arterioles near skin become narrower -> conserve heat When you are hot, the body loses more heat • Sweating: droplets of sweat evaporate, cooling the body • Vasodilation: arterioles near skin become wider, more blood flows near skin surface -> lose heat Human skin Vasoconstriction 血管收缩 • When we are cold blood flow in capillaries slows down because arterioles leading to the skin capillaries get narrower • Reduces the amount of heat lost from the blood by radiation Vasodilation 血管扩张 • When we are hot blood flow in capillaries increases because blood vessels to the skin capillaries get wider • Cools the body as blood (which carries heat around the body) is flowing at a faster rate through the skin’s surface and so more heat is lost by radiation