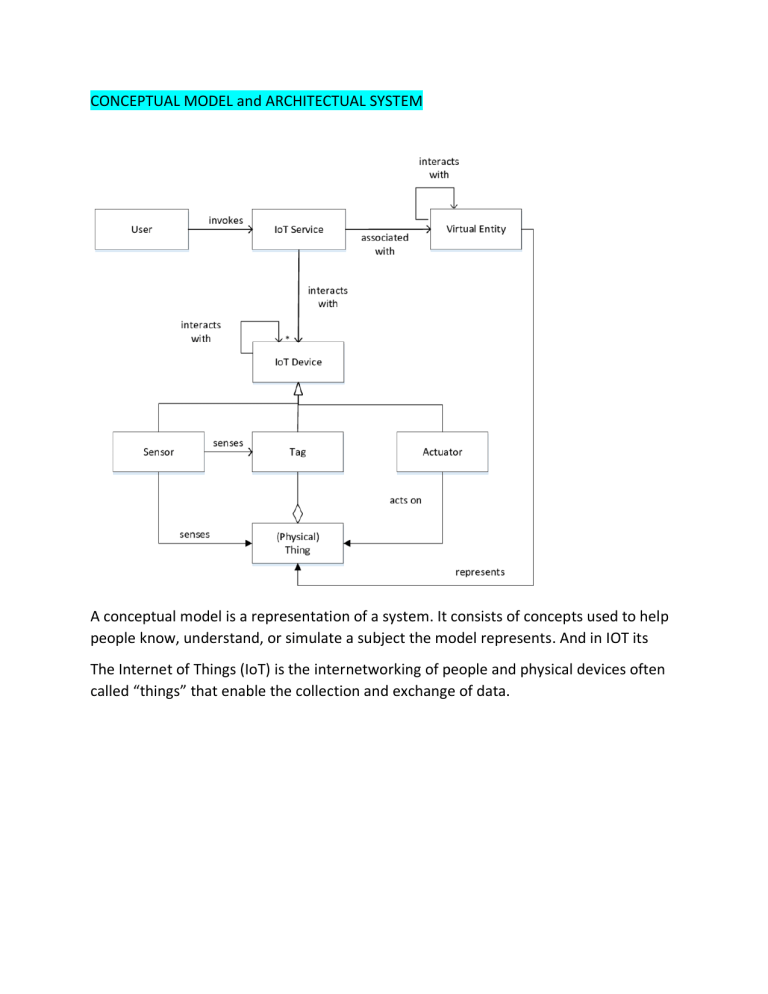
CONCEPTUAL MODEL and ARCHITECTUAL SYSTEM A conceptual model is a representation of a system. It consists of concepts used to help people know, understand, or simulate a subject the model represents. And in IOT its The Internet of Things (IoT) is the internetworking of people and physical devices often called “things” that enable the collection and exchange of data. Both wearable and non-wearable, smart medical devices are efficiently used for remote patient monitoring, care delivery, diagnosing, and more. IoT-based systems powering medical devices automate routine tasks like vitals collection, predict disease risks and disease flow, and improve efficiency of medical staff. The number of connections between people and things, as well as the volume of data that is generated by the “things,” is dramatically increasing. In this context, various kinds of data are generated by multiple devices, which operate in different ways and used by different applications with different aims. To realize the distributed execution of IoT systems over multiple resources, different requirements and quality factors must be satisfied. Traditionally, to reduce the effort for developing distributed systems, middleware architectures have been introduced that provide common services such as name and directory services, discovery, data exchange, synchronization, and transaction services, etc. Having those middleware makes the system much more complicated and having all of them in 1 place is very inefficient and costly. From that we must organize the middleware to increase the efficiency and lower the cost by working with the architecture of the system The architecture of a system reflects how the system is used and how it interacts with other systems and the outside world. It describes the interconnection of all the system’s components and the data link between them. The architecture of a system reflects the way it is thought about in terms of its structure, functions, and relationships. In architecture, the term “system” usually refers to the architecture of the software itself, rather than the physical structure of the buildings or machinery. The architecture of a system reflects the way it is used, and therefore changes as the system is used. For example, an airport may be designed using an architecture where the control tower and departures lounge are close together in the same building, while the control tower is further away in the same airport. Therefore, the system is always described in terms of its parts and their operations. In the same way, data is always described in terms of the elements which compose it and the operations which make it useful to an end-user. SENSORS IoT is a giant network with connected devices. These devices gather and share data about how they are used and the environment in which they are operated. It's all done using sensors, sensors are embedded in every physical device. Sensors continuously emit data about the working state of the devices. Iot provides a common platform for all these devices to dump their data. And a Common language for all the devices to communicate with each other. Data is emitted from various sensors and sent to iot platform securely, iot platform integrates the collected data from various sources. Further analytics is performed on the data and valuable information is extracted as per requirement.