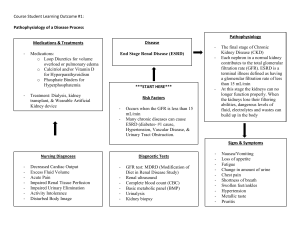
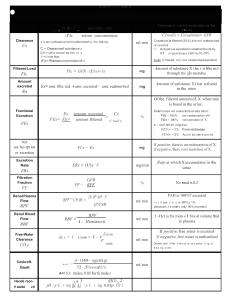
1. After retiring at the age of 67, Aquaman complains that his superpowers are waning and that he now feels fatigued more often than not. His BP is 168/99 mmHg. His doctor runs some routine tests which reveal an albumin excretion of 3g/24 hr. With the following information, calculate his GFR (rounded to the nearest full unit value): Plasma [creatinine] is 0.833 millimoles/L, urine [creatinine] is 8300 micromoles/L and urine flow rate is 1.7 ml/min. a) b) c) d) e) 2. When he was healthy, Aquaman’s glomerular filtration barrier restricted the passage of molecules based upon size and charge as well as the surface area available for filtration. If this barrier were to become more negatively charged which of the following would be TRUE: a) b) c) d) e) 3. Small molecules such as sodium would no longer go through the barrier water would no longer go through the barrier the barrier’s ability to restrict the passage of albumin would not change albumin would pass through the barrier with more difficulty albumin would pass through the barrier more easily A renal biopsy performed on Aquaman reveals (by microscopy) immune complex deposits in the glomeruli. This is consistent with which one of the following: a) b) c) d) e) 4. 16.9 ml/min 17.1 ml/min 16938.8 mL/min 1.69 L/min insufficient information to permit the calculation Membranous nephropathy Prostatic enlargement Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis Diabetic nephropathy Renal artery stenosis In CKD, there are how many stages?: a) 1 b) c) d) e) 5. In CKD, the last stage of disease progression is characterized by: a) b) c) d) e) 6. Slight decrease in GFR Normal or increased GFR decrease in GFR to below 15ml/min A sudden drop in GFR A sudden increase in blood pressure Which of the following is a cause of (intrinsic) renal acute kidney injury (AKI) a) b) c) d) e) 7. 2 4 5 6 Low blood pressure Prostate cancer Diabetes Bleeding ulcer Renal artery stenosis The kidneys, along with hypothalamic antidiuretic hormone production, function to help maintain sodium and water balance. Which of the following would best describe the situation wherein water is retained along with sodium, which is retained due to hyperaldosteronism, such that total ECF increases: a) b) c) d) e) Isovolemic hypernatremia Hypovolemic hyponatremia Hypovolemic hypernatremia Hypervolemic hyponatrema Hypervolemic hypernatremia 8. Antidiuretic hormone activates which ONE of the following: a) Epithelial sodium channels (ENac) b) ROMK channels (Renal outer medullary channels) c) NaKCC transporters d) V2 receptors e) NaH (Sodium Hydrogen exchanger) 9. Hydronephrosis can occur in which ONE of the following conditions: a) b) c) d) e) Vesicouretheral reflux Renal artery stenosis Diabetic nephropathy Hyperkalemia Mercury poisoning 10. In late diabetic kidney disease GFR typically changes how: a) No change b) Decreases c) Increases d) Drops suddenly to zero e) Cannot be accurately measured 11. Which one of the following is FALSE regarding GFR?: a) Rate at which plasma moves through the glomerular capillaries b) Units are in mmol/min c) Females have a lower GFR than males d) Children reach adult proportions by 2 years of age e) Cystatin C is a valid marker of GFR 12. Which ONE of the following is a cause of hypercalcemia: a) Hyperparathyroidism b) Hypoparathyroidism c) Vitamin D deficiency d) Hyperphosphatemia e) Acute pancreatitis 13. In diabetes insipidus which ONE of the following would not be expected to occur: a) Defects in AQP2 water channels b) Defects in V2 receptors c) Decreases in Vasopressin (ADH) levels d) increased urine output e) decreased thirst 14. Relying upon serum (plasma) creatinine alone to estimate GFR in cases of acute kidney injury is inaccurate because: a) b) c) d) e) 15. creatinine is no longer freely filtered by the glomerulus creatinine is secreted by the nephron plasma creatinine levels have not had time to reach a steady state muscle secretes more creatinine following acute kidney injury all of the above are true Which of the following is not used to assess GFR: a) b) c) d) e) Serum creatinine Serum sodium Cystatin C Inulin The MDRD formula Fast forward to the year 2024, “The Wasp” is diagnosed with diabetes. Twenty years later (2044) she has continued to exercise little, eats fast food regularly and has gained 33 pounds. She complains that she now feels fatigued more often than not. Her latest blood test and physical examination reveals that she has a plasma [K+] of 6.9 mM, pH is 7.18, pCO 2 is 33 mm Hg and plasma [HCO3-] is 15 mM. An ECG reveals peaked T waves. 16. Describe The Wasp’s acid base status: a) b) c) d) e) 17. primary respiratory acidosis with compensatory metabolic acidosis primary metabolic acidosis with primary respiratory acidosis primary metabolic acidosis with an underlying respiratory acidosis primary metabolic acidosis with compensatory respiratory alkalosis primary respiratory acidosis with compensatory metabolic alkalosis The most likely cause of the plasma [HCO3-] of 15 mM in “The Wasp” is: a) b) c) d) e) 18. With respect to compensatory changes which one of the following is false: a) b) c) d) e) 19. An increase in pH (alkalosis) increases lung ventilation (respiratory rate) Respiratory compensation in response to pH changes is immediate A decrease in pH (acidosis) stimulates ventilation to drop pCO2 A decrease in pH (acidosis) stimulates HCO3- production An increase in pH (alkalosis) decreases renal HCO3- production If “The Wasp” had emphysema and her pCO2 had been measured at 40 mmHg (along with a pH of 7.21 and HCO3- of 15 mM you could conclude that: a) b) c) d) e) 20. a reduction in GFR increased systemic fixed acid production decreased renal HCO3- production hyperventilation increased intestinal HCO3- losses The lungs have failed to respond to the altered pH The kidneys have not had enough time to compensate for the altered pH There is an excess gain of bicarbonate from the intestine/diet The lungs have increased their respiration rate Too little information to suggest anything One of the most recent advances for treating diabetes is the use of SGLT2 inhibitors. The reason this class of drugs is effective is outlined in which one of the following statements?: a) b) c) d) e) They increase the epithelial Na channel activity in the collecting duct They increase glucose uptake by the intestine They directly improve insulin secretion by the pancreas They inhibit sodium uptake by the collecting duct They inhibit glucose uptake by the proximal tubule