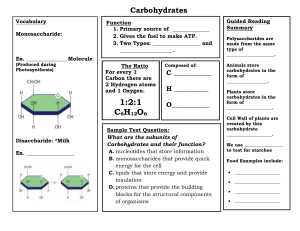
Physiology, Carbohydrates Holesh JE, Aslam S, Martin A. Publication Details Introduction Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients in the human diet, along with protein and fat. These molecules contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Carbohydrates play an important role in the human body. They act as an energy source, help control blood glucose and insulin metabolism, participate in cholesterol and triglyceride metabolism, and help with fermentation. The digestive tract begins to break down carbohydrates into glucose, which is used for energy, upon consumption. Any extra glucose in the bloodstream is stored in the liver and muscle tissue until further energy is needed. Carbohydrates is an umbrella term that encompasses sugar, fruits, vegetables, fibers, and legumes. While there are numerous divisions of carbohydrates, the human diet benefits mostly from a certain subset.[1][2][3] Structures Monosaccharide: The most basic, fundamental unit of a carbohydrate. These are simple sugars with the general chemical structure of C6H12O6. Examples: glucose, galactose, fructose Disaccharide: Compound sugars containing two monosaccharides with the elimination of a water molecule with the general chemical structure C12H22O11 Examples: sucrose, lactose Oligosaccharide: The polymer contains three to ten monosaccharides Examples: maltodextrins, raffinose Polysaccharides: Polymers containing long chains of monosaccharides connected through glycosidic bonds Examples: amylose, cellulose Types Simple Carbohydrates: One or two sugars (monosaccharides or disaccharides) combined in a simple chemical structure. These easily are utilized for energy, causing a rapid rise in blood sugar and insulin secretion from the pancreas. Examples: fructose, lactose, maltose, sucrose, glucose, galactose, ribose Foods: candy, carbonated beverages, corn syrup, fruit juice, honey, table sugar Complex Carbohydrates: Three or more sugars (oligosaccharides or polysaccharides) bonded together in a more complex chemical structure. These take longer to digest and therefore have a more gradual effect on the increase in blood sugar. Examples: cellobiose, rutinulose, amylose, cellulose, dextrin Foods: apples, broccoli, lentils, spinach, unrefined whole grains, brown rice Starches: Complex carbohydrates contain a large number of glucose molecules. Plants produce these polysaccharides. Examples include potatoes, chickpeas, pasta, and wheat. Fiber: Non-digestible complex carbohydrates that encourage healthy bacterial growth in the colon and act as a bulking agent, easing defecation. The main components include cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin. Insoluble: Absorbs water in the intestines, thereby softening and bulking stool. Benefits include regularity of bowel movements and a decreased risk of diverticulosis. Examples: brans, seeds, vegetables, brown rice, potato skins. Soluble: Helps decrease blood cholesterol and LDL levels, reduces straining with defecation, and blunts postprandial blood glucose levels. Examples are fleshy fruit, oats, broccoli, and dried beans. Issues of Concern Carbohydrates are associated with dental caries. Eating large amounts of sugary foods is known to lead to plaque formation, tooth decay, and cavities. The worst carbohydrate for dental decay is sucrose. On the other hand, fructose serves as an energy source for oral cavity bacteria.[4][5][6] Many people falsely believe that that diets high in carbohydrates lead to the development of type 2 diabetes when, in fact, the opposite is true. Data show that the risk of developing type 2 diabetes is lowered as the amount of calories from carbohydrates is increased. Diets that are high in carbohydrates tend to increase the sensitivity of insulin. Thus, today, healthcare providers usually recommend that type 2 diabetics eat a high carbohydrate diet. An additional benefit of a high carbohydrate diet for type 2 diabetics is that it lowers the risk of heart disease. Individuals who eat high fiber diets also tend to have low serum cholesterol and high HDL levels than people who consume a low fiber diet; the lowering of cholesterol also decreases the risk of heart disease. In many parts of Africa, people who eat high fiber diets tend to have a very low risk of intestinal cancer. But the exact amount of fiber to eat to prevent colon cancer remains unknown. Anecdotal reports maintain that eating fiber may lower blood pressure, lower the incidence of gallstones, and decrease blood sugars. Cellular Metabolism Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth where salivary amylase starts the breakdown. After breaking down throughout the digestive system, monosaccharides are absorbed into the bloodstream. As carbohydrates are consumed, the blood sugar levels increase, stimulating the pancreas to secrete insulin. Insulin signals the body’s cells to absorb the glucose for energy or storage. If blood glucose falls, the pancreas makes glucagon, stimulating the liver to release stored glucose. The body is not able to digest fiber, and therefore fiber does not provide calories or energy. It has a variety of health benefits including bulking stool for easier excretion preventing constipation, prebiotic properties, satiety, and intestinal issues. Function Nutrition Carbohydrates are an important part of a nutritional diet. The healthiest sources include complex carbohydrates because of their blunted effects on blood glucose. These options include unprocessed whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and legumes. While simple carbohydrates are acceptable in small amounts, white bread, sodas, pastries, and other highly processed foods are less nutritious and cause a sharp increase in blood glucose. Healthy adult diets should include 45% to 65% carbohydrates as part of the daily intake, equaling about 200 g to 300 g per day. Carbohydrates contain about 4 kcal/ gram (17 kJ/g). Fiber is an important carbohydrate as well. Healthy adults should consume about 30 g per day of fiber, as it is found to reduce the risk of coronary heart disease, strokes, and digestive issues. A glycemic index is a tool used to track carbohydrates and their individual effects on blood sugar. This scale ranks carbohydrates from 0 to 100 based on how rapidly the rise in blood glucose occurs upon consumption. Low glycemic foods (55 or less) produce a gradual increase in blood sugar. These foods include steel-cut oatmeal, oat bran, muesli, sweet potatoes, peas, legumes, most fruits, non-starchy vegetables. Medium glycemic foods (56 to 69) include quick oats, brown rice, and whole-wheat bread. High glycemic foods (70 to 100) increase the risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, obesity, and ovulatory infertility. These foods include white bread, corn flakes, white potatoes, pretzels, rice cakes, and popcorn.[7] Clinical Significance Two things that constantly affect the body include physical activity and diet. A diet needs to be nutritionally balanced, including the proper type and amount of carbohydrates. An increase or decrease in carbohydrates beyond the desired amount can affect both physiological and metabolic processes. An increase in simple carbohydrates may contribute to obesity, a disease that puts individuals at an even greater risk for further disorders such as cardiovascular disease. Carbohydrate intake also contributes to non-insulin-dependent diabetes (type 2 diabetes), a growing epidemic. However, foods rich in nonstarch polysaccharides and low-glycemic foods protect against diabetes. Increased sugar consumption also contributes to the development of dental caries.[8][9]