Electronic configuration and atomic structures notes(1)
advertisement

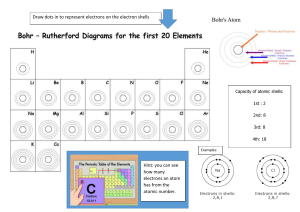
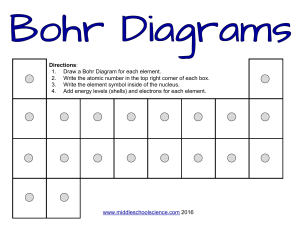
Grade 9 Chemistry Electronic Configurations and Atomic Structures Objective: ● Deduce the pattern for determining the electronic configuration of the first 20 elements and draw their atomic structures Electronic Configurations and Atomic Structures Electrons move around the nucleus of the atom in specific areas called shells. Only electrons with appropriate energy occupy a given shell. Each shell can accommodate a certain number of electrons. The arrangement of electrons in an atom is known as electronic configuration. This can be represented in writing using numbers or by drawing a shell diagram. Arrangement of Electrons on Shells ● First Shell - 2 Electrons ● Second Shell - 8 Electrons ● Third Shell – 8 Electrons (temporarily full) Electronic Configurations for Elements 1- 20 of the Periodic Table Copy and complete the Table Elements Number of Electrons Hydrogen 1 Helium 2 Lithium 3 Beryllium 4 Boron 5 Carbon 6 Nitrogen 7 Oxygen 8 Fluorine 9 Electronic Configurations 1 2, 1 Neon 10 Sodium 11 Magnesium 12 Aluminium 13 Silicon 14 Phosphorus 15 Sulphur 16 Chlorine 17 Argon 18 Potassium 19 Calcium 20 2, 8 2 ,8 ,6 2, 8, 8 Atomic Structures Diagram of potassium’ s Atomic Structure Activity Draw atomic structures for elements 1- 20 of the Periodic Table. Please ensure that: ● Electrons on the first shell are paired (put them beside each other at the top) ● Put the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus in terms of numbers e. g. 11p, 12n. ● Use x to represent the electrons.