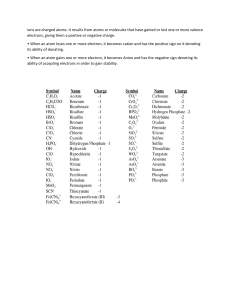
Phase Change - Deposition-gas to a solid; Sublimation-solid to gas; Vaporization- liquid to gas; Condensation-gas to liquid - Physical change = melting, freezing, dissolving, evaporating; Chemical change= boiling an egg, converting, exploding, burning, digesting Atomic Numbers - Number that identifies an element-Atomic number Weighted average mass of all occurring isotopes of an element-Atomic mass Symbolic method for expressing the composition of an atomic nucleus-Atomic notation Electron Configurations - Shorthand description of electrons by sublevels according to increasing energy-Electron configuration - Sublevels: 2,6,10,14 electrons in the sublevels; 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p 6s 4f 5d 6p 7s 5f 6d 7p; Ca 2+ 2 2 6 2 6 = 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p Chemical Formulas - Name of a chemical compound that indicates the # of atoms of each element-Chemical formula - Number of atoms from formula C17H19NO3 = 40atoms NaHCO3=sodium hydrogen carbonate; Mg(CLO4)2= Magnesium Perchlorate; PbO2=Lead (IV) oxide; Hg2Br2=Mercury (I) bromide; Al2(CrO4)3=Aluminum Cromate; AnCl2= Zinc Chloride; Nitrous acid=HNO2; Hypochlorous acid=HClO; hydrochloric=HCL; H2S=hydrosulfuric acid; HCLO4=perchloric acid; H2SO4=sulfuric acid; HNO3=nitric acid; SnO2=Tin dioxide; sulfuric acid=H2SO4; Periodic Trends: - Atomic radius= T to B (increase) L to R (decrease); - Metallic Character=T to B (increase)L to R (decrease); - Ion energy T to B (decrease) L to R (increase); Chemical Bonds - Formula Unit=simplest representative particle in a substance held together by ionic bonds - Covalent Molecule=simplest representative particle in a substance held together by covalent bonds; - Diatomic Molecule=A molecule composed of two nonmetal atoms held together by a covalent bond o Diatomic elements=hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine Chemical Bonds - Single Bond=one electron pair with two atoms; Double Bond= two electron pairs with two atoms; Triple Bond= three electron pairs with two atoms; Polar Bond= electrons shared unequally; Nonpolar Bond= electrons shared equally; - Structural Formula=A diagram that shows the chemical symbol of each atom & a dash representing each pair of bonding electrons - Lewis Structure Formula Bond Strength - Electronegativity= The ability of an atom to attract a shared pair of electrons; - Delta Notation=A method of indicating a partial positive & a partial negative charge in a chemical bond; - Bond Energy=amount of energy required to break a covalent bond; Molecular Geometry - VSEPR Theory= explains the shapes of molecules as a result of electron pairs about the central atom repelling each other; - Electron Pair Geometry=The geometric shape formed by bonding and nonbonding electron pairs about the central atom in a molecule; - Molecular Shape=geometric shape formed by atoms bonded to the central atom in a molecule; - Bond Angle=angle formed by two atoms attached to the central atom in a molecule; Gases - Henry's Law=solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the pressure of that gas above the surface of the solution. As the temperature increases, the solubility of a gas decreases; o Less pressure above gas = less soluble gas in solution; gas can escape easily Solutions - Miscible= liquids that dissolve completely in one another; - Immiscible= liquids that do not dissolve in one another and separate into two layers; - Supersaturated solution=solution containing more solute than can ordinarily dissolve at a given temperature Solution Concentration - Mass % (m/m%) = a solution concentration expression that relates the mass of solute in grams dissolved in each 100 g of solution; o Gives number of grams of solute per 100 grams of solution- if not 100 grams solution, determine grams of solute per “x” grams of solution – still use percent as solute mass o Percent of solute number = mass of solute out of total solution; - need all units to be in grams 15 % Na = 15 grams Na in solution Molarity= a molecular solution concentration expression that relates the moles of solute dissolved in each liter of solution - Ion Concentrations = you are given Molarity of total solution; need molarity of individual ions o calculate ions moles individually; write out ions charge individually & switch CHARGES; look at subscripts (charges) of individual ions to determine moles of each ion per solution; plug into molarity equation and solve for individual molarity