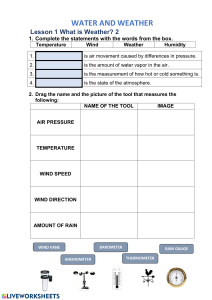
HYDROLOGIC CYCLE The sun's heat makes water on the Earth's surface turn into an invisible gas called water vapor, which is called evaporation. This vapor rises into the sky where it cools down and becomes tiny water droplets, a process called condensation. Clouds are made of these small droplets, and they get bigger when the droplets bump into each other. Eventually, these droplets become heavy and fall as rain. This falling of rain is known as precipitation. The rainwater flows into lakes, streams, and rivers, eventually reaching the sea. When the sun shines on these bodies of water, the cycle repeats: evaporation, condensation, and precipitation. This continuous process, known as the water cycle, keeps water moving from the ground to the sky, providing the water needed for plants, animals, and people to survive. PRECIPITATION – is any liquid or frozen water that forms in the atmosphere and falls back to the Earth. It comes in many forms, like rain, sleet, and snow. Precipitation forms in the clouds when water vapor condenses into bigger and bigger droplets of water. ➢ Rain: Up in the cold clouds, rain often starts as snow, but it melts into liquid as it descends through warmer air. Raindrops are typically between 0.5 millimeters to 6.35 millimeters in diameter. ➢ Freezing Rain: When rain encounters a thin layer of freezing air near the Earth's surface, it freezes on contact, creating freezing rain. ➢ Sleet: Sleet forms when snow partially melts as it passes through warm air, then refreezes into small ice pellets when it encounters cold air near the ground. ➢ Hail: Hail is produced during thunderstorms in cumulonimbus clouds. Strong updrafts carry water droplets up, where they freeze into ice. These ice particles can be carried up and down multiple times, adding layers and increasing in size before falling to the ground. ➢ Snow: Snowflakes form up in the clouds and remain as ice crystals throughout their descent, resulting in snowfall when they reach the Earth's surface. CONDENSATION NUCLEUS - tiny, suspended particle, either solid or liquid, upon which water vapor condensation begins in the atmosphere, about 1/100th the size of a cloud droplet. 3 WAYS TO FORM A CLOUD 1. Convective – due to intense heating of air at the ground which leads to expansion and vertical size of air. 2. Cyclonic – associated with the movement of large air-mass systems, as in the case of warm or cold fronts. a. Warm Front – warmer air mass that is advancing into a cooler air mass. b. Cold Front – colder air mass that is advancing into a warmer air mass. c. Stationary Front d. Occluded Front 3. Orographic – lifting of moist air masses over the windward side of the mountain range. FOG - Fog is a cloud that touches the ground. Fog shows up when water vapor, or water in its gaseous form, condenses. MEASURING PRECIPITATION We don’t measure rain by volume but by depth. Rainfall is measured in millimeters because it is a measurement of the depth of water that falls on a particular area, such as one square meter. Liters, on the other hand, are a measurement of volume. While rainfall does represent a volume of water, the depth of the water is a more useful measurement for understanding the impact of the rainfall on the ground. Therefore, millimeters are used to measure the depth of rainfall. RAIN GAUGE – use to measure rainfall over an area in a predefined period of time. TWO TYPES OF RAIN GAUGE 1. RECORDING GAUGE - it plots the rainfall against time. From that plot of data, we can easily extract information about the intensity and duration of rainfall, since which we may make a hydrological analysis of storms. 2. NON – RECORDING GAUGE - The non-recording gauge (original gauge) extensively used in the world is the Symon’s gauge. Non-recording gauges don’t record the rain but only collect the rain. Once the rain is collected, then it is measured by using a graduated cylinder. WEATHER RADAR - also called weather surveillance radar (WSR) and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, and estimate its type (rain, snow, hail etc.). WEATHER SATELLITE - or meteorological satellite is a type of Earth observation satellite that is primarily used to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth.