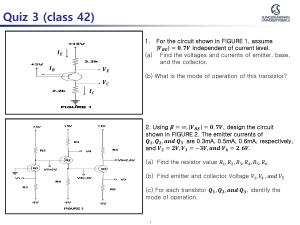
CLASS NOTES – 16-08-23 Vacuum Tube Diode: It is a device that controls electrical current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied. Vacuum tube triodes were also there at that time but they have several disadvantages: Bulky, hence less suitable for portable products. Higher operating voltages generally required. High power consumption; needs heater supply that generates waste heat and yields lower efficiency, notably for small-signal circuits. That’s why there was a need for transistors. Gold Surface charged N Transistor: The typical diagram of transistor is shown above. Transistor is a three-terminal device. A transistor is a small semiconductor that regulates or controls current or voltage flow. Transistors consist of three layers, or terminals, of a semiconductor material, each of which can carry a current. Based on these three layers, transistors can be categorised into 2 parts: 1. NPN Transistor 2. PNP Transistor As a transistor is made by combining two diodes, there are two junctions in a transistor. These junctions are named emitter junction and collector junction. Current flow diagram of pnp transistor is shown bellow: Mathematical computations: emitter current, Ie = Ie(p) + Ie(n) As the emitter doping is much higher than the doping in the base in a commercial transistor, the current in emitter will be approximately equal to the current due to holes. So, Ie = Ie(p) (approx.) In Je open condition, Ie = 0 Due to reverse collector base junction Jc, a reverse saturation current flows: So, -ICO = ICO(n) + ICO(p) The total collector current when emitter is forward bias −IC = ICO − IC1 (p) and, IC = IC1 (p) − ICO. Usually, Ic is always greater than ICO. In fact, Ic is of the order of milli Ampere while the ICO is of the order of micro Ampere. Hence, ICO = IC1(p) For pnp transistor 𝐼𝐸 is positive while both 𝐼𝐶 and 𝐼𝐶𝑂 are negative. This means that the collector current actually flows in the direction of opposite that is indicated using arrows. The currents are reverse for npn transistors. There are two quantities which are of great importance in the study of transistors. These are alpha and beta or , 𝜶 and 𝜷. Alpha is defined as DC current gain while beta is defined as maximum current gain. 𝜶= dc current gain = − 𝐼𝐶 𝐼𝐸 In CB configuration Small signal short ckt current gain 𝜶′ = − 𝜷 (𝒐𝒓 𝒉𝑭𝑬 )= max. current gain = 𝐼𝐶 𝐼𝐵 ∆ 𝐼𝐶 ∆𝐼𝐸 | 𝑉𝐶𝐵 =constant In CE configuration Small signal short ckt max. current gain 𝜷′ = ∆ 𝐼𝐶 ∆𝐼𝐵 | 𝑉𝐶𝐸 =constant Relationship between alpha and beta: We all know that, 𝐼𝐶 + 𝐼𝐵 + 𝐼𝐸 = 0 − 𝐼𝐸 = 𝐼𝐵 + 𝐼𝐶 𝜶= − 𝐼𝐶 𝐼𝐸 𝐼𝐶 = −α 𝐼𝐸 = α( 𝐼𝐵 + 𝐼𝐶 ) 𝐼𝐶 (1 − α) = α 𝐼𝐵 𝐼𝐶 𝐼𝐵 = 1−α =𝜷 α We can also determine collector current in terms of alpha and beta. We have, 𝐼𝐶 = −α 𝐼𝐸 + 𝐼𝐶𝑂 = α( 𝐼𝐶 + 𝐼𝐵 ) + 𝐼𝐶𝑂 𝐼𝐶 (1 − α) = α 𝐼𝐵 + 𝐼𝐶𝑂 𝛼 1 𝐼𝐶 = (1−α) 𝐼𝐵 + (1−α) 𝐼𝐶𝑂 𝑰𝑪 = 𝜷 𝑰𝑩 + (𝜷 + 𝟏) 𝑰𝑪𝑶 The above relation is quite useful in solving numerous problems. Relation between alpha and beta: Beta = (1-alpha)/alpha MOSFET: The metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which determines the conductivity of the device. MOSFET INVERTER: A MOSFET is a natural voltage-controlled switch. A high gate voltage turns on the MOSFET channel, allowing current to flow between drain and source, thereby turning a load. MOSFET is used in inverters because it is very efficient in switching, less resistance path between source and drain terminal which translates to less heat. CMOS Technology: VDD D G B S PMOS IN NMOS S G B D OUT GND The amount of current the MOSFET can provide depends on the transistor physical properties such as width, length, oxide thickness, etc., the gate voltage, and the load. CMOS working: When the low input voltage is applied to a CMOS inverter, then the PMOS transistor is switched ON whereas the NMOS transistor is switched OFF by allowing the flow of electrons throughout the gate terminal & generating high output voltage. Similarly, when the high input voltage is given to the CMOS inverter then, the PMOS transistor is switched OFF whereas the NMOS transistor will be switched ON avoiding as many electrons from attaining the output voltage & generating low logic output voltage. <-------------------------------------------------------------------------->