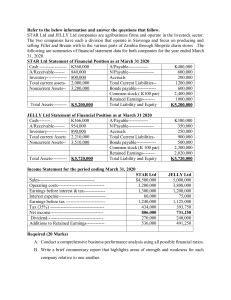
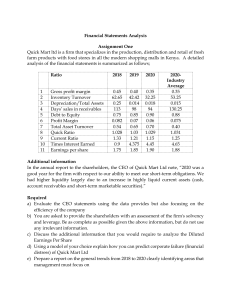
Chapter 7 The PreApproach— Planning Your Sales Call and Presentation Copyright © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. Prepared by Michael Madore University of Lethbridge Main Topics • • • • • 1 The Core Principles: Planning Strategic Customer Sales Planning—the PreApproach The Customer Relationship Model The Prospect’s Mental Steps Call Reluctance © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. Learning Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. 2 After studying this chapter, you should be able to: Explain the importance of sales call planning. List the four planning steps in order and understand them. Develop a customer benefit plan. Describe the prospect’s five mental steps in buying. © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. The Core Principles: Planning The salesperson needs to know what their purpose is. Often salespeople do not. © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 3 Begin Your Plan with Purpose and Passion Will Follow Purpose: is broad in scope is not a list of plans, goals, or objectives that differ from one sales call to another is a constant truth that guides your business life directs how you approach each sales call classifies your relationships Sales call purpose is to make a contribution to the welfare of the person or organization © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 4 Plan to Achieve Your Purpose How you think, how you act, what you accomplish today will determine your future— your tomorrow. Plan each day, do the best you can to carry out your plan and adjust to circumstances as you go, and then at the end of each day evaluate your day to ensure you are on your way toward a successful tomorrow. © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 5 What Is a Plan? A plan is a method of achieving an end. A plan involves what you want to accomplish and how you will do it. © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 6 What Is Success? Success is setting a goal and accomplishing it. Statistics show that individuals who establish goals tend to achieve them more than those who don’t. A recent study showed that individuals who wrote down their goals were 33 percent more successful in achieving them then those who did not write them down. © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 7 Strategic Customer Sales Planning —The Pre-approach Planning stage (often referred to as the preapproach) You need to be a strategic problem solver 8 Discover strategic needs Understand customer’s business Possess the needed knowledge Devise creative solutions Arrive at a mutually beneficial agreement Create value Exhibit 7.2 - The pre-approach involves planning the sales presentation. © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. Strategic Needs A seller understanding the full range of the customer’s needs is in a position to provide a product solution. The salesperson considers the needs of the buyer © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 9 Creative Solutions A salesperson is often faced with a specific, unique set of problems to solve. Due to this, a salesperson needs to follow a three-stage creative problem-solving process: 1. Finding the problem 2. Solving the problem 3. Implementing the solution © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 10 Mutually Beneficial Agreements Salespeople and customers say that a significant shift has occurred in their expectations of the outcome of sales agreements. Agreements are now more collaborative win–win arrangements. © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 11 The Customer Relationship Model Exhibit 7.3 - Consultative selling—customer relationship model. © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 12 Why Does Preparation Matter? Reasons for planning the sales call: Builds self-confidence Develops an atmosphere of goodwill Creates professionalism Increases sales © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 13 Elements of Sales Call Planning Exhibit 7.5 - Steps in the pre-approach: planning the sale. © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 14 Always Have a Sales Call Objective The pre-call objective If this call is successful, what will result? Focus and flexibility Writing down pre-call objective increases focus If pre-call objective turns out to be inappropriate, planning facilitates an easy change of tactics © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 15 Determining sales call objectives Make the goal specific 16 Goals are much more attainable when they provide concrete direction. Move toward your objective Guiding the customer in the direction of that pre-planned outcome is what is experienced salespeople do on most sales calls. If we can meet the spec, can you set up a trial? Can you schedule a demonstration before the end of the month? © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. Determining sales call objectives Set a SMART call objective Specific – to get an order is NOT specific Measurable – number, size Achievable – not too difficult to fulfill Relevant – has importance to you (e.g. quota) Timed – at this call or before the end of the financial year © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 17 Customer Profile Provides Insight The profile should tell you: Who is the decision maker? What is the buyer’s background? What are the desired business terms and needs? Who are your competitors on this account? What are the purchasing policies? What is the history of the account? What are the buyer’s critical needs? What pressure(s) is the buyer facing within their organization and their competitive environment? © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 18 Customer Benefit Plan: What It’s All About Step 1 - Select the FAB (features, advantages, and benefits ) to present Step 2 - Develop your marketing plan Step 3 - Develop your business proposition Step 4 - Develop a suggested purchase order © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 19 The Sales Presentation: An Overview of the Process 20 Exhibit 7.8 Major phases in your presentation: a sequence of events to complete in developing a presentation. © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. The Prospect’s Mental Steps Knowing the steps the prospect is going through makes building and delivering a presentation more effective Attention Interest Desire Conviction Purchase or Action © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 21 The Prospect’s Mental Steps Exhibit 7.9 - The prospect’s five mental steps in buying. © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 22 Attention From the moment you begin to talk, quickly capture and maintain the prospect’s attention This may be difficult at times because of: distractions, pressing demands on the prospect’s time, lack of interest © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 23 Interest Before meeting with prospects, determine their important buying motives. Prospects enter the interest stage if they listen to and enter into a discussion with you. © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 24 Desire Using the FAB formula, strive to bring prospects from lukewarm interest to a boiling desire for your product. © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 25 Conviction Buyers have to be convinced that your product is best for their needs and that you are the best supplier of the product. Strive to develop a strong belief that the product is best suited to the prospect’s specific needs. © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 26 Purchase or Action Once the prospect is convinced, plan the most appropriate method of asking the prospect to make a purchase or take some action. Closing the sale is the easiest step in the sales presentation. © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 27 28 Appointment making is a gesture of respect Prospects are busy people Be professional Be courteous © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 29 Be prepared – don’t just wing it VIDEO A well planned call can save time Establish your objectives Prepare an opening statement Briefly outline your message Ask for what you want Prepare for possible objections Confirm all contact information Call to confirm © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 30 Receptionist, secretary Their job is to filter who/what gets to the boss Be friendly, courteous Is a gift appropriate? They often have indirect (direct) influence on the sale Befriend the “little people” in the company They can’t buy the product but they can kill the sale Who needs influential enemies? © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. Voice Mail: The Dreaded Mechanical Gatekeeper Video 1. Be Prepared 2. Smile, sound enthusiastic 3. Plan to be brief – 25-40 seconds 4. Discuss benefits that are most attractive to the prospect. Customize your message. 5. Talk to a success story. 6. Leave your phone number, say them slowly and twice. 7. Make a call to action. Ask them to call you or mention that you’ll call them back at a later date. © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 31 Call Reluctance 32 Definition: refers to not wanting to contact a prospect or customer. Exploring the psychology: for many salespeople, owning up to call reluctance is the most difficult part of combating it. 40% of salespeople suffer career-threatening call reluctance at some point. 80% of 1st year salespeople who fail do so because of insufficient prospecting. Follow up, keep plugging, make calls. © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. Summary Careful planning of the sales call is essential to success in selling. There are four basic elements of sales call planning: have a sales call objective develop or review the customer profile develop your customer benefit plan plan your whole sales presentation © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 33 Coming up … The Approach Begin Your Presentation Strategically © 2020 McGraw-Hill Education Ltd. 34