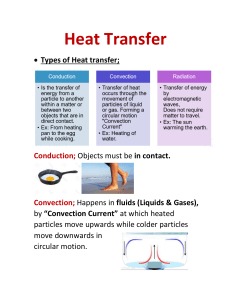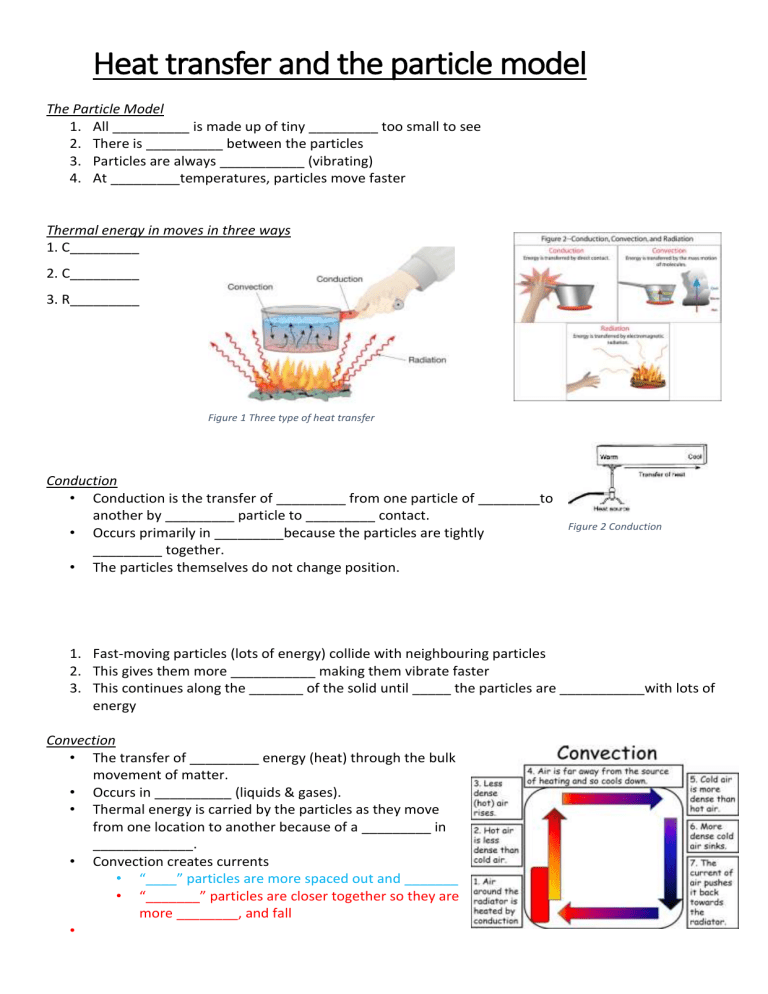
Heat transfer and the particle model The Particle Model 1. All __________ is made up of tiny _________ too small to see 2. There is __________ between the particles 3. Particles are always ___________ (vibrating) 4. At _________temperatures, particles move faster Thermal energy in moves in three ways 1. C_________ 2. C_________ 3. R_________ Figure 1 Three type of heat transfer Conduction • Conduction is the transfer of _________ from one particle of ________to another by _________ particle to _________ contact. • Occurs primarily in _________because the particles are tightly _________ together. • The particles themselves do not change position. Figure 2 Conduction 1. Fast-moving particles (lots of energy) collide with neighbouring particles 2. This gives them more ___________ making them vibrate faster 3. This continues along the _______ of the solid until _____ the particles are ___________with lots of energy Convection • The transfer of _________ energy (heat) through the bulk movement of matter. • Occurs in __________ (liquids & gases). • Thermal energy is carried by the particles as they move from one location to another because of a _________ in _____________. • Convection creates currents • “____” particles are more spaced out and _______ • “_______” particles are closer together so they are more ________, and fall • Density- a measure of how much mass is in a given volume. Radiation • • • • • • • Radiation is the transfer of (thermal) energy by _________________ _____________. Radiation does _______require _________ to transfer thermal energy. Two objects do not need to __________ in order for radiation to transfer heat between them Heat radiation can travel through a ___________ – this is how the heat from the Sun reaches us. All objects (matter) can transfer some heat by _____________ e.g. you feel the radiation of thermal energy from a camp fire The hotter the object is the ___________ heat it _______________. The radiation itself is not hot, but when it is _____________by an object it causes the particles to vibrate more rapidly, thus heating it. What type of heat transfer is happening at each one of the labels in the diagram below: W X Y Z