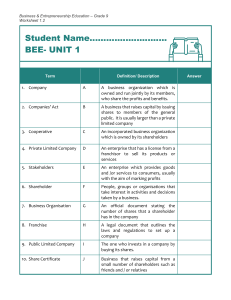
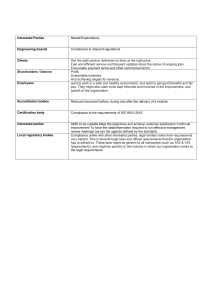
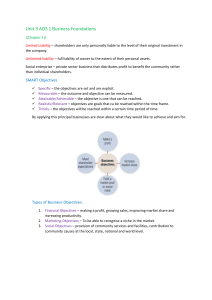
1.1 Introduction to business management Sustainability Definition: Meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs Private sector Definition: Portion of an economy not owned or directed by the government Features: - Private ownership and control - Profits can be earned by owners - Little or no government involvement - Largely privately funded Public sector Definition: Organisations are owned and controlled by the government on behalf of its citizens to provide essential and affordable goods or services for citizens that otherwise might not have been produced. Features: - Owned and controlled by the government - Provides essential goods and services to citizens - Financed by the government through taxes and other public funds - Answerable to the public for any decisions taken -Primary sector Definition: The primary sector extracts natural resources and raw materials. Includes agriculture, fishing, forestry and mining Secondary sector Definition: Includes both construction and manufacturing. Uses resources from the primary sector to manufacture finished goods or process raw materials to be used for other secondary sector businesses. Supports both the primary and tertiary sector Tertiary sector Definition: Refers to the area of economic activity and businesses that provides services Quaternary sector Definition: Area of economic activity involved with knowledge and the movement of information -Business plan Definition: Tool used to describe a business that is an evidence-based explanation of the why, how and what of a business. Elements: - Executive summary - Business description - Market analysis - Financial forecasts - Cash flow forecast - Marketing strategies - Organisation strategies - Business objectives - Mission and vision statement - Human resource plan - Type of organisation - Analysis such as PESTLE, SWOT, ratios - Profit and loss statement and balance sheet Reasons for starting a business - New business idea - Passion to make change - Market need - Earning a living - Control - Work-life balance Steps in setting up a new businesses: - Identifying marketing opportunities - Sourcing capital - Determining a location - Building a customer base - Business idea / mode/ plan - Ownership decisions and legal structure Problems for new businesses: - Competition - Cash flow problems - Human resources issues like finding the right staff - Insufficient marketing - Market research - Poor planning - Insufficient start up capital 1.2 Type of Organisations For profit commercial enterprise Definition: type of business that earns profits which are distributed to owners or shareholders; profits may have priority over other objectives Types: - Sole traders Partnerships For-profit privately held companies For-profit publicly held businesses Public limited company: Definition: A limited company that is incorporated with the legal right to sell shares to the general public. The share price is quoted on the national stock exchange and companies have limited liability. Features: - Initial public offering needed where company sells all or parts of business to external shareholders for the first time - Held companies meet yearly at annual general meeting to vote for or elect the board of directors Advantage: - Finances and capital can be raised through selling of shares to the public - Risk are shared among a large number of shareholders - Separate legal identity - Limited liability Disadvantage: - Profits shared between shareholders - High cost as it is expensive and time consuming to set up - Loss of control - Accounts publicly available Private limited company Definition: Company that is privately owned and often has family or friends as shareholders; the shares are not sold to the wider public and are not traded on a stock exchange market - Required documents: Memorandum of association which states the details of the company Articles of association which states the internal roles and responsibilities of the board of directors and shareholders Feature: - Number of shareholders limited to 20 - Shareholders have to be invited to join the board of directors as shares cannot be advertised and sold publicly - Limited liability which indicates that if a business experiences a financial collapse then the owners will only be liable for the capital contributed - Normally no legal requirement to publish detailed financial accounts for the public or provide quarterly forecasts to an exchange Advantage: - Control and ownership - Greater access to finances - Limited liability - Financial records are private Disadvantage: - Loss of privacy as company must report to the public and to shareholders - Strategic decision can take longer, as management has responsibility to communicate with the board, shareholders and often other stakeholders - Risk of takeovers - Profits shared between shareholders - Lengthier decision making as all shareholders need to discuss and agree on decisions - Shares cannot be traded publicly to raise finances Sole Trader Definition: Business owned and run by one person; there is no legal separation between the owner and the business Feature: - No legal formalities so it is easy to set up - The owner has complete control and keeps all profits - Flexible work hours - Unlimited liability so all of owner’s assets are potentially at risk - Lack continuity as the business does not have separate legal status and the business end when the owners die Advantage: - Total ownership and control - Simplest form of organisation with fewer legal restrictions for setting up the business - Flexibility - All profits - Fast decision making Disadvantage: - Unlimited liability - Limited capital and resources for set up - Largely rely own owner’s saving and resources, banks are often reluctant to loan to these businesses - Limited pool of ideas and limited experience - No continuity after death Partnership Definition: Business owned and run by 2 or more people who share the responsibility for the business and the profits; there is no legal separation between the business and the owners Feature: - More than one partner and up to around 20 - Share profits and risks - Unlimited liability Partnership agreement: - Amount of money put into the business - Sharing of profits and losses by each partner - Roles and responsibilities of each partner - Rules around accepting new partners or withdrawal of existing partners - Procedures for ending the business Advantage: - Partners can each have different skills which benefits the business - Greater efficiency and productivity as partners can specialise in different skills, productivity increases and helps reduce costs - More capital available than sole traders Disadvantages: - Risk of disagreements - Amount of capital raised is limited unless additional partners are taken on - Unlimited liability - Legal and financial responsibilities, mistakes made by one partner can reduce profits for all partners -- Social enterprises Definition: Organisation with social and environmental purpose as main priority For profit social enterprises Definition: Revenue and profit making business that integrates social and environmental impact directly into business model Features/difficulties - Measuring social and environmental impact may be more difficult as is qualitative data - Hard to remain true to purposes Cooperative Definition: A cooperative is a type of for profit social organisation that is established, owned and managed collectively by members. Each of whom has a financial interest in the business and a say in how the business is run. Features: - Profits are shared amongst members - Members share decision making - EAch member has the same voting rights on decision - Members are owners of the business - Operate in the private sector Non-profit social enterprises Non-governmental organisations - Purpose or mission to benefit society or the enviornmetn 1.3 Organisational objectives Mission statement Definition: Short statement that defines what the organisation does short term to achieve its vision Roles: - Communicating the purpose of the organisation to stakeholders - Informing decision making and strategy development - Developing measurable goals and objectives by which gauge the success of the organisation strategy: - Provide a sense of purpose and direction and act as a motivational force for employees Advantage: - Allows business to state it's current purpose and can be used to position the organisation in the minds of its stakeholders - Can be motivating force for employees and also provide a purpose which potential investors may be attracted to Disadvantage: - Can only provide a vague goal or objective and does not indicate how this objective will be achieved which could make them misleading or have little value - Focused mission statements require management time and resources to be effective Vision statement Definition: Sentence that refers to the ultimate goal of an organisation what it wants to achieve in the future. It is expressed as a long term aspiration Roles: - Help organisations set short term and long term objects. Difference between vision and mission statements - Mission is more concrete and complements the vision - Vision expresses company aspirations and what it would like to do whereas mission describes what it actually does Corporate social responsibility Definition: Management concept whereby a company integrates social and environmental concerts in their business operations and interaction with their stakeholders. Features: Advantage: - Increase customer base for customers that may want to buy from companies that have a good reputation, possible public recognition - Keep support from pressure groups, good publicity - Attract investors - Greater public awareness - Enhance company image - Customer loyalty - Reduced risks of negative publicity - Marketing opportunities Disadvantage: - Increases costs to relatively small businesses - May preclude to certain markets that insist on certain regulations that goes against CSR - Senior management must be fully committed otherwise risk backlash if actions seen as inconsistent or half-hearted Ethical objective Definition: Goals of a business based on a set of values or moral beliefs. Should cover all actions of an organisation and guide its decision making process and strategies. 1.4 Stakeholders Internal Stakeholders Definition: External Stakeholders Definition: Importance: - 1.5 External environment Internal and external economies and diseconomies of scale AO2 The difference between internal and external growth AO2 Reasons for businesses to grow AO3 Reasons for businesses to stay small AO3 External growth methods. • Mergers and acquisitions (M&As) • Takeovers • Joint ventures • Strategic alliances • Franchising 1.6 Growth and evolution Internal growth Definition: Occurs when business expands existing operations rather than growing by merging or acquiring other businesses. Typically occurs when business expands it's capacity and sells to a wider market Types: - Selling more - Widening product range - Expanding facilities and increase output of current product Advantages: - Economies of scale - Management will have full control of the process of growth in terms of speed, priorities and the amount of capital spend Will not lose its independence, less change to management is required so less disruption caused to the company Internal growth strategy might make the working life of the staff easier and more efficient. Motivation is likely to increase Disadvantages: - Method is considerably slower compare to external growth - May cause cash flow problem External growth Definition: Types: - Merger Acquisition Strategic alliances Joint ventures Franchising Merger Definition: 2 business combine to form new business; new business replaces the two that existed before the merger Features: - Two or more business join together and result in another single business - Directors made up of people from both businesses - Generally friendly - Occurs when two businesses become integrated by joining together and forming a bigger combined business. The owners of two businesses agree to join their firms together to make one business - Can take advantage of synergies Reasons for failure: - Conflicting cultures - Competition stronger than merged business - Poor management, leadership Acquisition Definition: One company purchases another company with permission of the board of directors. Takeovers Definition: When one company purchases another without the permission of the board of directors or the company. Usually try to purchase majority of shares wither through shareholders or stock markets Joint ventures Definition: When 2 businesses agree to combine resources for a specific goal and over a finite period of time. Advantages: - Cost and risk shared - Gain access to local knowledge of different market - Spread risk Limitation: - Different management style or objectives can lead to conflict and long decision making process - Any mistake can damage the reputation of both firms Strategic alliance Definition: When 2+ businesses work together to achieve a common objective but do not create a new enterprise in the process. Individuals in the alliance remain independent and may agree to share resources but otherwise compete regardless. More fluid as membership can change without destroying alliance Limitation: - More business involved the more challenging coordination and agreement becomes - Without legal existence, less force than a legally extant enterprise - Individual do not get capital strength of legal merger - No economies of scale - Greater fluidity of member = lack stability Franchising Definition: An individual's buys the right to operate under another business name. Franchisor sells franchise to a franchisee for a franchise fee and royalty Franchisor provide: - Stock - Uniforms - Training - Legal and financial help - Global advertisement Franchisee will: - Employ staff - Set price, wages - Create local promotions - Sell only products of franchisor - Pay royalty Franchisor adv: - Gains quick access to wider market - Cheap form of expansion - Receive additional funds - Make us of local knowledge and expertise Franchisor Lim: - Lose some control in day to day running of business - Damage brand image if not properly run - Not easy to revoke - Possible conflict Franchisee adv: - Known brand results in strong start up sales - Less risk of failure - Formate for selling product already established - Set up costs reduced - Secure supply of stock - Franchisor provide legal financial help Franchisor lim: - No control over what to sell or supplies - Expensive initial cost and less profit if paying royalties - Unlimited liability for the franchise Economies of scale Definition: The reduction in average costs that result from an increase in the scale of production. Fix costs are spread over an increased number of output Importance: - Customer enjoy lower prices due to lower costs which in turns increases market share - Could maintain current price and obtain higher profit margins Internal EoS Type: - Technical: large units of production can reduce costs because of the law of variable proportions.Invest in tech to reduce costs - Managerial: Afford managers specialising in one job, help improve efficiency - Financial: bank and other financial institutions change over rate of interest on loans or overdrafts to businesses they consider safe - Purchasing: Gain discounts by buying bulk - Marketing: Direct more effective marketing campaigns. More efficient to advertise a large number of products - Risk bearing: afford to product bigger product range and so spread risk External EoS Type: - Improved infrastructure - Growth of other industries that support the org e.g Shopping mall > independent stores Diseconomies of scale Definition: Refers to an increase in average unit cost as a business increases in size Example: - Communication problem - Overworked machinery and labourers - Alienation of workforce and slower decision making Multinational company Definition: MNC is a company that operates in two or more countries. A MNC needs to have a base in those countries not just sell goods and services there Features: - Operates in more than one country. Headquarters are located in one country (home country) whilst operations are carried out in a number of other countries (host countries) - Due to their international operations, they usually have a larger physical and financial assets and turnover - Often large-sized and exercise a greet degree of economic dominance - MNC may control production activity with large foreign direct investment in more than one developed and developing countries Positive impacts: - New competition hence more choice for consumers and possibly at a lower price - Tax revenue to the government of the developing country from profits made by MNC - Working opportunities, decrease unemployment rate, increase in income and standards of living may improve Negative impacts: - MNC competition can be threatening local companies - Profits made by MMC could be repatriated to their home country. The financial benefit may be limited