HST 702
LECTURE 1
Queen Victoria
- “Seemed to rule over an "empire on which a sun never set" because there was so much territory
- People saw her as a beloved sovereign
- Empire was around 400 million people which was about a quarter of the world's population at
the time
Kaiser Wilhelm II
- Chief architect of the world at the time
- Was at Queen Victoria's bed side at the time of her death
- Favourite grandson of Queen Victoria
- Gave a sense of unity
Vote
-
The world seemed all good and safe though it ended up all just being an illusion
People (especially Germany) felt that they were in a time of prosperity
Great Britain seemed to be able to conquer all and solve problems
Various things were invented such as trains, petroleum, first cars, electricity and even ideas like
the 'weekend'
The ability to vote varies from country to country
France: where it is democratic, men 21 and older can cote
Britain: there exists a parliamentary monarch
o 1/3 of the male population can vote and is based on a class system
o Essentially you need to be earning money to be eligible to vote
Germany: autocracy exists – the people can vote but it has next to no effect on decisions being
made (which are done by the Kaiser)
Russia: under a dictatorship by the tsar
Currents of Change
- Social change is starting to occur, the idea of capitalism is really taking height
- This starts to threaten the order of things, mainly to the upper class
- Two different larger movements start to come about
o Transforming the role and place of the worker (socialism)
o Transforming women's role in society {suffrage)
Working Class
- There exists a dramatic difference in classes
- Most lived short, hard lives with a horrible job and awful wages
- As a result, new workers movements start to develop
Karl Marx
- Trade unions start to form (organized and powerful)
- Socialist parties begin to form within Europe
- Socialists: largest part in parliament in Germany in 1914
-
People are seen as traitors and they are not acknowledged which leads to a lot of anxiety
1917: Russia explodes into being the most socialist
1905: Russian troops fire on protesting workers and go to arrest them
- Improve worker conditions?
o Russian troops tried to work with them and reason with them to avoid revolution
- Another danger: Patriotism
o Going to war would be a way to unite the population and stop workers from threating
the status quo and wanting change
- Women were also trying to gain political power
o They wanted the right to divorce and right to own their own property
o Believed that if they were able to vote then everything else will fall into place
Britain
- Most radical
- 1903: Women's “ocial and Political Union developed
o Led by Emmeline Pankhurst – also known as the Suffragettes
o 1913: Emily Davison and the King's Horse
She was a militant activist who fought for women suffrage rights
“he stepped in front of King George V's horse and suffered immensely
- World War One draws a lot of women into the industry which proves that they are capable of
doing the work
Ivan Bloch
- Thought differently… how this war was going to be different then the Franco-Prussian War and
it was not just a patriotic jaunt
- Saw it was going to be a war of entrenchment as these quick victories were a thing of the past
- Thought of it as a war of industry and that it was not going to be resolved quickly
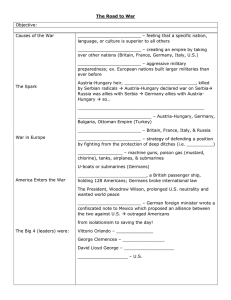
Long Term Causes of the War
Europe 1914: Looking at it before the war
Great Britain
- Seemed to be the ideal, they had a stable parliamentary government
- Economically powerful and had the largest empire the world has ever known
- Unmatched in its naval strength and is a predominate power
- Also the first nation to industrialize
- Challenges:
o Rises of new powers (military and industry) around them such as Germany who wants to
expand and seize a colonial empire
o They feel threatened by the expansionist dreams of other states
o Their backbone is their military, however, it needs industry to support it
Which in turn depends on the economic strength of the country
o Feels challenged by Germany and the USA with new electronics and development of
their industry
France
Russia
-
Since 1870 has been a republic (in which power is explicitly vested in their people – like a
democracy) with proportional representation
Has universal male suffrage
Unstable government prior to 1914; went through 43 governments from 1890-1914
Alsace and Loraine: boarders part of France and Germany and nationalists seek revenge on
Germany after they had "stolen" these territories from them
Though at this time they were no match for Germany as they lagged behind in industry
40% of the population still worked in agriculture (out in the country side)
Could only produce 1/6th the amount of steel that Germany produced
France and Russia had very good economic relations where Russia would even send loans
Absolutist under Tsar Nicholas II
Absolute monarchy: under dictatorship
Briefly allowed for a parliament
Huge state and empire with the largest population and as a result the largest army
o Managed by a gigantic bureaucracy
They were a disaster industrially as they lagged behind and was mostly ran by foreigners
Not a modern dynamic economy (80% of the people worked the land)
o Had a little bit of economic backwardness and adopted an older style way of doing
things with the idea of the absolute monarch
Tsar is obsessed with their military and it being great, not to concerned on the people and their
education
Ravaged by inner turmoil, workers started to strike in the city
Revolutionary movements started to show up, peasants would turn to violence and people were
ready to explode
Austria-Hungary
- ‘ussia's sworn enemy
- Authoritarian with an emperor: Franz Joseph
- Followed an old style monarch with a lot of power
- Seen as the direct source of the war
o Nation of many nationalities/very multiethnic
o Military orders had to be written in 15 different languages
o A lot of people – and a lot that didn't want to be ruled by the Germans
- Slavic nationalists felt that they identified more with the people of Serbia then they did their
own country; this caused them to become more radical
- Austria-Hungary didn't like that because they would collapse if even one part of their nation was
successful to break off and away (cause then others would want to do the same)
- ‘ussia doesn't want Austria-Hungary to grow so they protect Serbia from them
- Austria-Hungary fears disintegration
- Not a very powerful state as a result of these many things
Germany
- Allies with Austria-Hungary
- 1871: first became a nation – a young but determined and driven nation; restless and wanted to
be a big power
- Many wars were fought to unify it into a large state
-
-
-
Kaiser Wilhem II lead Germany
o The power of the state rested in his hands that of his military advisors
Reichstag
o Parliament with virtually no power (cannot introduce legislation)
o Wilhelm has a fetish to the army and navy – wants to build a large army
o Manages to build up a large navy to be able to challenge British forces to be able to
colonize Africa
This commences a naval race between Great Britain and Germany
Becomes a power house industrially
Their population is growing quite rapidly, but they manage to have the highest education rate in
Europe
Economically large
Obsessed with dispute advancements, the nations of Europe keep Germany from growing too
big and strong so Germany feels as though they are being conspired against
Paranoid from the prevention of growth as the powers holding them down completely surround
them
Internal Problems
o Growth of socialism and the importance of the individual
o Hostile feelings towards the ruling class and parliament: people want democracy
o Fear of revolution from the working class
Maybe a great patriotic action such as war would help to unite a fracturing nation
Imperialism
- Rush to claim territories; race to claim central areas outside of Europe
- This creates a lot of tension between the powers
- Start to see the rise of aggressive militarism
o Part of the Naval Arms Race preceding 1914 (to challenge Britain)
- It is seen that European armies double in size – more influence is given to the military leaders
Triple Alliance
- Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy (for a short time at the beginning of the war)
Triple Entente
- Great Britain, Russia, France
1901: Winston Churchill enters the parliament (British)
28 June 1914
- Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
- Conscription was enforced
o Where people were forced to join the army
- Germany was poised to build up their navy and if they do it would be a close threat to Britain
- Dreadnought
o British ‘oyal Navy's response to the naval race against Germany
o Very powerful, new warship
- War starts to seep into British ways of thinking
o Books were written about German invasion
o Britain was getting nervous and started to debate conscription because they figured a
war was bound to happen
-
Count Helmuth von Moltke becomes the chief of the German General Staff
o Convinced that a European war is bound to happen
o Know of Americans stationed in Belgium by orders of Wilson (USA president)
Europe and the Balkans
- Balkans: south east Europe (including Albania, Serbia, etc)
- Vital foundation for beginning of the first world war
Ottoman Empire
- Went into North Africa which shrunk to modern day Turkey
- Lots of wars and small tensions as a result of a power vacuum
1908
-
Austria-Hungary decides to take over Bosnia and Herzegovina with the reason being that Serbia
is an independent Slavic state
- Serbs want to unite Slavic people (those who are ethnically similar) under one flag
- Austria-Hungary wants to prevent this from occurring and them growing so they take Bosnia
- ‘ussians don't want Austria-Hungary to grow anymore so they ally with Serbia to back them up
- Austria-Hungary now has a problem: Bosnia is filled with a bunch of Slavic people who want to
be independent, not ruled by someone of a different nationality then them {they don't want to
be in the Austria-Hungary empire)
1914: As a result the tensions between Austria-Hungary and Serbia is huge
- Austria-Hungary is convinced that “Serbs are fueling Bosnian's separatist ideas