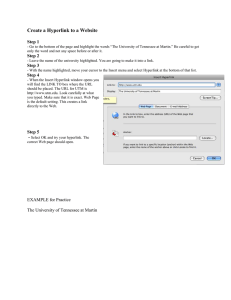
ASSIGNMENT 1 FRONT SHEET Qualification Unit number and title Submission date Re-submission Date Student Name Class BTEC Level 5 HND Diploma in Computing Unit 2: Networking Infrastructure Date Received 1st submission Date Received 2nd submission Huỳnh Tuấn Kiệt GCS1102 Student ID Assessor name GCS210886 Student declaration I certify that the assignment submission is entirely my own work and I fully understand the consequences of plagiarism. I understand that making a false declaration is a form of malpractice. kiet Student’s signature Grading grid P1 P2 P3 P4 M1 M2 Summative Feedback: Grade: Lecturer Signature: Assessor Signature: D1 Resubmission Feedback: Date: Assignment Brief 1 (RQF) Higher National Certificate/Diploma in Computing Student Name/ID Number: Unit Number and Title: Academic Year: Unit Assessor: Assignment Title: Issue Date: Submission Date: Internal Verifier Name: Date: Huỳnh Tuấn Kiệt - GCS210886 Unit 2: Networking 2022 Networking Infrastructure Submission Format: Format: • The submission is in the form of an individual written report. This should be written in a concise, formal business style using single spacing and font size 12. You are required to make use of headings, paragraphs and subsections as appropriate, and all work must be supported with research and referenced using the Harvard referencing system. Please also provide a bibliography using the Harvard referencing system. Submission • Students are compulsory to submit the assignment in due date and in a way requested by the Tutor. • The form of submission will be a soft copy posted on HYPERLINK "http://cms.greenwich.edu.vn/"http://cms.greenwich.edu.vn/. HYPERLINK "http://cms.greenwich.edu.vn/" • Remember to convert the word file into PDF file before the submission on CMS. Note: • • • The individual Assignment must be your own work, and not copied by or from another student. If you use ideas, quotes or data (such as diagrams) from books, journals or other sources, you must reference your sources, using the Harvard style. Make sure that you understand and follow the guidelines to avoid plagiarism. Failure to comply this requirement will result in a failed assignment. Unit Learning Outcomes: LO1 Examine networking principles and their protocols. LO2 Explain networking devices and operations. Assignment Brief and Guidance: Assignment scenario You are employed as a network engineer by Nguyen Networking Limited, a high-tech networking solution development company, which has branches in Ho Chi Minh City, Hanoi, Da Nang and Can Tho. The company has been contracted to implement a networking project from a local educational institute. The specification of the project is given below: • People: 200 students, 15 teachers, 12 marketing and administration staff, 5 higher managers including the academic heads and the programme managers, and 3 computer network administrators. • • Resources: 50 student lab computers, 35 staff computers, and 3 printers. Building: 3 floors, all computers and printers are on the ground floor apart from the IT labs – one lab located on the first floor and another located on the second floor. Task 1 The CEO of the company, Mr. Nguyen, has asked you to investigate and explain networking principles, protocols and devices and submit a report. You will need to produce a report that includes the following: • • • • • An introduction to provide an overview of your report. Benefits and constraints of different types of networks and networking standards. The impact of network topology, speed of communication and bandwidth requirements. Effectiveness of networking systems. Discussion on operating principles of networking devices and server types and networking software. • • Discuss the relationship of workstation hardware with networking software. Explore a range of server types and justify the selection of a server, considering a given scenario regarding cost and performance optimization. • For the given specification, identify the topology protocol for the efficient utilization of a networking system. Learning Outcomes and Assessment Criteria (Assignment 1): Learning Outcome Pass Merit P1 Discuss the M1 Compare LO1 benefits and common networking constraints of principles and how different network protocols enable the Distinction D1 Considering a given scenario, identify the topology protocol types and standards. P2 Explain the impact of network topology, communication and bandwidth requirements. P3 Discuss the operating principles of networking devices and server types. LO2 P4 Discuss the inter- dependence of workstation hardware with relevant networking software. effectiveness of networked systems. selected for the efficient utilization of a networking system. M2 Explore a range of server types and justify the selection of a server, considering a given scenario regarding cost and performance optimisation. Table of Contents P1 Discuss the benefits and constraints of different network types and standards .............................................. 3 • Introduction to Network: ....................................................................................................................... 3 • OSI Model ......................................................................................................................................... .... 3 • Types of common network .................................................................................................................... 5 • LAN .................................................................................................................................. .............. 5 • • WAN .................................................................................................................................. ............ 6 Network protocols ................................................................................................................................. 9 • Definition .................................................................................................................................. ........ 9 • Purposes of network protocols ........................................................................................................... 9 • Common network protocols ............................................................................................................. 10 • Network standards .............................................................................................................................. 13 • International Standards Organization ........................................................................................... 13 • Standards used in network ........................................................................................................... 14 P2 Explain the impact of network topology, communication and bandwidth requirements: ............................. 14 • Introduction to network topology ........................................................................................................ 14 1.1 Definition ..................................................................................................................................... 14 1.2 Physical topology: .................................................................................................................................. 15 1.3 Logical topology: ................................................................................................................................... 15 1.4 The difference between physical topology and logical topology ..................................................... 16 1.5 Popular topologies ....................................................................................................................... 17 2. Network Communication .............................................................................................................................. 23 2.1 Definition: ............................................................................................................................................... 23 2.2 The rules in the network communication: ........................................................................................... 24 3. Network Bandwidth: ..................................................................................................................................... 25 3.1 Definition: ............................................................................................................................................... 25 3.2 Why bandwidth requirement is needed for networks: ....................................................................... 26 P3 Discuss the operating principles of networking devices and server types ....................................................... 26 • Networking devices: ...................................................................................................................................... 26 • Switches: ................................................................................................................................................. 26 • Routers.............................................................................................................................................. ...... 27 • Gateways .................................................................................................................................................... 27 P4 Discuss the inter-dependence of workstation hardware with relevant networking software: ...................... 29 • Introduction to interdependence network ........................................................................................................ 29 • Workstation hardware .................................................................................................................................. 30 • Definition: ............................................................................................................................................... 30 • Example .................................................................................................................................................. 31 • Networking Software ......................................................................................................................................... 34 P1 Discuss the benefits and constraints of different network types and standards: 1. Introduction to Network: Figure 1 - Network A network consists of 2 or more computers linked together to share resources (such as printers and CDs), exchange files, and communicate with each other. Computers on a network can be linked via cables, phone lines, radio waves, satellites, or infrared rays. Two common types of networks include: − Local Area Network (LAN) − Wide Area Network (WAN) There are also the following types: Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN), Wireless WAN (WWAN). 2. OSI Model: The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model) is a conceptual model that characterizes and standardizes the communication functions of a telecommunication or computing system without regard to its underlying internal structure and technology. Its goal is the interoperability of diverse communication systems with standard communication protocols. Figure 2 - Model The model partitions the flow of data in a communication system into seven abstraction layers, from the physical implementation of transmitting bits across a communications medium to the highest-level representation of data of a distributed application. Each intermediate layer serves a class of functionality to the layer above it and is served by the layer below it. Classes of functionality are realized in software by standardized communication protocols. OSI divides the two-device communication into seven layers. A task or task group is assigned to each of these 7 classes. All the layers are independent and the tasks are assigned to them to implement the common networks independently. • Types of common network: 3.1 LAN: Definition: A local area network (LAN) is a collection of devices connected together in one physical location, such as a building, office, or home. A LAN can be small or large, ranging from a home network with one user to an enterprise network with thousands of users and devices in an office or school. Figure 3 - LAN • Characteristics: • LAN should be capable of providing high speed, and high capacity communications. • • • Has large bandwidth, can run online applications connected through the network such as conferences, movie screenings... • The connection range has a relatively small limit. • Low cost • Simple LAN administration • A minimum LAN requires a server (server), paired devices (Repeater, Hub, Switch, Bridge), a client computer (client), a network card (Network Interface Card - NIC), and cables (cable). to connect computers together . Benefits of LAN: • The basic LAN implementation does not cost too much. • It is easy to control and manage the entire LAN as it is available in one small region. • The LAN configuration is very easy due to the availability of required protocols in the Operating System (OS) itself. • The systems or devices connected on LAN communicate at a very high speed depending upon LAN type and Ethernet cables supported. The common speeds supported are 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, and 1000 Mbps. Gigabit Ethernet versions are evolving very fast. Cheaper versions will be available once the technology matures and mass production has been carried out. • With the help of file servers connected on the LAN, sharing of files and folders among peers will become very easy and efficient. • It is easy to set up security protocols to protect LAN users from intruders or hackers. • It is easy to share common resources such as printers and internet lines among multiple LAN users. • LAN users do not require their own hard disk and CD-ROM drives. They can save their work centrally on the network file server. • Application software such as MS Office, Anti-Virus, Adobe reader is stored in one system and are shared for all the LAN users. This helps them install application software with the click of a mouse. Constraints of LAN: • LAN covers small geographical area. • Security issues are big concern as it is easy to have access to programs and data of peers. Special security measures are needed to stop unauthorized access. • It is difficult to setup and maintain LAN and requires skilled technicians and network administrators. • In the server based LAN architecture, if server develops some fault, all the users are affected. • Appearance of virus in one system can spread very fast to all the LAN users very easily. 3.2 WAN: • Definition: • A wide area network (WAN) is a telecommunications network that extends over a large geographic area for the primary purpose of computer networking. Wide area networks are often established with leased telecommunication circuits. • In its simplest form, a wide-area network (WAN) is a collection of local-area networks (LANs) or other networks that communicate with one another. A WAN is essentially a network of networks, with the Internet the world's largest WAN. Figure 4 - WAN • Characteristics: • It connect devices that are separated by a broader geographical area than a LAN • It use Carriers such as phone companies or network providers • • It use serial connection. Benefits of WAN: • WAN covers larger geographical area. Hence business offices situated at longer distances can easily communicate.5 • Like LAN, it allows sharing of resources and application softwares among distributed workstations or users. • The software files are shared among all the users. Hence all will have access to latest files. This avoids use of previous versions by them. • Organizations can form their global integrated network through WAN. Moreover it supports global markets and global businesses. • The emergence of IoT (Internet of Things) and advanced wireless technologies such as LAN or LAN-Advanced have made it easy for the growth of WAN based devices. Messages can be sent very quickly across the globe with the help of applications such as whatsApp, facebook messenger etc. Constraints of WAN: • Initial investment costs are higher. • It is difficult to maintain the network. It requires skilled technicians and network administrators. • There are more errors and issues due to wide coverage and use of different technologies. Often it requires more time to resolve issues due to involvement of multiple wired and wireless technologies. • It has lower security compare to LAN and MAN due to wider coverage and use of more technologies. • Security is big concern and requires use of firewall and security softwares/protocols at multiple points across the entire system. This will avoid chances of hacking by intruders. 3.3 MAN: • Definition: - A metropolitan area network (MAN) is a computer network that interconnects users with computer resources in a geographic region of the size of a metropolitan area. The term MAN is applied to the interconnection of local area networks (LANs) in a city into a single larger network which may then also offer efficient connection to a wide area network. The term is also used to describe the interconnection of several local area networks in a metropolitan area through the use of point-to-point connections between them. Figure 5 - MAN • • Characteristics: • average bandwidth but the connection range is relatively large. • installation cost is higher than LAN. • network administration is more complex. Benefits of MAN: • It utilizes drawbacks of both LAN and WAN to provide larger and controllable computer network. • MAN requires fewer resources compare to WAN. This saves the implementation cost. • It helps people interface fast LANs together. This is due to easy implementation of links. • • It provides higher security compare to WAN. • It helps in cost effective sharing of common resources such as printers etc. • Like LAN and WAN, it also offers centralized management of data and files. Constraints of MAN: • It is difficult to manage the network once it becomes large. • It is difficult to make the system secure from hackers and industrial espionage. • Network installation requires skilled technicians and network administrators. This increases overall installation and management costs. • It requires more cables for connection from one place to the other compare to LAN. 4. Network protocols: 4.1 Definition: - Network protocols are a set of rules, conventions, and data structures that dictate how devices exchange data across networks. In other words, network protocols can be equated to languages that two devices must understand for seamless communication of information, regardless of their infrastructure, design disparities, and can exchange information with each other. 4.2 Purposes of network protocols: • Without protocols, devices would lack the ability to understand the electronic signals they send to each other over network connections. Network protocols serve these basic functions: • Address data to the correct recipients. • Physically transmit data from source to destination, with security protection if needed. • Receive messages and send responses appropriately. • Consider a comparison between network protocols with how a postal service handles physical paper mail. Just as the postal service manages letters from many sources and destinations, network protocols keep data flowing along many paths continuously. • Unlike physical mail, however, network protocols provide advanced capabilities. These include delivering a constant flow of messages to one destination (called streaming) and automatically making copies of a message for delivery to multiple destinations at once (called broadcasting). 4.3 Common network protocols: TCP/IP: • Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is the language a computer uses to access the internet. It consists of a suite of protocols designed to establish a network of networks to provide a host with access to the internet. • TCP/IP is responsible for full-fledged internet data connectivity and transmitting the data end to end by providing other functions, including addressing, mapping and acknowledgment. TCP/IP contains four layers, which differ slightly from the OSI model. Figure 6 - Transmission Control protocols HTTP: - The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, where hypertext documents include hyperlinks to other resources that the user can easily access, for example by a mouse click or by tapping the screen in a web browser. Figure 7 - Hypertext Transfer Protocol DNS: - Domain Name Server (DNS) is a standard protocol that helps Internet users discover websites using human readable addresses. Like a phonebook which lets you look up the name of a person and discover their number, DNS lets you type the address of a website and automatically discover the Internet Protocol (IP) address for that website. Figure 8 - DNS ICMP: - The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is a network layer protocol used by network devices to diagnose network communication issues. ICMP is mainly used to determine whether or not data is reaching its intended destination in a timely manner. Commonly, the ICMP protocol is used on network devices, such as routers. ICMP is crucial for error reporting and testing, but it can also be used in distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. Figure 9 - ICMP DHCP: • Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP - dynamic server configuration protocol) is a protocol that allows automatic IP address allocation along with other related configurations such as subnet mask and default gateway. The computer is configured automatically, thus reducing interference with the network. It provides a central database to keep track of all the computers on the network. The most important purpose is to avoid the situation where two different computers have the same IP address. • Without DHCP, machines can configure IP manually (static IP configuration). In addition to providing IP addresses, DHCP also provides other configuration information, such as DNS. Currently, there are two versions of DHCP: IPv4 and IPv6. 5. Network standards: - Networking standards define the rules for data communications that are needed for interoperability of networking technologies and processes. Standards help in creating and maintaining open markets and allow different vendors to compete on the basis of the quality of their products while being compatible with existing market products.During data communication, a number of standards may be used simultaneously at the different layers. The commonly used standards at each layer are − - Application layer − HTTP, HTML, POP, H.323, IMAP - Transport layer − TCP, SPX - Network layer −IP, IPX • Data link layer − Ethernet IEEE 802.3, X.25, Frame Relay • Physical layer −RS-232C (cable), V.92 (modem) • Standards are the set of rules for data communication that are needed for exchange of information among devices. It is important to follow Standards which are created by various Standard Organization like IEEE , ISO , ANSI etc. Types of Standards : • De Facto Standard. • De Jure Standard. 5.1 International Standards Organization: - The International Organization for Standardization is an independent, nongovernmental organization, the members of which are the standards organizations of the 165 member countries. it is the world's largest developer of voluntary international standards and it facilitates world trade by providing common standards among nations. More than twenty thousand standards have been set, covering everything from manufactured products and technology to food safety, agriculture, and healthcare. Figure 10 - ISO 5.2 Standards used in network: Some of the noted standards organizations are: • International Standards Organization ( ISO) • International Telecommunication Union (ITU) • Institute of Electronics and Electrical Engineers (IEEE) • American National Standards Institute (ANSI) • Internet Research Task Force (IETF) • Electronic Industries Association (EIA) P2 Explain the impact of network topology, communication and bandwidth requirements: 1. Introduction to network topology 1.1 Definition: - Network topology refers to the manner in which the links and nodes of a network are arranged to relate to each other. Topologies are categorized as either physical network topology, which is the physical signal transmission medium, or logical network topology, which refers to the manner in which data travels through the network between devices, independent of the physical connection of the devices. Logical network topology examples include twisted-pair Ethernet, which is categorized as a logical bus topology, and token ring, which is categorized as a logical ring topology. Figure 11 - Types of Network Topology 1.2 Physical topology: - Physical topology refers to the interconnected structure of a local area network (LAN). The method employed to connect the physical devices on the network with the cables, and the type of cabling used, all constitute the physical topology. This contrasts with logical topology, which describes a network's media signal performance and how it exchanges device data. Figure 12 - Physical Topology 1.3 Logical topology: • A logical topology is a concept in networking that defines the architecture of the communication mechanism for all nodes in a network. Using network equipment such as routers and switches, the logical topology of a network can be dynamically maintained and reconfigured. • Logical topologies contrast with physical topologies, which refer to the physical interconnections of all devices in the network. Figure 13 - Logical Topology 1.4 The difference between physical topology and logical topology: Comparison Chart: BASIS FOR COMPARISON Basic Types PHYSICAL TOPOLOGY LOGICAL TOPOLOGY Refer to how a network look and functions. Fashion in which data travels logistically. Bus, star, ring and mesh topologies. Logical bus and the logical ring. Founded on Physical connections of cables and devices. Cost, scalability, flexibility, bandwidth capacity, etcetera. Can affect Path traveled by data in a network. Data delivery causing lost packets or congestion. 1.5 Popular topologies: Mesh topology: • A mesh topology is a network setup where each computer and network device is interconnected with one another. This topology setup allows for most transmissions to be distributed even if one of the connections goes down. It is a topology commonly used for wireless networks. Below is a visual example of a simple computer set up on a network using a mesh topology. • The mesh topology has a unique network designin which each computer on the network connects to every other.It is develops a P2P (point-to point) connection between all the devices of the network.It offers a high level of redundancy, so even if one network cable fails, still data has an alternative path to reach its destination. Figure 14 - Mesh • Advantages: • The network can be expanded without disrupting current users. • Need extra capability compared with other LAN topologies. • A mesh topology is robust. • It has multiple links,so if any single route is blocked, then other routers should be used for data communication. • No traffic problem as nodes has dedicated links. • Dedicated links help you to eliminate the traffic problem • It helps you to avoid the chances of network failuer by connecting all systems to a central node. P2P links make the fault identification isolation process easy. • • • Manages high amounts of traffic, because multiple devices can transmit data simultaneously. • A failure of one device does not cause a break in the network or transmission of data. • Adding additional devices does not disrupt data transmission between other devices. • Every system has its privacy and security. Disadvatages: • Its is expensive due to the use of more cables.No proper utilization of systems. • Instation is complex because every node is connected to every node. • The cost to implement is higher than other network topologies, making it a less desirable option. • Building and maintaining the topology is difficult and time consuming. • The chance of redundant connections is high, which adds to the high costs and potential for reduced efficiency. • Because of the amount of cabling and the number of input-outputs,it is expensive to impeplement. • It requires a large space to run the cables. • • It requires more space for dedicated links. Star topology: In the star topology, all the computers connect with the help of a hub. This cable is called a central node, and all other nodes are connected using this central node. It is most popular on LAN networks as they are inexpensive and easy to install. Figure 15 - Star • • Advantages: • Easy to troubleshoot, set up, and modify. • Only those nodes are affected, that has failed. Other nodes still work. • Fast performance with few nodes and very low network traffic. • In Star topology, addition, deletion, and moving of the devices are easy. Disadvatages: • If the hub or concentrator fails, attached nodes are disabled. • Cost of installation of star topology is costly. • Heavy network traffic can sometimes slow the bus considerably. • Performance depends on the hub’s capacity • A damaged cable or lack of proper termination may bring the network down. Bus topology: Bus topology uses a single cable which connects all the included nodes. The main cable acts as a spine for the entire network. One of the computers in the network acts as the computer server. When it has two endpoints, it is known as a linear bus topology. Figure 16 - Bus • • Advantages: • Cost of the cable is very less as compared to other topology, so it is widely used to build small networks. • Famous for LAN network because they are inexpensive and easy to install. • It is widely used when a network installation is small, simple, or temporary. • It is one of the passive topologies. So computers on the bus only listen for data being sent, that are not responsible for moving the data from one computer to others. Disadvatages: • In case if the common cable fails, then the entire system will crash down. • When network traffic is heavy, it develops collisions in the network. • Whenever network traffic is heavy, or nodes are too many, the performance time of the network significantly decreases. • Cables are always of a limited length. Ring topology: • In a ring network, every device has exactly two neighboring devices for communication purpose. It is called a ring topology as its formation is like a ring. In this topology, every computer is connected to another computer. Here, the last node is combined with a first one. • This topology uses token to pass the information from one computer to another. In this topology, all the messages travel through a ring in the same direction. Figure 17 - Ring • • Advantages: • Easy to install and reconfigure. • Adding or deleting a device in-ring topology needs you to move only two connections. • The troubleshooting process is difficult in a ring topology. • Failure of one computer can disturb the whole network. • Offers equal access to all the computers of the networks. • Faster error checking and acknowledgment. Disadvatages: • Unidirectional traffic. • Break in a single ring can risk the breaking of the entire network Modern days high-speed LANs made this topology less popular. • In the ring, topology signals are circulating at all times, which develops unwanted power consumption. • It is very difficult to troubleshoot the ring network. • Adding or removing the computers can disturb the network activity. Tree topology: Tree topologies have a root node, and all other nodes are connected which form a hierarchy. So it is also known as hierarchical topology. This topology integrates various star topologies together in a single bus, so it is known as a Star Bus topology. Tree topology is a very common network which is similar to a bus and star topology. Figure 18 - Tree • • Advantages: • Failure of one node never affects the rest of the network. • Node expansion is fast and easy. • Detection of error is an easy process. • It is easy to manage and maintain. Disadvatages: • It is heavily cabled topology. • If more nodes are added, then its maintenance is difficult. • If the hub or concentrator fails, attached nodes are also disabled. Hybrid topology: • Hybrid topology combines two or more topologies. You can see in the above architecture in such a manner that the resulting network does not exhibit one of the standard topologies. • For example, as you can see in the above image that in an office in one department, Star and P2P topology is used. A hybrid topology is always produced when two different basic network topologies are connected. Figure 19 - Hybrid Topology • • Advantages: • Offers the easiest method for error detecting and troubleshooting. • Highly effective and flexible networking topology. • It is scalable so you can increase your network size. Disadvatages: • The design of hybrid topology is complex. • It is one of the costliest processes. 2. Network Communication: 2.1 Definition: • A communication network is the pattern of directions in which information flows in the organization. Channels of communication (networks by which information flows) are either formal networks or informal networks. Formal networks follow the authority chain and are limited to task-related communications. The informal network (grapevine) is free to move in any direction, skip authority levels, and is as likely to satisfy group members' social needs as it is to facilitate task accomplishments. • the act of substituting one thing for another; substitution; exchange. the changing of a prison sentence or other penalty to another less severe.the act of commuting, as to and from a place of work.the substitution of one kind of payment for another.Electricity. the act or process of commutating.Also called commutation test .Linguistics. the technique, especially in phonological analysis, of substituting one linguistic item for another while keeping the surrounding elements constant, used as a means of determining the constituent units in a sequence and their contrasts with other units. 2.2 The rules in the network communication: • Protocols are required for effective communication and include: • An identified sender and receiver o Common language and grammar o Speed and timing of delivery • • Confirmation or acknowledgment requirements The protocols used in network communications also define: • Message encoding o Message formatting and encapsulation o Message size o Message timing o Message delivery options The rules message encoding: • • Decoding reverses this process in order to interpret the information. • Encoding between hosts must be in an appropriate format for the medium. • Messages sent across the network are first converted into bits by the sending host. • Each bit is encoded into a pattern of sounds, light waves, or electrical impulses depending on the network media over which the bits are transmitted. • The destination host receives and decodes the signals in order to interpret the message. The rules message formatting and encapsulation: • Putting the letter into the addressed envelope. • Each computer message is encapsulated in a specific format, called a frame, before it is sent over the network. • There is an agreed fomat for letters and addressing letters which is required for proper delivery. - A frame acts like an envelope providing destination address and source address The rules message size: • Humans break long messages into smaller parts or sentences. • Long messages must also be broken into smaller pieces to travel acreoss a network. • • Each piece is sent in a separate frame. • Each frame has its own addressing information. • A receiving host will reconstruct multiple frames into the original message The rules message timing: • • • Access Method: that rule which determines when someone is able to send a message. • Flow Control: Another timing rule which affects how much information can be sent the speed that it can be delivered is Flow Control. • Response Timeout: If person A asks a question from person 8 and he does not hear a response within an acceptable time frame. The rules message delivery options: • Messages are delivered via different methods. Sometimes, it may be needful to send information to a single person. This o referred to as one to one delivery and is called unicast which implies that there is only one destination jungle destination) for the message being sent. • It may be needful to communicate information to more than one person perhaps a group of people (at the same time). This is referred to as one to many and is called multicast which implies that one sender to multiple destinations/ recipientsf or the same message being sent. Others times my warrant the information to be communicated to every person in the same area. This is referred to as one-to-all and is called broadcast which implies that one sender sends a message to all connected recipients. Network Bandwidth: 3.1 Definition: - The term bandwidth has a number of technical meanings but since the popularization of the internet, it has generally referred to the volume of information per unit of time that a transmission medium (like an internet connection) can handle. Figure 20 - Network Bandwidth • An internet connection with a larger bandwidth can move a set amount of data (say, a video file) much faster than an internet connection with a lower bandwidth. • Bandwidth is typically expressed in bits per second, like 60 Mbps or 60 Mb/s, to explain a data transfer rate of 60 million bits (megabits) every second. 3.2 Why bandwidth requirement is needed for networks: • A higher bandwidth allows you to use to upload and download larger amounts of data to your site. Faster data transmission speed. A higher bandwidth results in faster transfer speeds results in no frustration and greater customer satisfaction. • As technology is developing day by day. Users Demand for high speed internet, so to provide the highest data speed, higher bandwidth is required. • Bandwidth availability plays an important role when using VoIP or WebRTC services. If you do not have enough bandwidth or available bandwidth when making calls, you might experience voice quality problems that could result in choppy voice, unexpected issues, and a poor user experience. • Bandwidth is highly significant for determining how quickly a web page loads on a browser. The reason bandwidth is so important for determining how fast a web page loads is because it is the measurement of how fast the computer downloads data and determines the speed of the connection between the internet and the computer. Downloading web pages from the internet is one of the fastest ways to transfer data from a computer to the internet. Bandwidth is important to companies that use social media to interact with their clients. A computer system uses bandwidth when it sends a request to the server that contains the application software, data, and other information. P3 Discuss the operating principles of networking devices and server types: • Networking devices: 1.1 Switches: Definition: Figure 21 - Switches • A switch is a multiport bridge with a buffer and a design that can boost is efficiency(a large number of ports imply less traffic) and performance. A switch is a data link layer device .The switch can perform error checking before forwarding data, which makes it very efficient as it does not forward packets that have errors and forward good packets selectively to the correct • port only .In other words, the switch divides the collision doinaio of hosts, but broadcast domain remains the same. The operating principles in a network: • A network switch is a multiport network bridge that uses MAC addresses to forward data at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model. Some switches can also forward data at the network layer (layer 3) by additionally incorporating routing functionality. Such switches are commonly known as layer-3 switches or multilayer switches. 1.2 Routers: Definition: Figure 22 - Routers - A router is a device like a switch that routes data packets based on their IP addresses. The router is mainly a Network Layer device. Routers normally connect LANs and WANs together and have a dynamically updating routing table based on which they make decisions on routing the data packets. Router divide broadcast domains of hosts connected through it. • The operating principles in a network: - Routers work at the network layer (layer 3) of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model for networking to move packets between networks using their logical addresses (which, in the case of TCP/IP, are the IP addresses of destination hosts on the network) .Because routers operate at a higher OSI level than bridges do, they have better packet-routing and filtering capabilities and greater processing power, which results in routers costing more than bridges. 1.3 Gateways: • Definition: Figure 22 - Gateways - A gateway, as the name suggests, is a passage to connect two networks together that may work upon different networking models. They basically work as the messenger agents that take data from one system, interpret it, and transfer it to another system. Gateways are also called protocol converters and can operate at any network layer. Gateways are generally more complex than switches or routers. Gateway is also called a protocol converter. • • The operating principles in a network: • A network gateway provides interoperability between networks and contains devices, such as protocol translators, impedance matchers, rate converters, fault isolators, or signal translators. A network gateway requires the establishment of mutually acceptable administrative procedures between the networks using the gateway. Network gateways, known as protocol translation gateways or mapping gateways, can perform protocol conversions to connect networks with different network protocol technologies. • and other network parameters to client devices. It relies on the standard protocol known as Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol or DHCP to respond to broadcast queries by clients. Mail servers: • A mail server is the computerized equivalent of your friendly neighborhood mailman. Every email that is sent passes through a series of mail servers along its way to its intended recipient. Although it may seem like a message is sent instantly – zipping from one PC to another in the blink of an eye – the reality is that a complex series of transfers takes place. Without this series of mail servers, you would only be able to send emails to people whose email address domains matched your own – i.e., you could only send messages from one example.com account to another example.com account. • • Wed servers: • Web servers are software or hardware (or both together) that stores and delivers content to a web browser at a basic level. The servers communicate with browsers using Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). Web servers can also support SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) and FTP (File Transfer Protocol). • Web servers are also used for hosting websites and data for web applications. They can host single websites and multiple websites using virtualization. Database servers: • A database server is a machine running database software dedicated to providing database services. It is a crucial component in the client-server computing environment where it provides business-critical information requested by the client systems. Figure 23 - Client Applications P4 Discuss the inter-dependence of workstation hardware with relevant networking software: • Introduction to interdependence network : • The study of interdependent networks is a subfield of network science dealing with phenomena caused by the interactions between complex networks. Though there may be a wide variety of interactions between networks, dependency focuses on the scenario in which the nodes in one network require support from nodes in another network. For an example of infrastructure dependency see Fig. o Example: • Infrastructure networks. The network of power stations depends on instructions from the communications network which require power themselves.[Another example is the interdependence between electric and natural gas systems. • Transportation networks. The networks of airports and seaports are interdependent in that in a given city, the ability of that city's airport to function is dependent upon resources obtained from the seaport or vice versa. • Physiological networks. The nervous and cardiovascular system are each composed of many connected parts which can be represented as a network. In order to function, they require connectivity within their own network as well as resources available only from the other network. • Economic/financial networks. Availability of credit from the banking network and economic production by the network of commercial firms are interdependent. In October 2012, a bipartite network model of banks and bank assets was used to examine failure propagation in the economy at large. • • Protein networks. A biological process regulated by a number of proteins is often represented as a network. Since the same proteins participate in different processes, the networks are interdependent. • Ecological networks. Food webs constructed from species which depend on one another are interdependent when the same species participates in different webs. • Climate networks. Spatial measurements of different climatological variables define a network. The networks defined by different sets of variables are interdependent. Workstation hardware: • Definition: - A workstation (workstation) is a computer that is used by an individual or business to run scientific and technical applications. It has more powerful configuration, runs faster and more features than an ordinary computer. The peculiarity of workstations is that they are connected to each other through a network and serve many users at the same time. Workstations are built with outstanding components, mainly CPU, graphics, memory and multitasking capabilities. It is optimized to handle complex data such as drawings, math formulas, simulations .Workstations are commonly used in the fields of mechanical engineering, graphics, architecture, construction, and filmmaking. 3D, audio processing, image editing. • Example: • Network Card : • Cabling: • System bus: • Memory: • Processor: Figure 25 - Processor I/O devices • Networking Software: • Definition: • • Networking software is a foundational element for any network. It helps administrators deploy, manage, and monitor a network. Traditional networks are made up of specialized hardware, such as routers and switches, that bundle the networking software into the solution. Softwaredefined networking (SDN) separates that software from the hardware, making it easier to innovate and adapt the network to quickly meet changing network demands. The separation of functions from hardware, such as firewalls or load balancing, is called network functions virtualization (NFV). Example: • Some of the more popular examples of networking software include Logic Monitor, Datadog, Vallum Halo Manager and ConnectWise, among others. As always, it is recommended that you take the time to explore all the various options available and consult customer reviews before deciding on a particular product. REFERENCES 1/ Notes, S., Fundamentals, N., Notes, S. and Fundamentals, N., 2022. Part 1 - Introduction to Networking - Network Direction. [online] Network Direction. Available at: <https://networkdirection.net/study-notes/network- fundamentals/introduction-to-networking/> [Accessed 25 April 2022]. 2/En.wikipedia.org. 2022. OSI model - Wikipedia. [online] Available at: <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OSI_model> [Accessed 25 April 2022]. 3/ Services, P., 2022. What is a LAN? Local Area Network. [online] Cisco. Available at: <https://www.cisco.com/c/en_in/products/switches/what HYPERLINK "http://www.cisco.com/c/en_in/products/switches/what-is-a-lan-local-area-network.html"HYPERLINK "http://www.cisco.com/c/en_in/products/switches/what-is-a-lan-local-areanetwork.html"is HYPERLINK "http://www.cisco.com/c/en_in/products/switches/what-is-a-lanlocal-area-network.html"- HYPERLINK "http://www.cisco.com/c/en_in/products/switches/whatis-a-lan-local-area-network.html"a HYPERLINK "http://www.cisco.com/c/en_in/products/switches/what-is-a-lan-local-area-network.html"HYPERLINK "http://www.cisco.com/c/en_in/products/switches/what-is-a-lan-local-areanetwork.html"lan HYPERLINK "http://www.cisco.com/c/en_in/products/switches/what-is-a-lanlocal-area-network.html"- HYPERLINK "http://www.cisco.com/c/en_in/products/switches/whatis-a-lan-local-area-network.html"local HYPERLINK "http://www.cisco.com/c/en_in/products/switches/what-is-a-lan-local-area-network.html"HYPERLINK "http://www.cisco.com/c/en_in/products/switches/what-is-a-lan-local-areanetwork.html"area HYPERLINK "http://www.cisco.com/c/en_in/products/switches/what-is-a-lanlocal-area-network.html"- HYPERLINK "http://www.cisco.com/c/en_in/products/switches/whatis-a-lan-local-area-network.html"network.html HYPERLINK "http://www.cisco.com/c/en_in/products/switches/what-is-a-lan-local-area-network.html"> HYPERLINK "http://www.cisco.com/c/en_in/products/switches/what-is-a-lan-local-areanetwork.html" [Accessed 25 April 2022]. 4/ Flylib.com. 2022. LAN Characteristics | Local Area Networking. [online] Available at: <https://flylib.com/books/en/2.566.1/lan_characteristics.html> [Accessed 25 April 2022]. 5/ 2022. [online] Available at: <https://www.invialgo.com/2012/characteristics HYPERLINK "http://www.invialgo.com/2012/characteristics-of-wan/"- HYPERLINK "http://www.invialgo.com/2012/characteristics-of-wan/"of HYPERLINK "http://www.invialgo.com/2012/characteristics-of-wan/"- HYPERLINK "http://www.invialgo.com/2012/characteristics-of-wan/"wan/ HYPERLINK "http://www.invialgo.com/2012/characteristics-of-wan/"> [Accessed 25 April 2022]. 6/ Purple. 2022. The Advantages and Disadvantages of WANs | Purple. [online] Available at: <https://purple.ai/blogs/advantages-disadvantages-wans/> [Accessed 25 April 2022]. 7/ (MAN), A., Rehman, J. and Rehman, J., 2022. Advantages and disadvantages of metropolitan area network (MAN). [online] IT Release. Available at: <https://www.itrelease.com/2018/09/advantages HYPERLINK "http://www.itrelease.com/2018/09/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-"- HYPERLINK "http://www.itrelease.com/2018/09/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-"and HYPERLINK "http://www.itrelease.com/2018/09/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-"- HYPERLINK "http://www.itrelease.com/2018/09/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-"disadvantages HYPERLINK "http://www.itrelease.com/2018/09/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-"- HYPERLINK "http://www.itrelease.com/2018/09/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-"of HYPERLINK "http://www.itrelease.com/2018/09/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-"- metropolitan-areanetwork-man/> [Accessed 25 April 2022]. 8/ 2022. [online] Available at: <https://www.cloudflare.com/lear HYPERLINK "http://www.cloudflare.com/learning/network-layer/what-is-a-protocol/"ning/network HYPERLINK "http://www.cloudflare.com/learning/network-layer/what-is-a-protocol/"- HYPERLINK "http://www.cloudflare.com/learning/network-layer/what-is-a-protocol/"layer/what HYPERLINK "http://www.cloudflare.com/learning/network-layer/what-is-a-protocol/"- HYPERLINK "http://www.cloudflare.com/learning/network-layer/what-is-a-protocol/"is HYPERLINK "http://www.cloudflare.com/learning/network-layer/what-is-a-protocol/"- HYPERLINK "http://www.cloudflare.com/learning/network-layer/what-is-a-protocol/"a HYPERLINK "http://www.cloudflare.com/learning/network-layer/what-is-a-protocol/"- HYPERLINK "http://www.cloudflare.com/learning/network-layer/what-is-a-protocol/"protocol/ HYPERLINK "http://www.cloudflare.com/learning/network-layer/what-is-a-protocol/"> [Accessed 25 April 2022]. 9/ Protocols, T., 2022. Types of Networking Protocols | Top Four Major Protocols of Networking. [online] EDUCBA. Available at: <https://www.educba.com/types HYPERLINK "http://www.educba.com/types-of-networking-protocols/"- HYPERLINK "http://www.educba.com/types-of-networking-protocols/"of HYPERLINK "http://www.educba.com/types-of-networking-protocols/"- HYPERLINK "http://www.educba.com/types-of-networking-protocols/"networking HYPERLINK "http://www.educba.com/types-of-networking-protocols/"- HYPERLINK "http://www.educba.com/types-of-networking-protocols/"protocols/ HYPERLINK "http://www.educba.com/types-of-networking-protocols/"> [Accessed 25 April 2022]. 10/ 2022. [online] Available at: <https://www.examcollection.com/certification HYPERLINK "http://www.examcollection.com/certification-training/a-plus-network-ports-"- HYPERLINK "http://www.examcollection.com/certification-training/a-plus-network-ports-"training/a HYPERLINK "http://www.examcollection.com/certification-training/a-plus-network-ports-"HYPERLINK "http://www.examcollection.com/certification-training/a-plus-network-ports-"plus HYPERLINK "http://www.examcollection.com/certification-training/a-plus-network-ports-"HYPERLINK "http://www.examcollection.com/certification-training/a-plus-network-ports"network HYPERLINK "http://www.examcollection.com/certification-training/a-plus-network- ports-"- HYPERLINK "http://www.examcollection.com/certification-training/a-plus-network-ports"ports HYPERLINK "http://www.examcollection.com/certification-training/a-plus-network-ports-"protocols-purposes.html '> [Accessed 25 April 2022]. 11/ GeeksforGeeks. 2022. 14 Most Common Network Protocols And Their Vulnerabilities GeeksforGeeks. [online] Available at: <https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/14 HYPERLINK "http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/14-most-common-network-protocols-and-their-vulnerabilities/"HYPERLINK "http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/14-most-common-network-protocols-and-theirvulnerabilities/"most HYPERLINK "http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/14-most-common-networkprotocols-and-their-vulnerabilities/"- HYPERLINK "http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/14-mostcommon-network-protocols-and-their-vulnerabilities/"common HYPERLINK "http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/14-most-common-network-protocols-and-their-vulnerabilities/"HYPERLINK "http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/14-most-common-network-protocols-and-theirvulnerabilities/"network HYPERLINK "http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/14-most-common-networkprotocols-and-their-vulnerabilities/"- HYPERLINK "http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/14-mostcommon-network-protocols-and-their-vulnerabilities/"protocols HYPERLINK "http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/14-most-common-network-protocols-and-their-vulnerabilities/"HYPERLINK "http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/14-most-common-network-protocols-and-theirvulnerabilities/"and HYPERLINK "http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/14-most-common-networkprotocols-and-their-vulnerabilities/"- HYPERLINK "http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/14-mostcommon-network-protocols-and-their-vulnerabilities/"their HYPERLINK "http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/14-most-common-network-protocols-and-their-vulnerabilities/"HYPERLINK "http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/14-most-common-network-protocols-and-theirvulnerabilities/"vulnera HYPERLINK "http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/14-most-common-networkprotocols-and-their-vulnerabilities/"bilities/ HYPERLINK "http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/14-mostcommon-network-protocols-and-their-vulnerabilities/"> [Accessed 25 April 2022]. 12/ Tutorialspoint.com. 2022. Network Standardization. [online] Available at: <https://www.tutorialspoint.com/Network HYPERLINK "http://www.tutorialspoint.com/NetworkStandardization"- HYPERLINK "http://www.tutorialspoint.com/NetworkStandardization"Standardization HYPERLINK "http://www.tutorialspoint.com/NetworkStandardization"> [Accessed 25 April 2022]. 13/ Heavy.ai. 2022. What is Network Topology? Definition and FAQs | HEAVY.AI. [online] Available at: <https://www.heavy.ai/technical HYPERLINK "http://www.heavy.ai/technical-glossary/networktopology"- HYPERLINK "http://www.heavy.ai/technical-glossary/networktopology"glossary/network HYPERLINK "http://www.heavy.ai/technical-glossary/networktopology"- HYPERLINK "http://www.heavy.ai/technical-glossary/network-topology"topology HYPERLINK "http://www.heavy.ai/technical-glossary/network-topology"> [Accessed 25 April 2022]. 14/2022. [online] Available at: <https://www.learn2.com/team HYPERLINK "http://www.learn2.com/team-building-"- HYPERLINK "http://www.learn2.com/team-building"building HYPERLINK "http://www.learn2.com/team-building-"organizations/#:~:text=The%20common%20goal%20gets%20placed,to%20fulfill%20the%20comp any's%20vision.> [Accessed 25 April 2022]. 15/Google.com. 2022. Vallum Halo Manager - Google Search. [online] Available at: <https://www.google.com/search?tbm=isch HYPERLINK "http://www.google.com/search?tbm=isch&q=Vallum%2BHalo%2BManager%2B&imgrc=65Rclre UXNddQM"& HYPERLINK "http://www.google.com/search?tbm=isch&q=Vallum%2BHalo%2BManager%2B&imgrc=65Rclre UXNddQM"q=Vallum+Halo+Manager+#imgrc=65RclreUXNddQM HYPERLINK "http://www.google.com/search?tbm=isch&q=Vallum%2BHalo%2BManager%2B&imgrc=65Rclre UXNddQM"> HYPERLINK "http://www.google.com/search?tbm=isch&q=Vallum%2BHalo%2BManager%2B&imgrc=65Rclre UXNddQM" HYPERLINK "http://www.google.com/search?tbm=isch&q=Vallum%2BHalo%2BManager%2B&imgrc=65Rclre UXNddQM"[Accessed 25 April 2022].