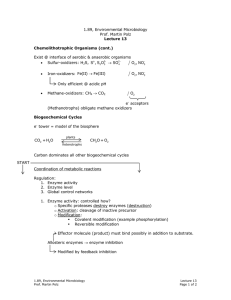
Difference Between NADH and NADPH November 15, 2017 by Lakna 5 min read Main Difference – NADH vs NADPH NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADP (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) are the most abundant types of coenzymes inside the cell, which are used as electron and hydrogen carriers. NADH and NADPH are the reduced forms of NAD and NADP, respectively. Though NADH and NADPH are structurally more similar, they differ by their role in the cell. The main difference between NADH and NADPH is that NADH is used in cellular respiration whereas NADPH is used in photosynthesis. NADH is produced in glycolysis and Krebs cycle and is used in the electron transport chain to produce ATP via oxidative phosphorylation. NADPH is produced in the light reaction of photosynthesis and is used in the Calvin cycle to assimilate carbon dioxide. Key Areas Covered 1. What is NADH – Definition, Production, Usage 2. What is NADPH – Definition, Production, Usage 3. What are the Similarities Between NADH and NADPH – Outline of Common Features 4. What is the Difference Between NADH and NADPH – Comparison of Key Differences Key Terms: ATP, Calvin Cycle, Coenzymes, Electron Transport Chain, Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, NADH, NADPH, Photosynthesis What is NADH NADH refers to the reduced form of NAD. NAD is one of the most abundant types of coenzyme inside the cell, involving in the oxidation-reduction reactions of the cellular respiration. It is mainly used in catabolic reactions. NADH is produced in glycolysis and Krebs cycle. Most dehydrogenases use NAD+ as a coenzyme, donating hydrogen and electrons to produce NADH. NAD+ is the oxidized form of NAD. Two NADHs are produced in glycolysis while six NADHs are produced in Krebs cycle. FADH2 is also produced in Krebs cycle. It also serves as another coenzyme as NADH. Both NADH and FADH2 are used in the electron transport chain. Electron transport chain is shown in figure 1. Figure 1: Electron Transport Chain Since NADH serves as an electron and hydrogen donor, it donates its electrons to the membrane proteins of the inner mitochondrial membrane. These electrons are used in the production of ATP via oxidative phosphorylation. What is NADPH NADPH refers to the reduced form of NADP. NADP is a coenzyme involved in oxidation-reduction reactions of photosynthesis. It is mainly used in anabolic reactions such as nucleic acid and lipid synthesis. NADPH is the most abundant form of NADP inside the cell. It is capable of donating hydrogen and electrons to a chemical reaction. Thereby, NADPH acts as a reducing agent. It structurally differs from NADH by the presence of an additional phosphate group in the 2’ position of ribose, which carries the adenine moiety. The role of NADPH in photosynthesis is shown in figure 2. Figure 2: NADPH in Photosynthesis NADPH is produced in the light reaction of photosynthesis by the enzyme ferredoxinNADP+ reductase. Its reduction power is used in the Calvin cycle, assimilating carbon dioxide. In animals, NADP is used in the pentose phosphate pathway. Similarities Between NADH and NADPH Both NADH and NADPH are reduced forms of the most abundant coenzymes inside the cell. Both NAD and NADH are involved in cellular metabolism. Both NADH and NADPH serve as hydrogen and electron donors. Both NADH and NADPH consist of two ribose molecules, which are attached together by phosphate groups and one ribose is connected to an adenine group, and the other ribose is connected to a nicotinamide group. Difference Between NADH and NADPH Definition NADH: NADH is the reduced form of NAD. NADPH: NADPH is the reduced form of NADP. Oxidized Form NADH: NAD+ is the oxidized form of the NADH. NADPH: NADP+ is the oxidized form of the NADPH. Involved in NADH: NADH is involved in cellular respiration. NADPH: NADPH is involved in photosynthesis. Produced in NADH: NADH is produced in glycolysis and Krebs cycle. NADPH: NADPH is produced in the light reaction of photosynthesis. Used in NADH: NADH is used in the electron transport chain to produce ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. NADPH: NADPH is used in the Calvin cycle to assimilate carbon dioxide. Free Phosphate Group NADH: NADH do not contain a free phosphate group. NADPH: NADPH contains a free phosphate group in the 2’ position of the ribose, which is attached to the adenine moiety. Type of Reactions NADH: NADH is involved in anabolic reactions. NADPH: NADPH is involved in catabolic reactions. Abundance NADH: NAD+ is the most abundant form while NADH is less abundant. NADPH: NADPH is the most abundant form inside the cell. Conclusion NADH and NADPH are the reduced forms of the NAD and NADP, respectively. Both NADH and NADPH serve as hydrogen and electron donors for reactions inside the cell. NADH is mainly involved in catabolic reactions whereas NADPH is involved in anabolic reactions. NADH is less abundant in the cell, while NADPH is more abundant in comparison to their oxidized forms. The main difference between NADH and NADPH is the role of each type of reduced coenzyme inside the cell.