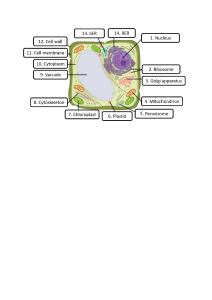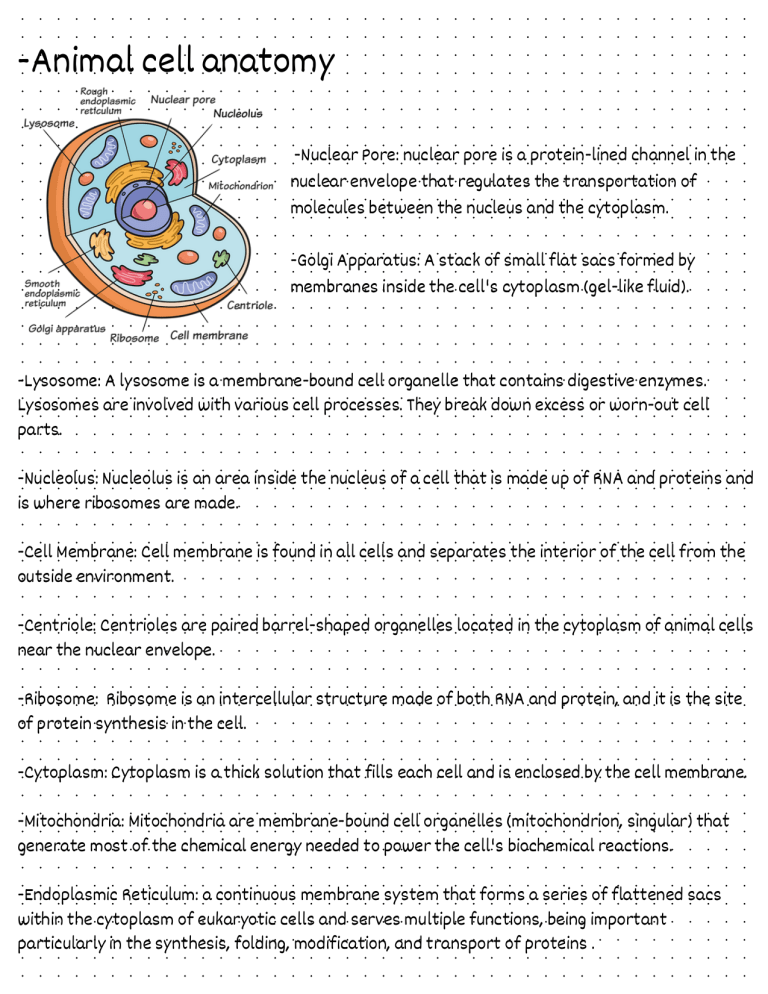
-Animal cell anatomy -Nuclear Pore: nuclear pore is a protein-lined channel in the nuclear envelope that regulates the transportation of molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. -Golgi Apparatus: A stack of small flat sacs formed by membranes inside the cell's cytoplasm (gel-like fluid). -Lysosome: A lysosome is a membrane-bound cell organelle that contains digestive enzymes. Lysosomes are involved with various cell processes. They break down excess or worn-out cell parts. -Nucleolus: Nucleolus is an area inside the nucleus of a cell that is made up of RNA and proteins and is where ribosomes are made. -Cell Membrane: Cell membrane is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. -Centriole: Centrioles are paired barrel-shaped organelles located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope. -Ribosome: Ribosome is an intercellular structure made of both RNA and protein, and it is the site of protein synthesis in the cell. -Cytoplasm: Cytoplasm is a thick solution that fills each cell and is enclosed by the cell membrane. -Mitochondria: Mitochondria are membrane-bound cell organelles (mitochondrion, singular) that generate most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell's biochemical reactions. -Endoplasmic Reticulum: a continuous membrane system that forms a series of flattened sacs within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells and serves multiple functions, being important particularly in the synthesis, folding, modification, and transport of proteins .