Evolution of Media: From Prehistoric to Information Age
advertisement

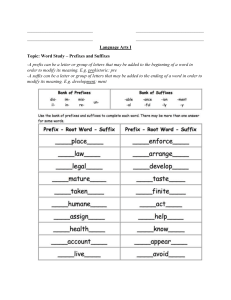
LESSON 2: Student Learning Objectives: • Identify accurately different traditional media and new media starting from Prehistoric Age to Information Age, • Appreciate the importance of knowing the history of media and the people behind its inventions, and • Create an infographic that shows the evolution of media. Media and its Purpose • Media involves communication channels through which news, entertainment, education, data, or promotions are disseminated. • Media is also designed to reach the mass audience or the majority of the public, hence the term mass media. Media and its Purpose • Media involves communication channels through which news, entertainment, education, data, or promotions are disseminated. • Media is also designed to reach the mass audience or the majority of the public, hence the term mass media. Why media Existed? • Media existed to inform the mass public of what is happening in the world. Have you ever wondered? • How media and information became of what they are now? • How people in the ancient days communicate or spread information to one another? Have you ever wondered? • Media and its impact have been around as far back as humans began to interact with different persons and tribes, integrating countries and creating different methods to communicate, express one’s thought, and pass knowledge and information. Ancient People Vs. New Gen People Prehistoric Age (before 1700s) • People discovered fire, developed paper from plants, and forged weapons and tools with stone, bronze, copper and iron. Prehistoric Age (before 1700s) Prehistoric Age (before 1700s) Prehistoric Age (before 1700s) Prehistoric Age (before 1700s) Prehistoric art as Earliest Form of Traditional Media • PETROGLYPHS • PICTOGRAPHS Can be carvings or engravings in rocks or caves Represent words or phrases through symbol. Used to refer to sketches or paintings that usually depict nature, early people’s way of life Prehistoric art as Earliest Form of Traditional Media • CAVE PAINTINGS These are painted drawings on cave walls or ceilings, mainly of prehistoric origin. Prehistoric art as Earliest Form of Traditional Media • CLAY TABLETS These were used as writing medium, specially for writing in cuneiform, throughout the Bronze Age and well into the Iron Age Cuneiform A system of writing used in the ancient Middle East. And was the most widespread and historically significant writing system in the ancient Middle East Prehistoric art as Earliest Form of Traditional Media • PAPYRUS It is a plant and material similar to thick paper that was used in Ancient times as a writing surface. Prehistoric art as Earliest Form of Traditional Media • PETROGLYPS • PICTOGRAPHS (CAVE PAINTINGS) • CLAY TABLETS • PAPYRUS Industrial Age (1700s-1930s) • Associate factories and machines • Starts in 18th century in Great Britain (Economy Development) Industrial Age (1700s-1930s) • People used the power of steam, developed machine tools, established iron production, and the manufacturing of various products. (including books through printing press) Industrial Age (1700s-1930s) • JOHANES GUTTENBERG He created the device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium such as paper or cloth and thereby transferring the ink. Printing Press of Mass Production (19th Century) • Printing Press It is a device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium such as paper or cloth and thereby transferring the ink. NEWSPAPER- The London Gazette (1640) • It is a serial publication containing news about current events, other informative articles about politics, sports, arts, and so on and advertising. It is usually, but not excessively, printed on relatively inexpensive, low-grade paper such as newsprint. TYPEWRITER (1800) • It is a mechanical or electromechanical machine for writing characters similar to those produced by printer’s movable type. • It operates by means of keys that strike a ribbon to transmit ink or carbon impressions onto paper. TYPEWRITER (1800) • CHRISTOPHER LATHAM SHOLES Father of Modern Typewriter The man behind the “QWERTY” typewriter keyboard TELEPHONE (1876) • A system for transmitting messages from a distance along a wire, especially one creating signals by making and breaking an electrical connection. TELEPHONE (1876) • ALEXANDER GRAHAMBEL Known to be the father who created a device for transmitting message from a distance along a wire, especially one creating signals and breaking an electrical connection. Industrial Age (1700s-1930s) • Motion Picture Photography/Projection (1890) • Commercial Motion Pictures (1913) • Motion Picture with Sound (1926) Industrial Age (1700s-1930s) • Presents a series of still images which, when shown on a screen, creates the illusion of moving images due to a certain phenomenon. • This optical illusion causes the audience to perceive continuous motion between separate objects viewed rapidly in succession. Industrial Age (1700s-1930s) • PRINTING PRESS • NEWSPAPER • TYPEWRITER • TELEPHONE • MOTION PICTURES Electronic Age (1930s-1980s) • The invention of the transistor ushered during this time. People harnessed the power of transistors that led to the transistor radio, electronic circuits, and the early computers. Electronic Age (1930s-1980s) • In this Age, long distance communication became more efficient. • The era was dubbed as the “Age of Implosion” TRANSISTOR RADIO (1940s) • It is a small portable receiver that uses transistor-based circuitry. It is a pocket size device that is used mainly for information dissemination, and later on for broadcasting entertainment like music etc. TELEVISION and PERSONAL COMPUTER (1941) OHD and LCD PROJECTORS • It is an optical device that projects an image (or moving images) on to a surface. This creates an image by shining a light through a small transparent lens • OVERHEAD DISPLAY • LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY Electronic Age (1930s-1980s) • TRANSISTOR RADIO • TELEVISION • PERSONAL COMPUTER • OHP,LCD PROJECTORS Information Age (1900s-2000s) • The Internet paved the way for faster communication and the creation of the social network • People advanced the use of microelectronics with the invention of personal computers, mobile devices, and wearable technology • Moreover, voice, image, sound and data are digitalized. We are now living in the Information Age WEB BROWSERS • It is a software application for retrieving, presenting and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. • MOSAIC (1993) • INTERNET EXPLORER (1995) WEB BROWSERS • It is a software application for retrieving, presenting and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. BLOGS • It is a discussion or informal website published on the WWW consisting of discrete, often informal diary-style text entries or post. 1999 1999 2003 SOCIAL NETWORKS • This is an online platform which people use to build social relations with other people who share similar personal or career interest, activities, backgrounds or real life connections. 2002 2003 2004 MICROBLOGS • It is a broadcast medium that exist in the form of blogging. • It differs from a traditional blog and its contents are typically smaller in both actual and aggregated file size. • It allows users to exchange small elements of content such as short sentences, individual images, or video links, which may be the major reason for their popularity. 2006 2007 VIDEO • This is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting and display of moving visual media. 2005 AUGMENTED REALITY • A technology that superimposes a computer-generated image on a user’s view of the real world, thus providing a composite view. VIRTUAL REALITY • The computer-generated simulation of a threedimensional image or environment that can be interacted with in a seemingly real or physical way by a person using special electronic equipment, such as a helmet with a screen inside or gloves fitted with sensors. VIDEO CHAT • A face to face conversation held over the Internet by means of webcams and dedicated software. SEARCH ENGINES • It is a software system that is designed to search for information on the WWW 1996 1995 PORTABLE COMPUTER • It is a computer that comes with a keyboard and display and one which can be easily relocated, or transported, although less convenient compared to a notebook. LAPTOP (1980) • A portable computer, usually battery- powered, small enough to rest on the user’s lap and having a screen that closes over the keyboard like a lid. TABLET (1993) • A tablet, or tablet PC, is a portable computer that uses a touchscreen as its primary input device. • Most tablets are slightly smaller and weigh less than the average laptop. NETBOOK (2008) • A small laptop computer designed primarily for accessing Internet-Based applications SMARTPHONES • A mobile phone that performs many of the functions of a computer, typically having a touchscreen interface, internet access, and an operating system capable of running downloaded applications. WEARABLE TECHNOLOGY • It is a category of technology devices that can be worn by a consumer and often include tracking information related to health and fitness. • Other wearable gadgets includes devices that have small motion sensors to take photos and sync with your mobile devices. Information Age (1900s-2000s) • WEB BROWSERS • SEARCH ENGINES • BLOGS • PORTABLE COMPUTERS • SOCIAL NETWORKS • LAPTOPS • MICROBLOGS • TABLET • VIDEO • NETBOOK • AUGMENTED REALITY • SMARTPHONES • VIRTUAL REALITY • WEARABLE GADGETS • VIDEO CHAT REMEMBER LESSON 2: