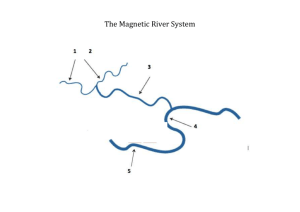
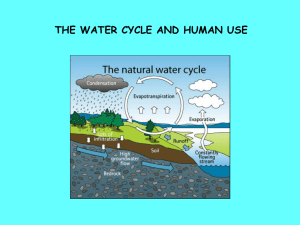
Runoff Runoff, also called overland flow or direct surface runoff (DSRO), is generated after precipitation when interception and infiltration are less than precipitation. Some of the infiltrated water reappears on the surface (interflow) and meet the overland flow. The runoff flowing down the slope creates/meets rivulets (small streams) which then meets large rivers and then to sea. The flow in a river/stream is known as stream flow. When GWT is high, GW flows into stream which is largely responsible for Base flow in a stream flow. Thus stream flow consists off DSRO and base flow. Natural flow/Virgin flow is stream flow unimpeded by any obstruction like reservoir, lake etc. Some of the generated surface runoff is stored in depression/puddles. It is called depression storage. The generated water which does not reach streams is called surface detention or detention storage. The water stored in the banks of river during high flood is called Bank Storage. Bank storage produce base flow during lean period. CATCHMENT CHARACTERISTICS The area surrounding a river whose surface runoff drains into the river is called drainage basin, watershed or catchment area of the river. The boundary line, along a topographic ridge, separating two adjacent drainage basins is called drainage divide. The river location at which all surface drainage from a basin comes together or drains as outflow from the basin in the stream channel is called concentration point or measuring point.The time required for DSRO from the outerrmost point in a drainage area to reach the concentration point is called the concentration time. This is a very significant variable since only such storms of duration greater than the time of concentration will be able to produce runoff from the entire catchment area and cause high intensity floods. The characteristics of the drainage net may be physically described by: (i) the number of streams (ii) the length of streams (iii) stream density (iv) drainage density The stream density of a drainage basin is expressed as the number of streams per square kilometre. stream density, Ds = N/A where N = number of streams; A = area of the basin • The Drainage density is expressed as the total length of all stream channels (perennial and intermittent) per unit area of the basin and serves as an index of the areal channel development of the basin Drainage density, Dd =L/A • Average stream slope = total fall of the longest water course/length of the longest water course • The shape of a drainage basin can generally be expressed by: (i) form factor (ii) compactness coefficient Form factor, Ff =W/L= A/L2 where W = axial width of basin, L = axial length of basin, i.e., the distance from the measuring point (MP) to the most remote point on the basin. Compactness coefficient, Cc = perimeter of the basin/ circumference of circular area, which equals the area of the basin. Runoff characteristics of streams • Streams can be classified as: (i) Perrenial: The streams with flows throughout the year. The continuous flow may be because of snowmelt (ex. Ganga), high baseflow due to ground water. (ii) Intermittent: Baseflow is not significant. Dries up during lean period except occasional flow due to rainfall. (iii) Ephemeral: Such streams have no groundwater/baseflow contribution. During storms, flow is high and sudden and then dries up. Ephemeral Runoff Volume Yield: The total quantity of surface water that can be expected during a given time period at the outlet of its catchment is called yield for that period. Annual yield and Seasonal yield . Rainfall-runoff relationship May be of the form: R = aP+b, a and b being constants R= cPd , c and d being constants (i) Empirical Relationships: Binnie’s Percentage Barlow’s Table Strange’s table In addition, we have several other formulae: (iv) Overland flow hydrograph (v) Unit hydrograph SCS-CN method of runoff estimation • Soil Conservation Services, USA, developed a method for estimating runoff from rainfall. This method is also referred as the CN (curve number) method. It is based on the water balance equation & two fundamental hypotheses: (1) ratio of the actual direct runoff to the potential runoff is equal to the ratio of the actual infiltration to the potential infiltration, and Q/(P-Ia) = F/S (2) the amount of initial abstraction is some fraction of the potential infiltration: Ia = λ S where, F=the cumulative infiltration excluding Ia, Q = actual runoff (mm), P = rainfall (mm), Ia = initial abstraction, which represents all the losses before the runoff begins and is given by the empirical equation. S = the potential maximum retention. Combining (1) and (2): For conveniece, S (mm) is represented by curve number (CN)as: CN = 25400/(S+254) value of CN lies between 0 and 100. CN=0 indicate S being very high, i.e., retention is very high where as CN=100 represents zero potential retention (impervious basin). CN depends upon Soil type [Group A (low runoff potential),B,C and D (high runoff potential]; Antecedent moisture condition (AMC, AMC-I (dry), AMC-II (avg cond.) AMC-III (saturated soil condition), and Land Use. SCS determined λ=0.2, thus, Q= (P-0.2 S)2/(P+0.8 S) for P>0.2 S (Standard SCS-CN equation) SCS-CN equations for Indian Conditions SCS-CN estimates runoff volume while Rational formula estimates peak discharge Advantages: • SCS-CN method is simple and relies on only one parameter, CN Flow Duration Curve: Stream flows vary with time, highest during monsoon and lowest in summer. Flow Duration Curve is the plot of the percent of time specified discharges were equaled or exceeded during a given period. • Step 1: Sort (rank) average daily discharges for period of record from the largest value to the smallest value, involving a total of n values. • Step 2: Assign each discharge value a rank (M), starting with 1 for the largest daily discharge value. • Step 3: Calculate exceedence probability (P) as follows: P = 100 * [ m / (N + 1) ] P = the probability that a given flow will be equaled or exceeded (% of time) m = the ranked position on the listing (dimensionless) N = the number of events for period of record (dimensionless)