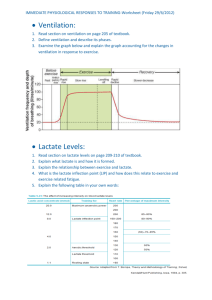
Week 2 Assignment: Lactate Threshold – SPHE314 “Lactate threshold is the exercise intensity at which there is an abrupt increase in blood lactate concentration” (Wilkinson, 2013). Lactate threshold is different depending on the person. It is the point where lactate production now exceeds lactate clearance. It is related to aerobic exercise because oxygen is constantly being consumed, which means less lactic acid is being produced. During anaerobic exercise, less oxygen is being consume, which means there will be more lactic acid build up (Ghosh, 2004). There are many factors that influence vo2max, such as gender, body composition, heredity, fitness level. One thing that cause differences in vo2 max is elevation. For example, most people would have a lower v02 max in Denver than they would in Philadelphia. This would decrease the threshold. Another difference could be the weather on a particular day. It is easier to consume oxygen when it is warm as opposed to it being a cold day. This would increase the threshold. The younger you are the higher your vo2 max would be because “after about age 25, your vo2 max declines at a rate of approximately 1 percent a year” (Myers, 2020). This means the threshold would decrease every year. The idea of lactate threshold training aims at increasing the vo2 max so that lactic acid sets in at a later time. “Research has indicated that training programs that are a combination of high volume, maximal steady-state, and interval workouts have the most pronounced effect on lactate threshold improvement” (Roberts & Robergs 1997, Weltman 1995). One type of this training is high volume training. This involves increasing the time amount of time exercising and could look like adding a minute to a workout every week for 12 weeks. Another type of training, called HIIT, or high interval intensity training can increase the lactate threshold by alternating very high strain activity (above lactate threshold) and low strain activity (below lactate threshold). The study that I found examines obese women and exercise in their 20s to 40s age range performing aerobic exercise at their lactate threshold. The time period for the study was 12 weeks. The results showed that at the beginning of the study vo2 lactate threshold was at 24 ml/kg/min. After 12 weeks it rose to 28.85 ml/kg/min. After an additional 12 weeks of not exercising, it went down to 25.05 ml/kg/min. The study also showed an increase in the number of calories burned during the same amount of time. (Park, et. al, 2019). References: Ghosh A. K. (2004). Anaerobic threshold: its concept and role in endurance sport. The Malaysian journal of medical sciences : MJMS, 11(1), 24–36. Kravitz, L., & Dalleck, L. (2008). Lactate Threshold Training. Retrieved from https://www.unm.edu/~lkravitz/Article%20folder/lactatethreshold.html Myers, C. (2020). Factors Affecting VO2 Max. Retrieved December 21, 2020, from https://www.livestrong.com/article/356549-factors-affecting-vo2-max/ Park, H. Y., Kim, S., Kim, Y., Park, S., & Nam, S. S. (2019). Effects of exercise training at lactate threshold and detraining for 12 weeks on body composition, aerobic performance, and stress related variables in obese women. Journal of exercise nutrition & biochemistry, 23(3), 22– 28. https://doi.org/10.20463/jenb.2019.0019 Week 2 Assignment: Lactate Threshold – SPHE314 Robergs, R.A., & Roberts, S. 1997. Exercise Physiology: Exercise, performance, and clinical applications. St Louis, MO: Mosby. Wilkenson, S. (2013, September 07). Lactate threshold (lactic acid part 4). Retrieved December 21, 2020, from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9cqKg9kXfV