Macromolecules & Enzymes Worksheet: High School Biology
advertisement
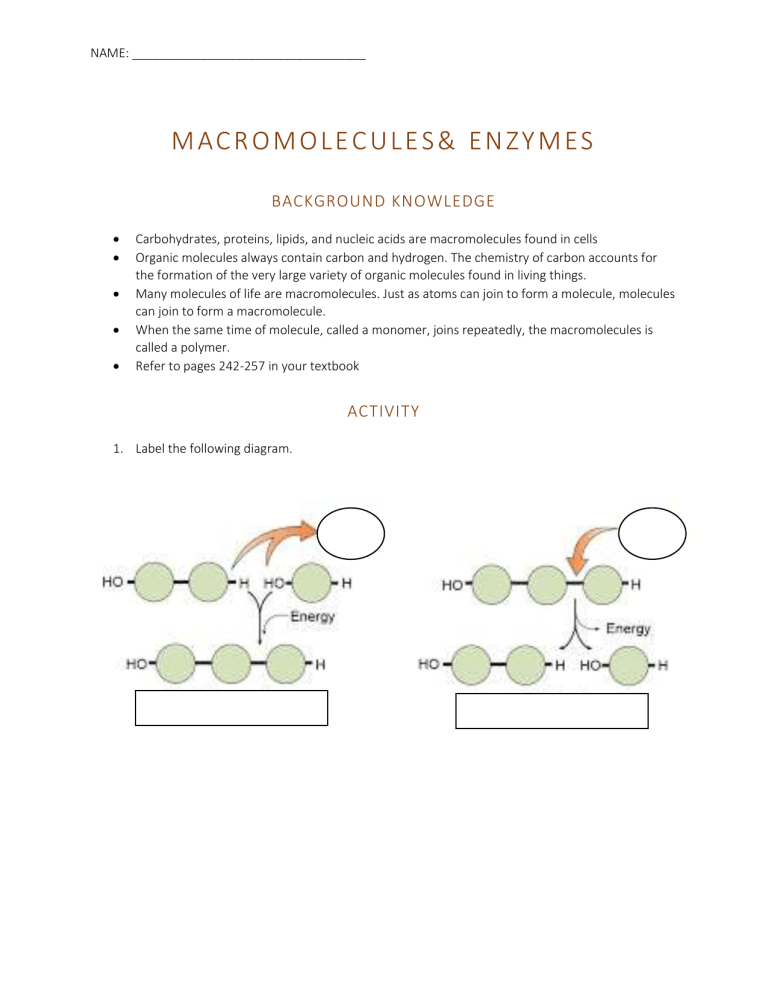
NAME: __________________________________ MACROMOLECULES& ENZYMES BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids are macromolecules found in cells Organic molecules always contain carbon and hydrogen. The chemistry of carbon accounts for the formation of the very large variety of organic molecules found in living things. Many molecules of life are macromolecules. Just as atoms can join to form a molecule, molecules can join to form a macromolecule. When the same time of molecule, called a monomer, joins repeatedly, the macromolecules is called a polymer. Refer to pages 242-257 in your textbook ACTIVITY 1. Label the following diagram. NAME: __________________________________ 2. Draw a sketch showing the dehydration synthesis of two glucose molecules to form a macromolecule. What is this macromolecule called? Draw the hydrolysis of this molecule to form 2 glucose molecules. 3. Draw the hydration synthesis of a fat molecule from 3 fatty acid molecules bonded with one glycerol molecule. Draw the hydrolysis of a fat molecule. 4. Draw the dehydration synthesis of 2 amino acid molecules to form a dipeptide. Draw the hydrolysis of the dipeptide. NAME: __________________________________ 5. Using the diagram below, draw how this enzyme action would change under competitive inhibition. 6. In your own words, explain how enzyme speed up chemical reaction rates.




