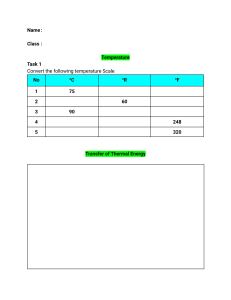
Thermal physics 1. Kinetic particle model of matter 1. Describe the properties and the particles structure of the three states of matter. 2. What are the terms for the changes in state between solids, liquids and gases (gas to solid and solid to gas transfers are not required)? 3. The kinetic model explains the behaviour of materials by describing what is happening to the particles of which they are made. Can you explain why the random motion of microscopic particles in a suspension is evidence for the kinetic particle model of matter? 4. Can you use the kinetic model to describe the pressure and the changes in pressure of a gas in terms of the forces exerted by particles colliding with surfaces? 5. Describe qualitatively, in terms of particles, the effect on the pressure of a fixed mass of gas of: (a) a change of temperature at constant volume; (b) a change of volume at constant temperature 6. Boyle’s law 7. How to explain the idea of ‘absolute zero’? How to convert temperatures between kelvin and degrees Celsius? 2. Thermal properties and temperature 1. Can you describe how and why solids, liquids and gases expand when their temperatures rise? 2. Can you describe some of the everyday applications and consequences of thermal expansion? 3. Can you describe melting and boiling in terms of energy and temperature? 4. What are the melting point and boiling point of water at standard atmospheric pressure? 5. Will heating always lead to an increase in temperature? 6. Can you explain changes of state using the kinetic particle model? 7. Which one will evaporate more quickly, hot water or cool water? Why? 8. Why evaporation causes cooling of a liquid? Why evaporation causes the cooling of an object in contact with an evaporating liquid? 9. How can you speed up the evaporation of a liquid? Why? 10. What are the differences between boiling and evaporation? 11. How to define ‘specific heat capacity’? 12. Can you design an experiment to measure the specific heat capacity of a solid and a liquid? 3. Transfer of thermal energy 1. What are the three types of thermal energy transfer? 2. Will there be thermal energy transferred from water at 0℃ to ice at 0℃? 3. What is ‘thermal conductor’? What is ‘thermal insulator’? Can you give some examples? 4. Find two spoons at room temperature: one is metal, the other is wooden. Use your finger to touch them one by one. Which of them feels warmer? Can you explain why? 5. How to explain conduction in non-metals? 6. How to explain conduction in metals? 7. Is thermal energy transferred in liquids and gases mainly by conduction? 8. Can you describe and explain convection currents? 9. Conduction and convection both carry thermal energy from a warmer place to a cooler place. What’s the main difference between them? 10. If you’re going to put an electric heater in your room in winter, where should you install it, near the floor or near the ceiling, to allow the convection current flow through the room? 11. Can you describe the properties of ‘infrared radiation’? 12. How to choose different types (colours, textures) of surfaces to increase / decrease the rate of absorption / emission of infrared radiation? 13. How does the temperature affect the rate of absorption and emission of infrared radiation? 14. Adding insulation to a house can help to avoid a lot of energy wastage in winter, and also help to prevent from becoming uncomfortably hot in summer. How to build a well-insulated house? 15. Referring to Figure 11.32 on P205, explain how a vacuum flask is designed to reduce the thermal energy transfer. 16. A car engine burns fuel and so gets very hot. How does the cooling system (referring to Figure 11.34 on P206) help to speed up the thermal energy transfer and prevent the engine from overheat? 17. Please read through section ‘Thermal energy transfer, climate and weather’ on P206~207. Make sure to know how the temperature of the Earth is affected by factors controlling the balance between incoming radiation and radiation emitted from the Earth’s surface. 18. Please read through Experimental 11.1~11.3 (P192~195, P198, P203) on demonstrating the conduction, convection and radiation. Make sure you’re familiar with the apparatus listed, the setup and the procedures. Think about the possible phenomenon, and try to explain reasonably. 19. If you are interested, you may research more applications and consequences of thermal energy transfer.