Chem 3550 Chapter 16:
advertisement

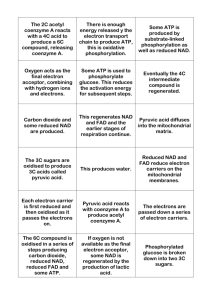
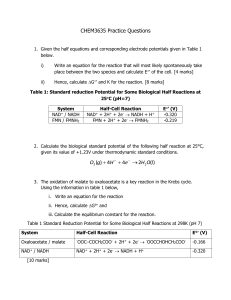
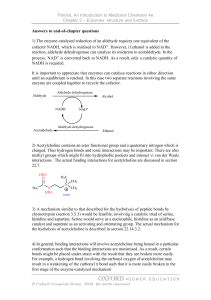
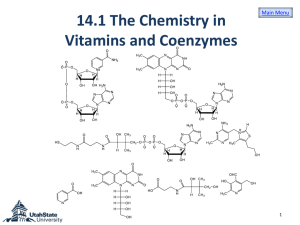
Chem 3550 Chapter 16: Production of NADH and NADPH: The Citric Acid Cycle, the Glyoxylate Cycle (Skip), and the Pentose Phosphate Pathway • Technically, not part of the CAC -- but produces substrate CAC • E3 is also found in -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex At least know that the 3 compoments are E1, E2, and E3 Intricate Details of the Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex These reactions take place in the mitochondrial matrix Product of glycolysis Transported into matrix Thioester High Energy Intermediate Derived from Vitamin B1 -- see Table 6.1 on page 166. Lipoamide -- a key component of E2 Acetyl-CoA -- a high E compound Hydrolysis of this compound produces significant amount of free energy Structure of Coenzyme A (don’t have to memorize!) Coenzyme A (abbrev. CoASH) has role in carrying acetyl or acyl groups Coenzyme A does not cross biological membranes NAD+ is an oxidizing agent, typically to oxidize alcohols NADH is a reducing agent, typically to reduce ketones and aldehydes Structure of NAD+ -- don’t have to know! Oxidized Reduced form form Typically involved in oxidizing alkanes