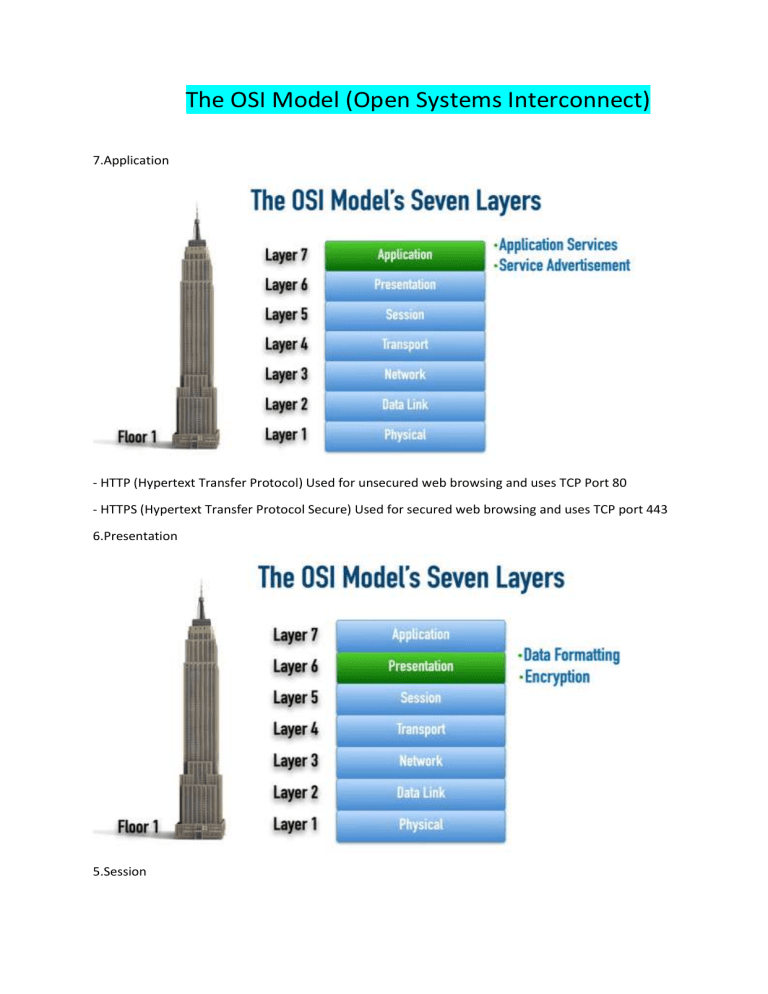
The OSI Model (Open Systems Interconnect) 7.Application - HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) Used for unsecured web browsing and uses TCP Port 80 - HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) Used for secured web browsing and uses TCP port 443 6.Presentation 5.Session 4.Transport-network connections – segments Tail Drop - Occurs when a packet is dropped when it tries to enter a queue because the queue is full RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol) -A Layer 4 protocol used to stream voice and video TCP (Transport Control Protocol) Connection-Oriented Layer 4 protocol that is considered RELIABLE UDP (User Datagram Protocol) Connectionless Layer 4 protocol that is considered UNRELIABLE 3.Network – Routers- Packets (datagrams) 2.Data Link- MAC (Media Access Control) Address – A 48-bit address ‘burned-in’ to a network interface card (NIC) by its manufacturer – Frames –(SWITCH) Types of Synchronization - Isochronous: Devices look to a common external device for chocking Asynchronous: Devices use their own internal clocks and use one or more start/stop bits Synchronous: Clocking is shared between sender and receiver over a separate channel 1.Physical – Cables -Bits (Protocol Data Unit: The name given to data at a specific layer of the OSI Model) Broadband - Different conversations can use different frequency ranges Baseband - One conversation uses the entire frequency range Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away TCP/IP Model 4.Application - Application - Presentation - Session 3.Transport 2.Internet 1.Network Access NETWORK AND TRANSPORT LAYER Network IP, ICMP, UDP and TCP -IP - Router -UDP (User Datagram Protocol) - TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) -ICMP – Ping (An CMP – based networking utility that can check reachability to a specified IP address) can we ping Gateway addresses TRANSPORT - UDP – for Voice Tel. - TCP-3way handshake Headers Layers 3 and 4 TCP Header Source Port - Destination Port Sequence Number Acknowledgment Number (if the ACK flag is set) Data Offset – Reserved – Flags - Window Size Checksum – Urgent Pointer (if the URG flag is set) Options (0-320 bits) -Source Port: 16bit field that identifies the sending port -Destination Port :16-bit Field that identifies the receiving port -Sequence Number: 32-bit field that specifies the first sequence number if the SYN flag=1, or the accumulated sequence number if the SYN flag=0 -Acknowledgment Number: 32-bit field that specifies the next sequence number the sender of an ACK expects (if the ACK flag =1) -Data Offset: 4-bit field that specifies the size of the TCP headers, with a unit of measure of 32-bit words (the minimum value is 5, and the maximum value is 15) -Reserved: 3-bit field reserved for future use, where each bit is set to a value of 0 -Flags: A series of nine 1-bit fields, each representing a different TCP flag (The SYN, ACK and URG flags) -Checksum: 15-bit field used for error -checking both the header and payload of the segment -Urgent Pointer: 16-bit field indicating the last urgent data byte (if the URG flag=1) -Options: A field whose size is in the range of 0-320 bits and can be used to indicate a variety of additional TCP options UDP Header Source Port – Destination Port Length – Checksum -Source Port: 16-bit field that identifies the sending port - Destination Port: 16-bit field that identifies the receiving port - Length: 16-bit field that specifies the combined length of the UDP header and data -Checksum: 16-bit field that can be used to perform error checking of the header and data (optional for IPv4 and required for IPv6) IPv4 Header IPv6 Header Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) – The largest frame or packet that can be transmitted or received on an interface. Don’t Fragment (DF) Bit: A bit in an IP4 header that prevents a packet from being fragmented. Note: IPv6 does not have a DF bit, and it uses a ‘Packet Too Big’ ICMPv6 message. Ports and Protocols *Well-Known Ports:0-1023 Offer well-known network services *Registered Ports: 1024-49151 Registered with the Internet Assigned Number Authority *Ephemeral Ports: 49152-65535 Dynamic Ports or Private Ports Flooding – When a switch forwards a copy of a frame out all of its ports, except the port on which it was received. We doing it when we don’t know where the destination of the MAC is! All ports on a hub belong one collision domain!!! Module 2: Recognizing the Pieces and Parts of a Network Modem (Modulator/Demodulator) - Modulates binary data into analog signals and demodulates analog signals into binary data Carrier-Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) Carrier-Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA) Flooding - When a switch forwards a copy of a frame out all of its ports, except the port on which it was received Default Route - A route that is used when a router does not have a more specific routing table entry for the destination network. *Directly Connected *Statically Configured *Dynamic Routing Protocol *Redistributed FULL-DUPLEX - Allows simultaneous transmission and reception of packets on a network segment. HALF-DUPLEX - Allows a device on a network segment to either transmit or receive packets at any one time, but not transmit and receive packets simultaneously BROADCAST DOMAIN - An area of network throughout which a broadcast can travel (subnet or a VLAN)- HUB -All ports on a hub belong one broadcast domain – HUB It could be even VIRTUAL LOAD BALANCER RANSOMWARE ATTACK - Occurs when a system contains malware (software written to be intentionally malicious), and the user is asked to pay ransom to prevent their data from being publicly posted or permanently encrypted. Module 3: Describing Network Topologies - If one link fails, other links continue to function - Centralized device is a potential single point of failure - Popular in modern networks N*(n-1) / 2 5*(5-1) / 2=10 FULL MESH PARTIAL MESH -optimal path -Might be Suboptimal Path -Not Scalable -More Scalable -More Expensive -Less Expensive Token Ring -A legacy LAN technology that used a ring topology and had bandwidth options of 4 Mbps or 16 Mbps Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) -A legacy LAN technology that operated at 100 Mbps and used two counter-rotating rings (to provide fault tolerance) and used fiber optic cabling for its transmission. Physical ring topology – we can call it circle topology. Sets a back off timer to avoid collisions! VPN -logical tunnel connecting the two routers. Point – To – Multipoint Topology Variants Two topology’s at one network -in this case point-to-point and multipoint topology. *Infrared *Bluetooth More advanced tech is available. *Cloud Base Tech. *Offers Quality of Service. SD-WAN Controller - intend base networking. The Control Plane function are decoupled from the routers and performed by the SD-WAN Controller. Physical WAN connections can use a wide variety of technologies (4G&5G Cellular Data, MPLS, or Cable Modem) SD-WAN controller can simultaneously send out appropriate configuration commands to routers to provide consistent QoS, security, and predictable performance Sensor: A SCADA component that detects a specific characteristic (temperature, water level, etc.) of a system Control: A SCADA component that can alter a condition (temperature, water level, etc.) Remote Telemetry Unit (RTU): A SCADA component that can receive information from a SCADA sensor and send instructions to a SCADA control SCADA Master: A SCADA component that uses a communications network to receive information from one or more RTUs and send instructions to those RTUs Module 4: Understanding Network Services Only do unicast – this could be an issue. Transport Mode- does not encrypt the information Tunnel Mode – encrypt everything. 10.0.0.1 – private IP address. 192.0.2.1- public address (set up a tunnel) so we can access Branch A WEB SERVICES Common HTTP Verbs POST- create a new record on the web server GET – getting a WEB page PUT – updating an existing record DELETE – delete a record HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): TCP Port 80 HTTPS (HTTP Secure): TCP Port 443 – passwords, credit cards information PBX (Private Branch Exchange) – A privately owned phone system used in large organizations (Key systems were privately owned phone systems for smaller installations) Ones the connection is established the phone 3800 connect to 1012 without the Call Agent Laptop A wants an IP address from DHCP Server and the DHCP server will communicate with the MAC address of laptop A (IP address of laptop A will be all 0) The way Laptop B receive an IP is the Router is set up to have DHCP Relay Agent to allow the packet to reach the DHCP server Laptop B Ip will be 172.16.1.100/24 FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name) – A complete DNS name that uniquely identifies a host DNS – translator between fully qualified domain names and IP addresses. - Out off Ipv4 addresses (public) - API- Application Programming interface A way for one piece of software to communicate with another piece of software SBI – Southbound Interfaces Centralized Control Plane – SDN protocol (Open Flow) Open Flow NBI – Northbound Interfaces RESTful APIs JSON – java script object notation Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) – A Session Layer protocol responsible for setting up, maintaining, and tearing down sessions Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) – A Transport Layer protocol that gets encapsulated inside UDP segments and is used to transmit voice and video media





