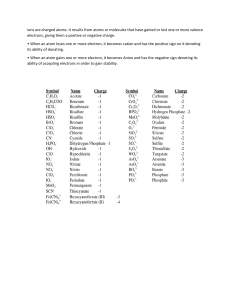
Grade 11 elite Biology Chemistry Review Matter: refers to anything that takes up space and has mass. Element: is a substance that cannot be broken down to simpler substances by ordinary chemical means, and it’s both non-living and living. Atoms: are the smallest part of an element that displays the same properties. Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus. Mass number: the sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus. The three best-known subatomic particles are: 123- positively charged protons uncharged neutrons negatively charged electrons. Protons and neutrons are located within the nucleus of an atom, and electrons move about the nucleus. Done by Dr.Abed alfatah Alhawamdeh WhatsApp number: 00962790836453 periodic table: is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements by increasing atomic number. Groups: The vertical column of the periodic table that signifies the number of valence electrons in an element, Each atom in a group within the periodic table has the same number of electrons in its valence shell. Periods: The horizontal rows in the periodic table that signify the number of electron shells in an element. Isotopes: are atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons. Changing the number of neutrons can make the nucleus less stable and so it breaks apart, as it breaks apart it releases radiation that can be detected. For example, the element carbon has three naturally occurring isotopes: Radioactive Isotopes Some isotopes of an element are unstable, or radioactive and called Radioactive Isotopes. for example, carbon 14. 1- Low Levels of Radiation: The chemical behaviour of a radioactive isotope is essentially the same as that of the stable isotopes of an element. This means that you can put a small amount of radioactive isotope in a sample and it becomes a tracer by which to detect molecular changes and can be used to detect tumours. Onther example of low levels of radiation uses is Positron-emission tomography (PET) scans can be used to detect coronary artery disease and memory disorders like Alzheimer's. Done by Dr.Abed alfatah Alhawamdeh WhatsApp number: 00962790836453 2- High Levels of Radiation: Radioactive substances in the environment can harm cells, damage DNA, and cause cancer. This Radiation can be used for good to sterilize hospital and dental equipment. High radiation can also be used to kill cancer cells. Electrons and Energy One of the more common models of atoms is the Bohr model, developed by the physicist Niels Bohr (1885–1962). In Bohr models of atom Electrons orbit the nucleus at particular energy levels (electron shells). The first shell contains up to two electrons, and thereafter each shell is most stable when it contains 8 electrons. Atoms with an atomic number above 20 may have more electrons in their outer shells. The outermost, or valence, shell helps determine the atom’s chemical properties and how many other elements it can interact with. Because the negatively charged electrons are attracted to the positively charged nucleus, it takes energy to push them away and keep them in their own shell. The more distant the shell, the more energy it takes. valence shell: the outermost shell. The valence shell is important, because it determines many of an atom’s chemical properties. If an atom has only one shell, the valence shell is complete when it has two electrons. In atoms with more than one shell, the valence shell is most stable when it has eight electrons. This is called the octet rule. The electrons in the valence shells play an important role in determining how an element undergoes chemical reactions. Atoms with fewer than eight electrons in the outer shell react with other atoms in such a way that after the reaction each has a stable outer shell. As we will see, the number of electrons in an atom’s valence shell determines whether the atom gives up, accepts, or shares electrons to acquire eight electrons in the outer shell. Molecules and Compounds ➢ ➢ ➢ ➢ molecule exists when two or more elements bond together. compound: is a molecule containing at least two different elements. Ion: an atom that has a charge because it has lost or gained an electron. Ionic bonding: ionic compounds are held together by an attraction between negatively and positively charged ions. ➢ Covalent bonds: a covalent bond is a type of chemical bond characterized by the joint sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Covalent bonds form when atoms share valence electrons with other atoms to achieve a full shell of outer electrons. Done by Dr.Abed alfatah Alhawamdeh WhatsApp number: 00962790836453 Nonpolar and Polar Covalent Bonds ➢ Nonpolar covalent bonds: this is when the sharing of electrons between two atoms is equal. ➢ Electronegativity: this is when one atom is able to attract electrons to a greater degree than the other atom. ➢ Polar covalent bonds: these are covalent bonds where the electrons are not shared equally Done by Dr.Abed alfatah Alhawamdeh WhatsApp number: 00962790836453