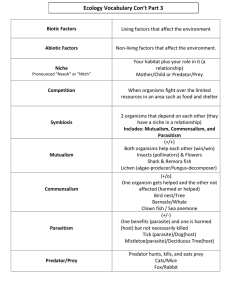
Worksheet # 03 Name: Michael Jon A. Tolentino Course/ Year: BS ARCH 4A I. Date: 10/10/2023 Professor: Define each of the following words or terms. 1. Parasitism - Parasitism is generally defined as a relationship between the two living species in which one organism is benefitted at the expense of the other. 2. Mutualism - Mutualism, association between organisms of two different species in which each benefits. 3. Symbiosis - A symbiosis is an evolved interaction or close living relationship between organisms from different species, usually with benefits to one or both of the individuals involved. 4. Predation - Predation, in animal behavior, the pursuit, capture, and killing of animals for food. 5. Competition - Competition is a relationship between organisms in which one is harmed when both are trying to use the same resource related to growth, reproduction, or survivability. 6. Pollination - Pollination is the act of transferring pollen grains from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma. 7. Endoparasites - A parasite that lives in the internal organs or tissues of its host 8. Ectoparasites - A parasite that lives outside the body of the host 9. Predator - An organism that preys upon other organism 10. Parasites - A parasite is an animal or plant that survives on or within a host organism. II. Completion. 1. Symbiosis refers to any relationship in which two species live closely together. Species always live together in communities, but some species interact in a much more intimate way. 2. Competition happens when organisms of the same or different species attempt to use an ecological resource in the same place at the same time. 3. Some plants are better able to compete than others in a given portion of an ecosystem. These species exclude their competitors from that part of the ecosystem; this is called competitive exclusion. 4. Predator refers to the organism that kills and consumes and Prey is an organism turns into someone's dine. 5. Commensalism happens when one member of the association benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed. Commensalism means literally 'at table together'. 6. It must be emphasized that parasite and host interact and that excessive harm done to a host, which makes it less competitive , also endangers the survival of the parasite species. 7. Theory predicted either that mutualist populations became infinite in size or that an equilibrium was unstable (tended to go to extinction when perturbed from equilibrium point) 8. Parasitism can be differentiated into ectoparasites and endoparasites, depending respectively, on whether they live on or in the host. Lice, flea, ticks, etc. are examples of ectoparasites . 9. Woody plants are usually too hard for the haustoria to be able to penetrate. If plants are densely packed, dodder will spread rapidly to adjacent plants. It can cause a great deal of damage to wheat or lucerne fields. 10. Cercariae are produced after several generations of sporocysts. The cercariae make their way into the water and make contact with a human. III. Discussions 1. Discuss the following comprehensively: 1. Dispersal Mutualisms In dispersal mutualism, the interaction of species are a mutually beneficial relationship. These includes the dispersal of spores, seeds, and other propagules that move from one place to another. When propagules disperse, it can also reproduce and make a new ecological relationship in a new area. Birds is a good example of a dispersal agent wherein it conumes fruits and disperse them in air through dropping. Dispersal mutualism benefit both the dispersal and reproduction that aids in a functioning ecosystem. 2. Cleaning Mutualisms In cleaning mutualism, the interaction between species are a mutual beneficial relationship through cleaning services. Species called “cleaner” will remove unwanted substances from another species which is called “client.” A good example of this is a cleaner fish that cleans parasites from larger fish. Birds that get off ticks from mammals. These interactions helps in the health an well being of the client and the cleaner served as their food source. 3. Parasitism in Plants Parasitism in plants is a type of ecological relationship where one plant, known as the parasite, benefits at the expense of another plant, known as the host. The parasite derives essential nutrients, water, or physical support from the host plant, often causing harm or even death to the host. This interaction is detrimental to the host plant and is an example of a one-sided, negative relationship in nature. Some well-known plant parasites include mistletoe and dodder. 4. Parasitism in Animals Parasitism in animals is a type of ecological relationship where one animal, known as the parasite, benefits at the expense of another animal, known as the host. The parasite relies on the host for resources such as food, shelter, or a place to reproduce, often causing harm to the host in the process. This interaction is typically one-sided, with the parasite benefiting while the host is negatively affected. Examples of animal parasites include ticks, fleas, and tapeworms. IV. Assignment. Discuss the issue on “Biodiversity's Response To Ecosystem Productivity Depends On Historical Plant And Animal Relationships”. Biodiversity, or the variety of life in an ecosystem, can be influenced by how productive that ecosystem is. The response of biodiversity to ecosystem productivity depends on the historical relationships between plants and animals within that ecosystem. These historical relationships often involve coevolution, where plants and animals have evolved together, each influencing the other's survival and reproduction. For example, in some cases, highly productive ecosystems may support a greater diversity of species because certain plants and animals have specialized interactions that benefit one another. Understanding these historical plant and animal relationships is essential for managing and conserving biodiversity in ecosystems.