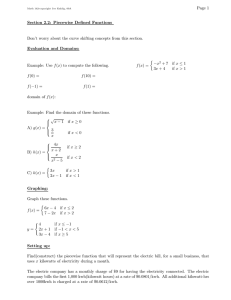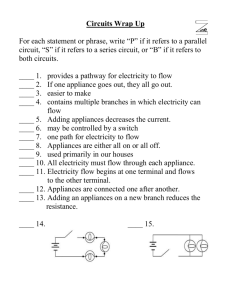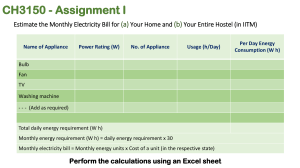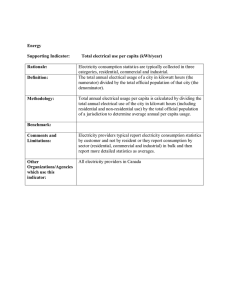
04/10/2023 LO: Energy and power What is power? Some Most All Physics 2b • Be able to explain the difference between energy and power • Be able to describe the link between power, fuel use and the cost of using domestic appliances • Be able to recall the equations to calculate power Keywords: Power rating, watt, kilowatt, kilowatt hour (kWh) BLP objective Collaboration Respecting and recognising other view points, adding to a drawing from the strength of teams Making Links Seeing connections between events and experiences, building patterns. 04/10/2023 Literacy objective • Can you use standard English to share your opinion with the class? • Can you write your answers using standard English, scientific keywords and taking care of spellings and punctuation? Starter On your post it write down your definition of power. Then write it much more simply so you can explain it to a Year 5 student. Power Appliances in your home have power ratings these are given in watts. The power rating tells you how much energy is transferred to the device a second. Power The more powerful an appliance, the faster the rate at which it transfers energy. Make a list of ten appliances you used yesterday – put them into order of how much power they used! Power Calculations Calculate the power 1. A microwave transfers 30kJ in two minutes 2. My nutribullet transfers 800kJ in 30 seconds 3. I spent 7 minutes straightening my hair this morning, my straighteners transferred 252kJ of energy. What is their power? Extension 1. My toaster was on for 2 minutes, it has a power rating of 103W. How much energy was transferred? 2. My tumble dryer has a power of 500W and was used for 45 minutes – what was the energy transferred? Investigating power Around the lab are a selection of different appliances. You need to find out its power by looking at the labels and fill in the table. Use the unit on the appliance. You have 15 minutes – you need to do all questions except the extension – we’ll do these later. Paying for electricity When you pay for electricity you are paying for the electricity company to generate a voltage that we call the mains electricity. You are then charged for the number of hours you use your appliances. Paying for electricity Energy use is calculated in kilowatt hours (kWh) or joules – this is the unit electricity companies use to calculate your bill. An example calculation An oven with power rating of 12 kW is used for 1 hour Energy used in kWh = 12kW x 1 hour = 12kWh An example calculation A laptop with power rating of 6 kW is used for 3 hours Energy used in kWh = 6kW x 3 hour = 18kWh An example calculation A microwave with power rating of 7000 W is used for 87 minutes Calculating the electricity bill Each kWh has a charge, for example 7p. You just multiply the number of kilowatt hours by the cost per unit. Calculating the electricity bill Complete the extension activity on the practical worksheet. After answering question 2 – calculate the cost of running each appliance. The month has 30 days – calculate the months electricity bill. Energy saving bulbs These two bulbs have the same brightness but the one on the right has a much lower power. Why? Use your definitions of your keywords to formulate your answer. Learning consolidation Describe the link between power, fuel use and the cost of using appliances.