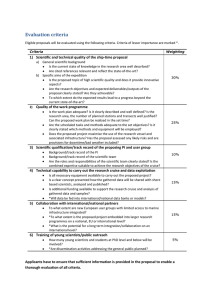
An Overview of Feedback Control Hoofdmodule Industrial Control Systems Amin Mannani Copyright Notice This work has been made using the text, formulas and figures from the following book. Feedback Control of Dynamic Systems, 8th edition (Global Edition) By Franklin, Powell, Emami-Naeini ISBN 10: 1-292-27452-2 All parts of this work are under the copyright of the above book. Language & Concept ⚫ Manual vs. Automatic Control ⚫ Automatic Controllers: control goals ⚫ ⚫ – Regulators: reaching a constant final value – Servo or tracking systems: tracking a reference signal Automatic Controllers: architecture – Open loop controller: no measurement of the output is used – Closed-loop or feedback controllers: output measured and used Feedback System Fundamentals – Stability – Tracking – Disturbance rejection – Robustness A Simple Feedback System ⚫ A household furnace controlled by a thermostat – Diagram shows the direction of information flow Figure 1.1: Feedback control: (a) component block diagram of a room temperature control system (b) plot of room temperature and furnace action A Simple Feedback System ⚫ Components of a feedback control loop: – Controller – Process – Actuator (power, speed, reliability) – Sensor (low noise, reliability, linearity) – Input filter (if required) to convert reference to the (electrical) signal accepted by controller Figure 1.2: Component block diagram of an elementary feedback control A First Analysis of Feedback ⚫ Automobile cruise control (no-dynamics version) – A 1° change in throttle angle causes a 10 mph change in speed – A 1% change in the road grade changes the speed by 5 mph Figure 1.3: Component block diagram of automobile cruise control A First Analysis of Feedback ⚫ Automobile cruise control (no-dynamics version) – A 1° change in throttle angle causes a 10 mph change in speed – A 1% change in the road grade changes the speed by 5 mph Figure 1.4: Block diagram of the cruise control plant A First Analysis of Feedback ⚫ Automobile cruise control (no-dynamics version) – Open-loop cruise control Figure 1.5: Open-loop cruise control A First Analysis of Feedback ⚫ Automobile cruise control (no-dynamics version) – Closed-loop cruise control Figure 1.6: Closed-loop cruise control Prob. 1.3: Papermaking Machine ⚫ ⚫ ⚫ To control: – Density of the fibers (or, of the thick stock) – Moisture content of the final product How does it work? – Stock from machine chest is diluted by the white water out of the CV valve – A meter supplies reading of the consistency – At the dry end there is a moisture sensor Identify the following by drawing the block diagram of the system: – Process, process desired output signal, – Sensor and actuator; actuator output signal – Controller; controller output signal – Reference signal and error signal Figure 1.12: Closed-loop cruise control Prob. 1.3: Pap. Machine (Cont.) Control of paper machine consistency Control of paper machine moisture Prob. 1.6: Transducers with Electrical Output ⚫ Temperature sensor: Thermistor – ⚫ Resistance changes with temperature Pressure sensor: Strain gage – Resistance changes with strain, ⚫ Liquid level sensor: Float connected to a potentiometer ⚫ Flow meter: – a turbine actuated by the flow with a magnet to trigger an external circuit Prob. 1.6: Transducers with Electrical Output ⚫ Linear position: direct mechanical interaction – For precise cases LVDT, etc. ⚫ Rotational position sensor: potentiometer, encoder ⚫ Linear velocity: – ⚫ Rotational velocity: Rate gyro, tachometer – ⚫ ⚫ RADAR, rack-and-pinion, tachometer use of Hall effect (magnetic to electrical) Acceleration: – Mass movement restrained by a spring measured by a potentiometer – A piezoelectric material (current proportional to acceleration) Force, torque: dynamometer – Based on spring/beam deflection measured by a potentiometer