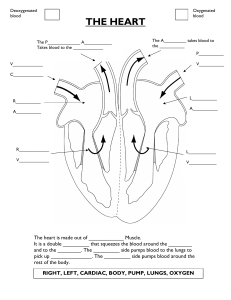
LESSON 1, Part 1 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Learning Objectives: Identify normal cardiac anatomy and physiology Identify and describe heart valves Describe normal electrical components of the heart Understand normal cardiac mechanical events Define Cardiac Output & describe its influencing factors Discuss the anatomy and function of coronary arteries Lesson Introduction: This first lesson will review and examine basic cardiac structures. The human heart has 2 systems that must both be functional for the heart to produce heartbeats and sustain life. The 2 systems are the mechanical system, and the electrical conduction system. The mechanical system is the component that includes cardiac muscle, valves, heart chambers, as well as coronary arteries. This system ensures blood flow through the heart, and from the heart to support the body The electrical conduction system is responsible for generating impulses that will act as messages, “telling” the mechanical system to function. STRUCTURE & FUNCTION OF THE HEART Let’s begin by comparing the R side and the L side of the heart… - R side: - the right ventricle (RV) is a pump for the pulmonary system - the RV delivers un-oxygenated blood from the body, to the lungs - it projects its volume against minimum resistance (the lungs) - because the RV meets limited resistance in the lungs, it does not require extreme strength or thick musculature to perform its role - thin walls: 4-5 mm in thickness - tricuspid and pulmonic valves - L side: - the left ventricle (LV) is a pump for the systemic circulation - the LV delivers oxygenated blood received from the lungs, to the body - it projects its volume against a large maximum resistance (the body) - LV requires more strength and thicker muscle than the RV because the LV meets high resistance as it ejects blood throughout the body - thick walls: 8-15 mm thickness (about 2-3 times that of the RV) - mitral and aortic valves To reinforce the heart’s anatomy, you can view illustrations on the following sites http://innerbody.com/image/cardov.html (this site has animation capabilities) http://www.texasheart.org/HIC/Anatomy/anatomy2.cfm Can’t ctrl+click on these underlined links? Just copy and paste the complete address into the location bar of your browser and click “enter”. Anatomical location: - the heart lies obliquely behind the costal cartilages, between the 2 nd and 6th ribs - the broad portion is called the base (upper right area) - the pointed end of the heart is the apex (lower left area) - PMI (point of maximum impulse) is heard best at the apex …Proceed to Lesson 1, Part 2