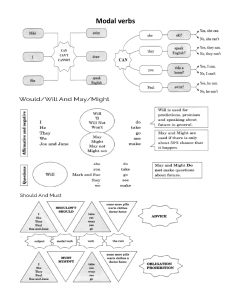
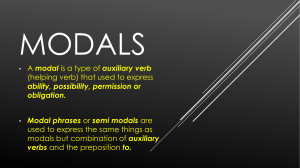
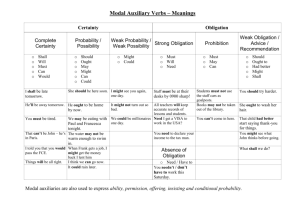
9 English Quarter 1 – Module 1: Modals English – Grade 9 Alternative Delivery Mode Quarter 1 – Module 1: Modals First Edition, 2020 Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for exploitation of such work for profit. Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalties. Borrowed materials (i.e., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names, trademarks, etc.) included in this module are owned by their respective copyright holders. Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from their respective copyright owners. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim ownership over them. Published by the Schools Division of Capiz Schools Division Superintendent: Salvador O. Ochavo Jr., EdD, Ceso V Assisstant Schools Division Superintendent: Nicasio S. Frio, Ceso VI Development Team of the Module Authors: Angelie B. Magcanam Annie B. Binibini Hilda D. Delaflor Leny B. Duran Agnes I. Farillon Ma. Christina A. Soriano Editors: Allen O. Aguirre Ma. Rita F. Villareal Management Team: Salvador Dale Artates Shirley A. De Juan Segundina F. Dollete Salvador Ochavo, Jr. Printed in Capiz Department of Education – Schools Division of Capiz Office Address: Banica, Roxas City Telephone: (036) 6518-456 E-mail Address: capizdeped.gov.ph 9 English Quarter 1–Module 1: Modals Introductory Message For the facilitator: Welcome to the English 9 Alternative Delivery Mode (ADM) Module 1 on Modals! This module was collaboratively designed, developed and reviewed by educators both from public and private institutions to assist you, the teacher or facilitator in helping the learners meet the standards set by the K to 12 Curriculum while overcoming their personal, social, and economic constraints in schooling. This learning resource hopes to engage the learners into guided and independent learning activities at their own pace and time. Furthermore, this also aims to help learners acquire the needed 21 st century skills while taking into consideration their needs and circumstances. As a facilitator, you are expected to orient the learners on how to use this module. You also need to keep track of the learners' progress while allowing them to manage their own learning. Furthermore, you are expected to encourage and assist the learners as they do the tasks included in the module. ii For the learner: Welcome to the English 9 Alternative Delivery Mode (ADM) Module 1 on Modals! This module was designed to provide you with fun and meaningful opportunities for guided and independent learning at your own pace and time. You will be enabled to process the contents of the learning resource while being an active learner. This module has the following parts and corresponding icons: What I Need to Know This will give you an idea of the skills or competencies you are expected to learn in the module. What I Know This part includes an activity that aims to check what you already know about the lesson to take. If you get all the answers correct (100%), you may decide to skip this module. What’s In This is a brief drill or review to help you link the current lesson with the previous one. What’s New In this portion, the new lesson will be introduced to you in various ways such as a story, a song, a poem, a problem opener, an activity or a situation. iii What is It This section provides a brief discussion of the lesson. This aims to help you discover and understand new concepts and skills. What’s More This comprises activities for independent practice to solidify your understanding and skills of the topic. You may check the answers to the exercises using the Answer Key at the end of the module. What I Have Learned This includes questions or blank sentence/paragraph to be filled in to process what you learned from the lesson. What I Can Do This section provides an activity which will help you transfer your new knowledge or skill into real life situations or concerns. Assessment This is a task which aims to evaluate your level of mastery in achieving the learning competency. Additional Activities In this portion, another activity will be given to you to enrich your knowledge or skill of the lesson learned. Answer Key This contains answers to all activities in the module. iv At the end of this module you will also find: References This is a list of all sources used in developing this module. The following are some reminders in using this module: 1. Use the module with care. Do not put unnecessary mark/s on any part of the module. Use a separate sheet of paper in answering the exercises. 2. Don’t forget to answer What I Know before moving on to the other activities included in the module. 3. Read the instruction carefully before doing each task. 4. Observe honesty and integrity in doing the tasks and checking your answers. 5. Finish the task at hand before proceeding to the next. 6. Return this module to your teacher/facilitator once you are through with it. If you encounter any difficulty in answering the tasks in this module, do not hesitate to consult your teacher or facilitator. Always bear in mind that you are not alone. We hope that through this material, you will experience meaningful learning and gain deep understanding of the relevant competencies. You can do it! v What I Need to Know This module will help you learn to use modals in a sentence. At the end of the lesson, the students are expected to: 1. express permission, obligation and prohibition using modals and 2. use the appropriate modal to complete the sentences. What I Know A. Choose an appropriate modal to fill in the blanks in each sentence. Write the letter of your answer on your paper. 1. You _____ leave if you’re finished. A. can B. could C. may D. might 2. _____ I come in? A. can B. could C. may D. might 3. We _____ not get into the concert without tickets, so we want him. A. can B. could C. may D. might 4. _____ I open the windows? A. can B. could C. may D. might 5. Danny _____ save his money. A. has to B. have to C. must D. must have to 6. I _____ clean the kitchen yesterday. A. have to B. had to C. must D. must have to 7. She _____ speak loudly. A. must B. hasn’t C. don’t has to D. must not 8. Does Harold _____ finish the project this week? A. must B. have to C. must to D. have to 9. You _____ use safety glasses at all times. A. must to B. don’t has to C. has to D. must 10. You _____ bring your identification. A. has to B. have to C. have must D. has to 1 Lesson 1 Modals Modal verbs help when speaking about ability, making requests and offers, asking permission, and more. The modal verbs in English differ from other verbs, because they are not used separately, and do not indicate a specific action or state, they just reflect its modality, the attitude of the speaker to the action. This lesson will help you understand modal verbs and will inspire you all the more for you to further develop your understanding of the target concepts, themes and enhance your communication skills. What’s In Direction: Read the conversation between Nicole and Mia. Answer the questions that follow on your paper. Nicole: Shall we start? Mia: Yes, we probably should. Nicole: So, can you tell me something about modal verbs? Mia: Sure. What would you like to know? Nicole: I must know everything about them. Mia: That might take a long time. Nicole: You will help me though, right? Mia: I think I could teach you. Mia: Even though it may be challenging. What do call the underlined words in each sentence? What are the uses of these words? 2 What’s New To communicate effectively, one should understand on what appropriate words may be used to express permission, prohibition and obligation. This lesson will help you gain an understanding on the different modals or modal verbs, its usage, and importance in communication. CHOOSE THE MODAL A. Choose the correct answer from the choices given. Write your answer on your paper. can – 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. could may –might You ___leave if you’ve finished. ___I come in? We ___not get into the concert without tickets, so we want him. ___I open the window? ___you turn the heating up a bit, please? B. Fill in the following blanks with appropriate modals. Write your answer on your paper. -cannot - must not 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. You ___ play music. You___ eat in the conference room. You ___ drive here. You ___ wear a hat in class. You ___use your phone in a bus. C. Choose the correct modals that would complete the sentence. Write your answer on your paper. -Has to/Have to -Must 1. She _____ work tomorrow. 2. I _____ finish my homework last night. 3. They _____ bring the money tomorrow. 4. You _____ wear the uniform at all times. 5. You _____ wait until 10 am. 3 What is it? MODAL VERBS are used to express permission, prohibition and obligation or no obligation. PERMISSION: CAN, MAY, COULD Can is most often used to ask for or give permission. Use can to say that someone has permission to do something. Examples: Can I borrow a pen? You can sit here, the seat is free. Could is also used to ask permission (but not to give it) could is more formal and polite than can, we can also use could to say that someone was allowed to do something in the past. Examples: Could I ask you something? Both staff and students could use the ice rink. May is the most formal way to ask for and permission. Examples: May I see your passport, please? Customers may request a refund within a period of 30 days. PROHIBITION Modal verbs of prohibition are the opposite of giving permission. The modal verbs used are the following: can, must and may as well as the past form could, they are used as negatives. CAN’T is normally used to show inability, but in these examples it shows prohibition. It is like you are saying you do not have the ability because of the rules. Examples: You can’t go into that restaurant without a tie. You can’t drive in this country unless you are over eighteen. We couldn’t study in the library after 5 pm. MAY NOT is the formal way to prohibit something Examples: You may not smoke in this house. You may not wear shoes in the office. 4 MUST NOT this modal verb is known to be the strongest way to prohibit something, or make a rule against something. Examples: You must not use a cell phone during class hours. You must not write with pencil. MODAL VERBS OF OBLIGATIONS Two types of Modal Verbs of Obligations Those that primarily express a firm obligation on necessity must and have to. Examples: I must hand in my thesis by tomorrow. I really must call my parents. Must shows us that the obligations comes from the speaker. Note: The verb must only exist in the simple present and present perfect forms. While the present form can express obligation, necessity, certainty or strong probability; the present form only expresses a strongly felt opinion or supposition. All Persons Present Present Perfect Affirmative must Must have Negative Must not, mustn’t must not have, mustn’t have If other tenses are required, the speaker or writer must use forms of the synonymous modal verb “have to”. This modal auxiliary has all normal tenses, including progressive or continuous forms; these are not common but need to be used in some cases. Principal Tenses Present Present Perfect Has to, Affirmative have to Negative Does not have to (doesn’t have to), do not have to (don’t have to) Progressive or Am having to, is Continuous having to, are Past Future Has had to, have had to Had to Will have to Has had not to, have had not to Did not have to, didn’t have to Will not have to, won’t have to Has been having to, have been Was having to, were having to Will be having to 5 having to having to In the spoken English, and in the present form only, have to is often substantiated by the word got. Example: I have to. - I’ve got to. Examples of must and have to being used to express. a. Firm obligations on necessity. b. Certainty or strong probability. c. Must have only: supposition. a1) You must see a doctor at once! a2) I have to be at school tomorrow at 8 a.m. I have an exam! a21) I've got to be at school tomorrow at… a3) You mustn't touch that plate, it's too hot. a4) I had to see a doctor, because I felt very sick. a5) I had to break the window! I lost my key! a6) The manager isn't here, he's had to go to Paris on urgent business. a7) Tomorrow the President will have to open Parliament. a8) She's having to move because she can't stand the noise. a9) I'm having to take out this detonator very slowly, to avoid an explosion. a10) Oh you're so kind! You didn't have to do it as well as that! b1) b2) b3) b4) He must be over eighty, he was born in 1930. If my brother's not in London, he has to be in New York. I've got all the right answers, I must be one of the winners! If I remember correctly, it has to be here. c1) I can't find my laptop, I must have left it in the train. c2) If they're out, they mustn't have heard the news. Recommendation or moral obligation - should and ought to The verb should only exists in the simple present, and present perfect forms Forms of should: All persons Present Present perfect Affirmative should Affirmative Negative should not, shouldn't should not have, shouldn't have 6 The verb ought to only exists in simple present and present perfect forms Forms of ought to: All persons Present Present perfect Affirmative ought to Affirmative Negative ought not to, oughtn't to ought not to have, oughtn't to have Should and ought to are more or less synonymous Examples: a1) You should stop smoking ( You ought to stop smoking.) a2) It's raining hard, the children ought to come indoors. a3) I didn't know you were married ! You ought to have told me ! a4) If you'd wanted to succeed, you should have worked harder at school. a5) This pullover's got holes in it, I should get a new one. a6) This pullover's got holes in it, I ought to get a new one. a7) That's awful ! You really oughtn't to have done that, you know! What’s More Activity 1 PERMISSION A. Choose the correct answer from the choices given. Write your answer on your paper. can – could may –might 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. You ___put your shoes and coat over there. ___we have something to drink? We are thirsty. Students ___ register for online classes beginning next week. We ___ go to any shop in the mall we wanted to. Tom ___ go with you. ___ I leave early? ___ I use your restroom, please? ___ I try this coat on? 7 9. You ___ leave work now, I’ve got it covered. 10. You ___go as soon as you have finished your exam. Activity 2 PROHIBITION B. Fill in the following blanks with appropriate modals. Write your answer on your paper. -cannot - must not 1. You ___use your phone in a bus. 2. You ___ smoke in the office. 3. Did they tell you that you ____ come into this area. It’s restricted to staff only. 4. Children under ten ___use the pool without adult supervision. 5. You ____eat anymore chocolate. 6. You ___ take a mobile phone into the examination room. 7. I’m afraid you ___take the exam until you pay your remaining tuition fee. 8. You ___ smoke anywhere in the train. 9. You ___ leave your bike there. 10. You ___ bring your pet inside the mall. Activity 3 OBLIGATION C. Choose the correct modals that would complete the sentence. Write your answer on your paper. -Has to/Have to -Must 1. Students _____ register by last week. 2. You _____ arrive on time. 3. We _____ use the password. 4. Denny _____ save his money. 5. I _____ clean the kitchen yesterday. 6. She _____ speak loudly. 7. Does Harold _____ finish the project this week? 8. You _____ use safety glasses at all times. 9. You _____ bring your identification. 10. Students _____ use a pen on the test. 8 What I Have Learned Direction: Answer the following questions and write your answer on your paper. 1. What are modals? 2. What modal/s are used to express permission, obligation, and/or prohibition? What I Can Do Direction: Construct possible sentences base from the pictures using modals expressing permission. Write your answer on your paper. May I drink water, please? 9 10 Assessment Write five things that are prohibited in your respective homes using can’t, must not and may not. Write your answer on your paper. 1____________________________________________________________________. 2. ___________________________________________________________________. 3. ___________________________________________________________________. 4. ___________________________________________________________________. 5. ___________________________________________________________________. The coronavirus outbreak is severely disrupting the global economy. Almost all the nations are struggling to slow down the transmission of the disease by testing and treating patients, quarantining suspected persons through contact tracing, restricting large gatherings, maintaining complete or partial lock down. What activities are prohibited in your respective places during the Enhanced Community Quarantine (ECQ). Use can’t, must not and may not in your sentences. Write your answer on your paper. 6. ___________________________________________________________________. 7. ___________________________________________________________________. 8. ___________________________________________________________________. 9. ___________________________________________________________________. 10. __________________________________________________________________. Anne’s mother imposes some obligations on Anne. What are these external obligations? 11 Ex. Study her lessons She has to study her lessons. 1. Make her room tidy ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 2. Make a daily revision of her lesson ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 3. Help her mother in the kitchen ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 4. Take out the rubbish every day ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 5. Mop the floor every weekend ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 12 Additional Activities Anne thinks some obligations on her own. What are these internal obligations? Write your answer on your paper. Ex. Write a letter to my best friend every month I must write a letter to my best friend every month. 1. Get the new album of my favorite band ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 2. Watch my favorite TV series every night ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 3. Brush my teeth before bed ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 4. Write something on my blog every day ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 5. Buy a new pair of shoes every month ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 13 Answer Key 14 References Almonte, Soliaban et al. English 9 Learner’s Material, First Edition. 2014. Published by the Department of Education Most Essential Learning Competencies (MELC) KG to Grade 12 SY 2020-2021. Accessed May10, 2020. https://www.deped-click.com/2020/05/most-essentiallearning competencies.html https://www.dreamstime.com/modal-verbs-word-concept-cubes-image171715008, Retrieved July 3, 2020 https://linguapress.com/grammar/modal-obligation.htm, Retrieved July 3, 2020 https://daily.jstor.org/the-hidden-life-of-modal-verbs/, Retrieved July 2, 2020 15 For inquiries or feedback, please write or call: Department of Education – SDO – Capiz – Curriculum Implementation Division Banica, Roxas City Telefax: (036) 651 – 8456 Email Address: capizdeped.gov.ph 16