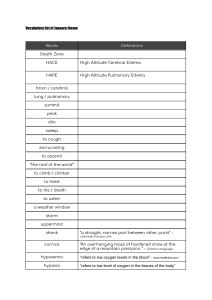
Heart Failure Heather Brown DNP, RN NSG 420 12 edition-2023 Objectives for Heart Failure Compare left and right sided heart failure Identify assessment findings Describe pharmacological treatments Prioritize care for the client Let’s Take a Basic Look Animation Heart Failure Cardiac Output Heart Rate Stroke Volume CO=HR x SV . Risk Factors Primary risk factors Hypertension CAD Prior heart damage Risk Factors Contributing risk factors Advanced age(non modifiable) Diabetes(type 1 not modifiable type 2 modifiable Tobacco use (modifiable) Obesity (Modifiable) High serum cholesterol lab to look at tryglycerides Pathophysiology Heart Failure in General Ventricular failure leads to: Low blood pressure (BP) Low CO Poor renal perfusion ( check urine output) minimum 30ml per hour Decreased ejection fraction(echocardiogram) Abrupt or subtle onset Compensatory Mechanisms Hypertrophy Increase in muscle mass and cardiac wall thickness Initially effective Over time leads to poor contractility, increased O2 needs, and risk for dysrhythmias Hypertrophied Heart Chambers Fig. 35-1. A, Dilated heart chambers. B, Hypertrophied heart chambers. Systolic vs Diastolic HF Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. Case Study N.B. is a 78-year-old woman admitted to the hospital with shortness of breath. She has a history of hypertension and CAD. Case Study What factors in N.B.’s history increase her risk for heart failure? Age, hypertension,CAD What other factors might you question N.B. about? Family history, tobacco use, vapining, nicotine, i&o Assess Your Patient Left-Sided Heart Failure Most common form Results from left ventricular dysfunction Blood backs up into left atrium and pulmonary veins Pulmonary congestion Pulmonary edema Left Side HF Right-Sided Heart Failure Blood backs up into the right atrium and venous circulation Jugular venous distention Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly Vascular congestion of GI tract Peripheral edema Most commonly caused by leftsided HF Right Side HF Case Study N.B.’s admission assessment reveals the following: Alert and oriented to person, place, and time Fine crackles bilateral lower lobes Shortness of breath on minimal exertion O2 saturation 89%, room air Heart Failure Acute Complications Clinical Manifestations Pulmonary edema Life-threatening situation – alveoli fill with fluid Most commonly associated with left-sided HF Pulmonary Edema Clinical Manifestations Anxious, pale, cyanotic Cool and clammy skin Dyspnea Orthopnea Tachypnea Use of accessory muscles Cough with frothy, bloodtinged sputum Crackles, wheezes, rhonchi Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema Crackles Case Study What interventions will you plan for N.B.? Pulmonary Edema Tx Chronic Heart Failure Clinical Manifestations Fatigue Dyspnea Orthopnea Paroxysmal noctournal dyspnea Tachycardia Chronic Heart Failure Clinical Manifestations Edema Dependent, liver, abdominal cavity, lungs Edema may be pitting in nature Sudden weight gain of >3 lb (1.4 kg) in 2 days may indicate worsening ( have patient weight themselves every day same time of day) Pitting Edema Diagnostic Studies Echocardiography Ejection fraction- greater than 50% is normal Chest x-ray EKG, stress test Cardiac catheterization BNP (NT-proBNP) ABGs ADHF Collaborative Management Continuous monitoring and assessment: VS, O2 saturation, urinary output Lung sounds Supplemental oxygen Mechanical ventilation if unstable High fowlers position RECAP Nursing Assessment Objective data VITAL SIGNS (T, P, R, BP, O2 sat) Skin color and temperature Edema Lung sounds Frothy, blood-tinged sputum Heart rate and sounds Changes in LOC (level of consciousness) . RECAP Nursing Assessment Objective data Serum electrolytes (K+ cardiac) (Na-neuro) BUN, creatinine Liver function tests BNP (beta natriuretic peptide) Below 100is normal Chest x-ray Ejection fraction Echocardiogram EKG/telemetry Problems Impaired gas exchange Impaired cardiac output Fluid imbalance Activity intolerance Treatment . Teaching What would you include in a teaching plan for N.B.? Patient Teaching Medication compliance Daily weight BP & pulse monitoring Respiratory status Low salt & heart healthy diet Smoking cessation Weight management Teach S/S of worsening Objectives Review Compare left and right sided heart failure Identify assessment findings Describe pharmacological treatments Prioritize care for client Audience Response Question A patient with left-sided heart failure is prescribed oxygen at 4 L/min per nasal cannula, furosemide (Lasix), spironolactone (Aldactone), and enalapril (Vasotec). Which assessment should the nurse complete to best evaluate the patient’s response to these drugs? a. Observe skin turgor b. Auscultate lung sounds c. Measure blood pressure d. Review intake and output Audience Response Question Which topics would the nurse plan to include in discharge teaching for the patient? SELECT ALL THAT APPLY a. How to monitor and record daily weight b. Importance of stopping exercise if heart rate increases c. Symptoms of worsening heart failure d. Purpose of chronic antibiotic therapy e. How to read food labels for sodium content f. Instructions on how to take medications Finish with a Smile! References Lewis, S., Heitkemper, M., Dirkson, R., O’Brien, P., Bucher, L. (2023). Medical-Surgical Nursing: Assessment and management of clinical problems (12th ed.). St. Louis, MO: Elsevier.