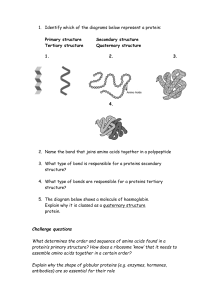
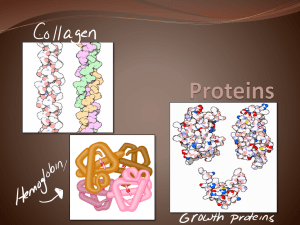
Structure of an amino acid (diagram). What does this diagram show? The amine group, contains an individual nitrogen bonded to two separate hydrogens. What part of the amino acid is highlighted? What part of the amino acid is highlighted? The carboxyl group, contains a carbon, double bonded to an oxygen atom and a single bond to a hydroxyl (OH-) group. Why does the R group effect the amino acid? 1 2 What type of bond occurs between two amino acids? 1 The R group can contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen (and other elements) in different bonding patterns to form different amino acids. 2 What type of reaction occurs when two amino acids form a peptide bond? Peptide bond, formed between the available carbon and nitrogen. Condensation reaction. The hydroxyl group within the carboxyl group and a hydrogen from the adjacent amine group bind to form H2O. ? What test is used for identifying proteins? What results are expected? What process can speed up the development of positive results in a biuret test? When several amino acids join, what form of a protein is produced? Biuret test. A positive result for proteins turns the solution purple. A negative test keeps the solution blue. Heating the solution in a water bath. Polypeptide. When two amino acids join, what form of a protein is produced? Dipeptide. What structure does the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide produce? Primary structure. What structures are found at the ends of the primary structure of a polypeptide chain? Amine group (NH2) and carboxyl group (COOH). Lysine, Valine, Alanine and Ascorbic acid are all types of these. What is the shape the polypeptide chain is twisted and folded into as the secondary structure? What characteristic gives the tertiary structure the shape that is closely related to its function? Amino acids. α-helix. (Another form is the betapleated sheet, a flattened chain). Complex, 3D folded structure. Which type of bond forms between R groups, are common, but are not strong? Hydrogen bonds. Which type of bond forms between an amino acid which is positively charged and another which is negatively charged? Ionic bond. This is if they are close enough to each other. These bonds are not strong and easily broken. Which type of bond forms between amino acids that contain sulfur in the R-groups? Disulfide bridge. Quite strong covalent bonds. These proteins are typically long and thin, as well as insoluble used for structure and support. Fibrous proteins. Examples of fibrous proteins include: collagen (tendons – connective tissue), actin and myosin (used for muscle movement) and keratin (hair). These proteins are more spherical in shape with metabolic / biochemical functions. Globular proteins. Examples of globular proteins include: enzymes and myoglobin (stores oxygen in muscle tissue). Proteins that involve more than one peptide chain form which type of structure? Quaternary structure. An example of this is haemoglobin; having four polypeptide chains with associated haem groups. What name is given to the associated groups which are not made from amino acids in a peptide? Prosthetic group. Haem within haemoglobin is an example of this. Which two compounds are used in the Biuret test? Sodium hydroxide (added first) then dilute copper sulfate (in equal amounts). Describe what protease is and what it is made from? An enzyme that breaks down proteins, that is made of different amino acids.