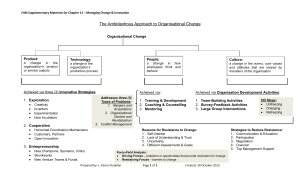
What’s involved in Organisational Culture? LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the meaning, importance, and origins of organisational culture. 2. Discuss cultures of conflict and cultures of inclusion. 3. Identify and discuss how technology and innovation affect organisational culture. 4. Describe how effective organisations manage their culture. WHAT DO WE MEAN BY ORGANISATIONAL CULTURE?# 1-3 LEVELS OF ORGANISATIONAL CULTURE LEVELS OF ORGANISATIONAL CULTURE LEVELS OF CULTURE AT ZAPPOS • Artifacts are at the first level of organisational culture and are the easiest to see. What are some Zappos artifacts you can observe? • Values appear at the next level of organisational culture. You can infer a culture’s values from the behaviour of organisational members. Which values appear in Zappos? • Organisational members will unconsciously behave according to an organisation culture’s assumptions. You also can infer these from observed behaviour. Which assumptions appear at Zappos? FUNCTIONS OF ORGANISATIONAL CULTURE Provides a sense of identity to members and increases their commitment to the organisation Serves as a sense-making device for organisation members Reinforces the values of the organisation Serves as a control mechanism for shaping behaviour How does Zappos demonstrate these functions? DOES CULTURE MATTER? • Culture boosts organisational performance when it is... Strategically relevant Strong Emphasises innovation and change to adapt to a changing environment • Culture and competitive advantage – Creating a culture that supports sharing and helping other employees can have positive performance results. • Strong and weak cultures – Strong cultures are not always better than weak cultures; they must be positive not negative • Culture and unethical conduct – Underlying many organisational problems is a culture that pushes for visible results and individual performance above all else. HOW LEADERS CREATE AND MAINTAIN CULTURE • Varies by industry and national identity/society • Culture is influenced by company founders and leaders Culture is shaped early on then reinforced by philosophy, values, vision, and goals Cultural choices influence company structure, compensation system, customer relations and human resources policies, individual behaviour, and motivation All these items reinforce culture • Culture may need to change due to changes in strategy, technology, or organisational structure • Culture may vary across different areas of the organisation CULTURE IN FOUR LAYERS 10 PARADIGM 11 THE CULTURAL WEB OF AN ORGANISATION 12 CULTURAL WEB ELEMENTS Stories tend to be about heroes, villains mavericks, successes, disasters, how things were. • What core beliefs do the stories reflect? • What stories are commonly told e.g. to newcomers? • How do these stories reflect core assumptions and beliefs? • What norms do the mavericks deviate from? Symbols are objects, events, acts or people that convey, maintain or create meaning over and above their functional purpose. • What objects, people or events do people particularly identify with? • What are these related to in the history? • What aspects of strategy are highlighted in publicity? CULTURAL WEB ELEMENTS What are the power structures? • Where does power reside? • Who makes things happen? • Indicators include: o o o status claim on resources symbols of power What are the organisational structures? • How formal/informal are the organisational structures? • Do structures encourage collaboration or competition? • What types of power structure do they support? CULTURAL WEB ELEMENTS What are the control systems? • What is most closely monitored/controlled? • Is emphasis on reward or punishment? • Are controls rooted in history or current strategies? • Are there many/few controls? What are the routines and rituals? • Which routines are emphasised? • Which are embedded in history? • What behaviour do routines encourage? • What are the key rituals? • What assumptions and core beliefs do they reflect? • What do training program emphasise? • How easy are routines/rituals to change? CULTURAL WEB OF ZAPPOS 16 ZAPPOS’ CULTURAL WEB ELEMENTS ZAPPOS’ CULTURE • What cultural web elements did you identify? • What is the key to success at Zappos? CULTURES FOR MANAGING CONFLICT There are four kinds of cultures of conflict. These vary based on active or passive norms and agreeable or disagreeable norms. Disagreeable Agreeable Active Dominating Collaborative Passive Passive-Aggressive Avoidant EFFECTS OF TECHNOLOGY AND INNOVATION ON CULTURE • Using intranets, social media and the cloud to build and maintain culture – Issue is not just about using the latest technologies but about leveraging the right technologies for creating and maintaining a positive culture – Ways in which intranets influence culture Their scope Their openness to employee feedback and contributions The frequency with which they are updated The number of intranets The use of symbols, stories and ceremonies EFFECTS OF TECHNOLOGY AND INNOVATION ON CULTURE • Building and maintaining culture in the cloud – Harder to reinforce cultural values – Affect employee identification with the organisation • Innovation and culture – Innovation: the process of creating and doing new things that are introduced into the marketplace as products, processes, or services Radical (disruptive) innovation: A major breakthrough that changes or creates whole industries Systems innovation: Creates new functionality by assembling existing parts in new ways Incremental innovation: Continues the technical improvement and extends the applications of radical and systems innovations WAYS TO MANAGE ORGANISATIONAL CULTURE • Take advantage of the existing culture Managers must first be fully aware of the culture’s values and what behaviours or actions those values support • Teach the organisational culture through socialisation Socialisation is the process through which individuals become social beings Organisational socialisation is the process through which employees learn about the firm’s culture and pass their knowledge and understanding on to others CHANGING THE ORGANISATION’S CULTURE • Managing symbols: organisation culture is understood and communicated through the use of stories and other symbolic media • Difficulty of change: culture can be difficult to change when upper management inadvertently reverts to old behaviours • Stability of change: new values and beliefs must be seen as stable and as influential as old ones Changing value systems requires enormous effort because value systems tend to be self-reinforcing MANAGING ORGANISATIONAL CHANGE