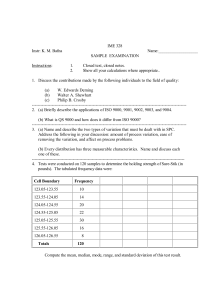
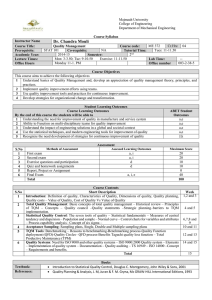
Case Study 3: ISO Adoption Introduction ISO 9000, equivalent to BS5750 and EN29000, is a set of requirements for quality management systems that is widely accepted. It offers recommendations and criteria to assist businesses in creating and maintaining efficient workflows, boosting client pleasure, and consistently enhancing their goods or services. The most well-known standard in this family, ISO 9001, specifies the requirements for attaining and proving excellence in quality management. The Article, “ISO 9000 Implementation and Value Added: Three Case Studies'' by John Seddon in 2012, discusses majorly three cases of ‘Tech.Co.’, ‘Laserco’, and ‘Systems Co.’. I will be discussing the benefits of Implementing ISO 9000, its negative consequences, and why companies still see value in implementing ISO 9000 even when performance indicators indicate the opposite. Benefits: The case study highlights the benefits of implementing ISO 9000 for various firms. Tech. Co. benefits from compliance with government and industry standards, leading to commercial prospects and improved working procedures. Laserco benefits from establishing a formal quality management framework and process improvement. Systems Co. sees a well-structured framework for process control and quality management as its main benefit. Overall, implementing ISO 9000 can lead to improved business processes and efficiency. Some other benefits mentioned in the case studies are: Clarity of Working Procedures: Documenting procedures is a requirement of ISO 9000, which can make it clearer how tasks are carried out. This may help in optimizing procedures and reduce overall errors. Creation of Manuals: The adoption of ISO 9000 led to the development of manuals outlining the processes for a number of business-related functions, such as sales orders and quality control. These manuals can be very useful training and reference tools. Control and Standardization: Control over processes, particularly sales administration, was emphasized during ISO 9000 implementation. It sought to guarantee that protocols were adhered to consistently and that mistakes were kept to a minimum. Discipline and Quality Focus: The first objective was to establish a quality emphasis and build more discipline within the engineering function. The framework for accomplishing this goal was laid by ISO 9000. Mistakes and Waste Reduction: While not quantified, Laserco claimed reductions in time, errors, and waste as a result of ISO 9000 implementation. Standardized processes and procedures can help reduce errors and improve efficiency. Audit and Surveillance: The adoption of ISO 9000 requires ongoing audits and monitoring by outside assessors, which can aid firms in identifying non-conformities and areas for development. These evaluations could be used as a way to conduct independent quality control. Customer Focus: Positive aspects of ISO 9000 include the auditor's attention on comprehending "what matters to the client." It emphasizes how crucial it is to match business procedures with client requirements and expectations. For Example, One of the biggest automobile manufacturers in the world, Ford Motor Company, embraced ISO 9000 standards to enhance its quality control procedures and lower operating expenses. Ford's implementation of ISO 9000 helped them standardize their manufacturing processes and establish clear quality control procedures. This resulted in better product quality and fewer defects in their vehicles. Also, it helped streamline their operations and reduce waste. By identifying and eliminating inefficient processes, they were able to cut down on production costs, which ultimately improved their bottom line. And, Improved product quality and reliability led to higher customer satisfaction levels. Ford's customers experienced fewer issues with their vehicles, resulting in increased loyalty and repeat business. Stephens, B. (1997), "Implementation of ISO 9000 or Ford’s Q1 Award: effects on organizational knowledge and application of TQM principles and quality tools", The TQM Magazine, Vol. 9 No. 3, pp. 190-200 Negative Consequences: Although the firms experienced and benefited from implementing ISO 9000, there were several negative consequences and difficulties. Some of them are mentioned below Complexity of Procedures: Nine manuals of processes, one for each category of product, were produced, resulting in extensive and complex paperwork. It was difficult for administrators to navigate and successfully implement the procedures as a result of this intricacy. Resistance and Conflict: The implementation of ISO 9000 procedures led to disputes between the administrative and sales staff. Salespeople resented the strict rules since they were used to a more flexible approach. As a result of this resistance, there were ongoing disagreements and damaged working relationships. Loss of Customer Focus: The focus on adhering strictly to ISO 9000 procedures sometimes overshadowed the importance of promptly and courteously addressing customer needs and requests. The emphasis on proving customers wrong in case of disputes could damage customer relationships. Misalignment with Quality Goals: While ISO 9000 was chosen as a way to boost discipline and quality, it appeared that the implementation process placed more of an emphasis on compliance and documentation than it did on really raising the standard of the product. The company may not have seen a major gain in product quality or customer satisfaction as a result of its emphasis on following ISO 9000 regulations. Perception of Completion: There was a chance that the company would have seen ISO 9000 certification as the completion rather than the start of their quality journey. They may have been discouraged from looking for more significant adjustments and enhancements to their processes because of this view. Bureaucracy and Documentation Overload: The firm had initially adopted ISO 9000 in hopes of enhancing quality and productivity. However, over time, the emphasis on following rules and documentation had created needless red tape. Information overload and inefficiency may result from the management system's emphasis on recording every procedure and change. Lack of Performance Measures: Implementing ISO 9000 did not always result in the creation and application of performance metrics that were in line with the objectives of the company and its target audience. Lack of pertinent performance metrics may make it more difficult for the company to assess its performance and make improvements. The experience of Boeing, one of the top aerospace businesses in the world, serves as an example of the effects of applying ISO 9000. In order to enhance its quality management systems and achieve a competitive edge in the aerospace sector, Boeing embraced ISO 9000 standards in the 1990s. There were advantages, but there were also serious drawbacks and difficulties. Boeing saw an increase in the amount of paperwork and documentation needed to meet ISO 9000 regulations. This administrative load occasionally made decision-making slower and less agile. Additionally, the emphasis placed by ISO 9000 on compliance and documentation occasionally created a workplace environment in which workers were more focused on meeting standards on paper than actual quality improvements. Significant time and human capital had to be set aside for the implementation process. It could be an expensive project, especially for a big company like Boeing. Weiss, L. A. (1997, May). Quality Digest article. Companies still see value in implementing ISO 9000, why? In today's fiercely competitive global marketplace, businesses are perpetually in pursuit of strategies to enhance operational efficiency, elevate product quality, and augment customer satisfaction. ISO 9000, the internationally recognized quality management standard, has been heralded as a means to achieve these aspirations. However, certain organizations, on their journey to ISO 9000 certification, encounter unforeseen challenges and perplexing performance indicators that seemingly defy the expected benefits. This enigma prompts a pressing question: Why do companies persist in implementing ISO 9000 even when performance indicators appear to suggest a contrary outcome? Organizations often persist with ISO 9000 despite initial signs of dissatisfaction. This is due to the potential for bureaucracy, rigid adherence to procedures, and internal conflicts. The strict documentation and documentation can stifle innovation and frustration among employees. Additionally, the shift in power dynamics within the organization can lead to inefficiencies, misunderstandings, and monotony among employees. ISO 9000 challenges are not due to its design but rather the systemic nature of quality management. These standards aim to foster continuous improvement but can vary across organizations. Ideally, ISO 9000 should enhance operational efficiency, reduce errors, and minimize waste. However, if organizations focus on conforming to procedures and escalating bureaucracy instead of enhancing quality, it can become a double-edged sword. The ISO 9000 paradox arises from the gap between documentation and genuine quality improvement. While the standards emphasize meticulous procedure documentation, it doesn't necessarily lead to continuous improvement. Organizations may prioritize certification over quality enhancement, focusing on documentation but neglecting performance data analysis. This results in documentation becoming a ritualistic formality, despite the importance of data-driven decision-making in enhancing quality. Namara, Sarah Joy, "Do Companies Value Maintaining ISO 9000 Certification? 2009 Case Study of 41 US Companies First Certified in 2000" (2009). Masters Theses & Specialist Projects. Paper 143. With these challenges and unintended consequences in mind, it is essential to comprehend why organizations persist in pursuing ISO 9000 certification despite performance indicators that may suggest a contrasting outcome. 1. Market Necessity:: The industry has made ISO 9000 certification mandatory across a wide range of sectors. Government organizations, major enterprises, and foreign clients frequently demand ISO 9000 conformity as a condition of doing business. Because of this, organizations are forced to pursue accreditation despite the difficulties they face. 2. Perception of Value: Despite certain drawbacks, organizations usually see inherent value in the ISO 9000 guiding principles. A high emphasis on quality, process improvement, and customer happiness is included in these concepts. They may outweigh the temporary difficulties encountered during implementation because of how closely they correspond with more general business goals. 3. Foundational Step for Progress: For businesses looking to start a quality improvement journey, ISO 9000 might be the first step. Despite the fact that the implementation process's early phase may place an emphasis on processes, it provides the groundwork for fostering a more robust quality culture in the future. 4. Acquiring Insights through Failures: Many businesses that struggle with difficulties during ISO 9000 implementation eventually learn important lessons. They gradually modify their procedures, develop their knowledge of the standards, and give priority to a balanced strategy that combines documentation and real quality enhancement. 5. Competitive Edge: An effective differentiation in a crowded market is ISO 9000 certification. Businesses that earn certification can use it as a marketing tool to demonstrate their dedication to quality, which may draw clients who favor vendors with well-established quality management systems. 6. Global Acknowledgment: Worldwide acceptance of ISO 9000. Due to the fact that it creates a universally recognized language for quality management, this international standard can be very beneficial for businesses involved in worldwide trade. ISO 9000 is a quality management standard that promotes a culture of excellence and continuous improvement, despite performance metrics indicating otherwise. The main motivations for businesses to continue seeking ISO 9000 certification are market demands, perceived intrinsic value, and long-term potential for progress. Despite challenges, ISO 9000 remains a crucial tool for businesses seeking a culture of quality and long-term improvement, despite not always leading to quick performance gains. The results may vary depending on the application across different organizations. Conclusion: ISO 9000, a globally recognized quality management standard, provides businesses with a structured framework for improving processes, enhancing product quality, and boosting customer satisfaction. This case study examines the experiences of Tech. Co., Laserco, and Systems Co. in implementing ISO 9000. Despite the benefits such as improved procedures, documentation, and customer-focused approach, negative consequences like increased bureaucracy and internal conflicts can occur. Despite these challenges, companies continue to see value in pursuing ISO 9000 certification due to market necessity and the perceived value of ISO 9000 principles. ISO 9000 is often seen as the first step towards broader quality improvement efforts, as companies learn from initial difficulties and adapt their processes. ISO 9000 serves as a competitive edge, a globally acknowledged standard, and a testament to a commitment to quality, making it a valuable asset for businesses in a competitive global market. Despite challenges and potential pitfalls, ISO 9000 remains a critical tool for organizations aiming to cultivate a culture of quality and long-term improvement. References: 1. Wikipedia contributors. (2023). ISO 9000. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_9000 2. Stephens, B. (1997), "Implementation of ISO 9000 or Ford’s Q1 Award: effects on organizational knowledge and application of TQM principles and quality tools", The TQM Magazine, Vol. 9 No. 3, pp. 190-200. https://doi.org/10.1108/09544789710168975 3. Weiss, L. A. (1997, May). Quality Digest article. https://www.qualitydigest.com/april98/html/as9000.html 4. Namara, Sarah Joy, "Do Companies Value Maintaining ISO 9000 Certification? 2009 Case Study of 41 US Companies First Certified in 2000" (2009). Masters Theses & Specialist Projects. Paper 143. http://digitalcommons.wku.edu/theses/143 This case study is the part of Academic learning process in the course Logistics and Supply Chain Management, Introduction to Logistics and Supply Chain Management – (Sep 24). I, Author of this Article, I, the Author of this case study, am only trying to express my views on the article published by John Seddon, in April 1996 on the topic of ISO 9000 implementation and value-added: Three case studies. and mean no disrespect and only honest opinions are presented. Siddhanta Poudel Email: siddhantapoudel7@gmail.com