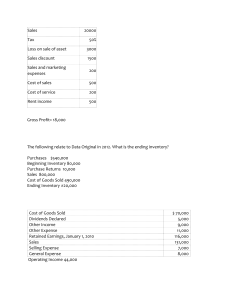
NET INCOME COMPUTATION IS PRESENTED IN THE INCOME STATEMENT OR THE STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE. Start 4/11/22 Another Illustration A company earned a total revenue of 975,000 and the expenses incurred is 587,900. What is the Net Income(NI)? Net Income = Revenue – Expenses Note: Revenue (Sales or Service income) NI = R E NI = 975,000 587,900 NI = P 387,100 result of operation of the business 1. THE DOUBLE ENTRY SYSTEM AND THE RULES OF DEBIT AND CREDIT The Double-Entry System This means that the business has dual effect to the account as it has effect on both the debit side and credit side. The account debited are entered in the left side and the account credited are entered in the right side. The Normal Balances of an Account The increase of an assets is recorded in the left side (Dr. side) and decrease in recorded in the right side (Cr. side). While, it is reversed for the liabilities and owner’s equity. Sample Journal Entry ( Debit & Credit) : BALANCES Accounts Assets ( Ex. Cash) Normal Dr. Increases Dr. Decreases Cr. Contra Assets Cr. Cr. Dr. Liabilities Cr. Cr. Dr. Owner’s Equity Cr. Cr. Dr. Owner’s Withdrawals Dr. Dr. Cr. Income/Gain/Revenue Cr. Cr. Dr. Expenses/Losses Dr. Dr. Cr. ACCOUNTING EVENTS AND TRANSACTIONS Accounting events are those economic occurrence that causes changes to the elements of financial statements. Transactions are particular event that involving transfer of something of value between two entities. BALANACE SHEET OR STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITION The Account Titles Assets are classified into two: current assets and non-current assets. Per revised PAS 1 (Philippine Accounting Standards No. 1). The entity shall classify assets as current when: 1. It is expected to realize the asset, or intends to sell or consume it, in its normal operating cycle;( 12 months or one year) 2. It holds the assets for the purpose of trading; (inventories) 3. It expects to realize the assets within twelve months after the reporting period; or 4. The asset is a cash or a cash equivalent (as defined in PAS no. 7) unless the asset is restricted from being exchanged or used to settle a liability for at least twelve months after the reporting period. Those assets that are not classified as current shall be recognized as non-current assets. Operating cycle is the time between the acquisitions of the assets for processing and their realization in cash or cash equivalents. The entity’s normal operating cycle is considered to be 12 months if not clearly identified. Current Assets Cash. This includes coins, currency, checks, money orders, bank deposits and drafts. That are used as medium of exchange that a bank will accept for deposits at face value. Cash Equivalents. An account used for short-term, highly, liquid investments that are readily convertible to known amount of cash that are subject to an insignificant risks of change in values. ( Marketable Securities-share of stocks/common stock) Petty Cash Fund. Money set aside for petty or small amount of expenses. Notes Receivables. The account used to account written pledged from customer that will pay the business at a fixed amount of money at a certain date. (issuance of check) Accounts Receivables. These are claims against customers arising from sale of service or goods on credit. Estimated Uncollectible Accounts (Allowance for Bad Debts) . A contra asset account that is to account for the provision of possible losses from uncollected accounts. This is presented as reduction to the accounts receivable accounts to get the net realizable value of the accounts receivables. Balance Sheet: Accounts Receivable Less: Estimated Uncollectible Accounts P2,000 500 P1,500 Advances to Employees. An account used to track the collectibles from employees for allowing them to make cash advances that are deductible to the payroll or the salaries and wages. Inventories. These are assets that are held for sale in the ordinary course of business, still in the process of production for such sale, or in the forms of materials or supplies to be consumed in the production of goods or rendering service. Merchandise Inventory, end. This refers to the inventory that are still unsold as at the end of the period is determine by physical counting. Supplies Inventory or Unused Supplies. Refers to the cost of supplies and stationaries still unused as of the end of the period. Prepaid Expenses. These are expenses paid for by the business in advance. These accounts are arranged according to its liquidity (its readiness to be converted into cash) in the balance sheet. v Accrued income/Accrued Revenue is a current asset and would sit on the balance sheet (the Statement of Financial Position) under trade receivables Noncurrent Assets ( Fixed Assets) Property, Plant and Equipment. The account use for tangible assets that are held by an enterprise for use in supply or production of goods or services, for rental to others, or for administrative purposes that are to be used for more than one (1) period. Land - an account title for the site where the building used as office or store is constructed. Building - account title for a finished construction owned by the business where operations and transactions took place. Equipment includes calculators, typewriters, adding machines, computers, steel filing cabinets and the like. If these are used in the office, the account title is Office Equipment and if used in the store, Store Equipment. Trucks, jeeps, vans, automobiles and other kinds of motor vehicles are used exclusively for delivering goods, the account title is Delivery Equipment. Accumulated Depreciation. A contra asset account used to accumulate all the depreciation charges. Balance Sheet: Building P50,000 Less: Accumulated Depreciation 10,000 P40,000 Intangible Assets. An asset that has no physical substance, but identifiable and nonmonetary assets held for use in the production or supply of goods and services, for rental to others or for administrative purpose. Trademark, Copyrights. End 4/11/11-12 end end 4/11/2022 Liabilities are classified into two: current liabilities and non-current liabilities. Per revised PAS 1 (Philippine Accounting Standards No. 1). The entity shall classify liability as current when: 1. It is expected to settle the liability in its normal operating cycle; 2. It holds the liability primarily for the purpose of trading; 3. It liability is due to be settled within twelve months after the reporting period; or 4. The entity does not have an unconditional right to defer settlement of the liability for at least twelve months after the reporting period. Those liabilities that are not classified as current shall be recognized as non-current liabilities. Current Liabilities ( Credit side ) Accounts Payable. An account used for obligation that are lend by accepting goods from suppliers and the company agrees to pay the amount in the future. Notes Payable (Short-Term). An account of obligation that are used for amount lend from the debtors in exchange of a promissory note that is payable within one year. Accrued Liabilities. This account is used when there are unpaid expenses incurred by the company. (Accrued expenses) Unearned Income. This is the account used when payment is receiving before providing services or before the products or goods are delivered. Current Portion of Long-term Debt. This are portion of the mortgage notes, bonds and other long-term obligations that are payable within 1 year after the reporting period or the balance sheet date. Example: For example, if a company owes a total of $100,000, and $20,000 of it is due and must be paid off in the current year, it records $80,000 as long-term debt and $20,000 as CPLTD. Non-current liabilities Notes Payable (Long -Term). An account of obligation that are used for amount lend from the debtors in exchange of a promissory note that is payable for more than 1 year. ( Check issuance ) Mortgage payables. This is to account a long-term debt of the entity that has pledged certain assets as security to the creditor. If the loan is not paid the creditor will foreclose the mortgage asset to be sold to enable the entity to settle the claim. Owner’s Equity ( Capital) Capital. From Latin word “Capitalis”, means “property”. This is the investment account used to record original and additional investment of the owner of the business entity. Increase by the amount of profit earned during the year and decrease with a loss. Journal Entry 4/12 Machines & Equipment P100,000 ( Asset –debit) Bebar, Capital P100,000 ( Credit Side – normal ) Invest M & E # 4/12 Cash P 20,000 ( Asset –debit) Bebar Capital P20,000 (credit side – normal) Withdrawals. When the owner of a business entity withdraws cash or other assets rather than directly reducing the owner’s equity account. Bebar’s withdrawal …. P5,000 Cash ………………………….. P5,000 Income Summary. The temporary account (nominal account ) used to close the income and expenses at the end of the accounting period. This accounts shows the profit if the balance is credit but if the balance of this account is debit then it signifies loss. INCOME STATEMENT OR STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL PERFROMANCE Income ( Credit Account - credit side normal position ) Sales. This are revenues that are earned as a result of selling merchandise. Sales Returns & Allowances ( to be deducted in the sales ) - this is a reduction from sales account for goods that were sold but were returned by the buyer for bad order or not conforming with the order. This is a reduction from sales account. Sales Discounts ( to be deducted in the sales ) - refers to the discount given to the buyers for early payment of merchandise sold on account or collection within the discount terms. This is also a reduction from sales account. Example: Credit term - 2/10, n/30 Service Income - In general, this is the account title used for all types of income derived from rendering of services. Sometimes the account title used is Service Revenue. Other specific income account titles used are: Professional Income - the account title generally used by professionals for income earned from the practice of their profession or may be specified as Accounting or Auditing Fees Income for Accountants, Legal Fees Income for Lawyers, Dental Fees Income for Dentists, Medical Fees Income for Doctors, etc. Rental Income - for income earned on buildings, space or other properties owned and rented out by the business as the main line of its activity. Interest Income - for income received by the business arising from an amount of money borrowed by a customer and usually covered by a promissory note. This is typical in lending institutions. Miscellaneous Income - for income earned by the business which is not the main line of its activity and could not be clearly classified. COST AND EXPENSES Cost Cost of Sales. The cost of the sold goods and products as incurred from the purchase or produce of product during the period. Also known Cost of Goods Sold. Example: How to compute the Cost of Sales Beginning Inventory (ending in Dec 31, 2021) Jan 1,2022 Purchases……………………………………………. P5,000 Add: Freight In ………………………………………. 400 Total Purchases ………………………………………. P 5,400 Less : Purchase Return & allowances ………… P300 Purchase Discount (10%) ………………………... 500 800 Total Goods Available for Sale (TGAS) Less: Merchandise ending Inventory (Dec, 31, 2022) ……………… Cost of Sales or Cost of Goods Sold P 2,000 4,600 ( Net purchases) P6,600 1,000 P5,600 ====== Freight In - refers to transportation cost incurred in buying goods. Under periodic system, this is not an expense on the part of the business buyer but "cost" which is an adjunct account to purchases while under perpetual inventory system, it is treated as merchandise inventory. Purchases - the account title for "merchandise" purchased under the periodic Inventory system. Under perpetual inventory system, the account title is "merchandise inventory". Purchase Returns & Allowances - under periodic inventory system, this refers to the cost of merchandise that were purchased but later returned to the suppliers for bad order or does not conform with the specifications. This is a reduction from purchases account, under perpetual inventory system it is a reduction to merchandise inventory account. Purchase Discounts - refers to discount availed for early payment of merchandise under Periodic Inventory System. This is also a reduction from purchased purchases account. Under perpetual inventory system, it is also a reduction from merchandise inventory account. Merchandise Inventory, beginning - the merchandise inventory at the beginning of the period which is usually dated Jan. 1 is an asset but will turn into "cost" when such period ended. Expenses refer to decreases in economic benefits during the accounting period in the form of outflows or depletion of assets or incurrence of liabilities that result in decrease in equity, other than those relating to distribution to equity participants. Losses represent other items that meet the definition of expense and may, or may not, arise in the cause of the ordinary activities of an enterprise. Losses represent decreases in economic benefits and as Such are no different in nature from other expenses. Hence, they are not regarded as constituting a separate element. Salaries and Wages. The payments to the labor force as a result of employee-employer relationship Utilities Expense. Expenses related to the use of telecommunications facilities, consumption of electricity, fuel and water. Rent Expense. The amount of used supplies in the conduct of business operation. Insurance Expense. The portion of premiums paid on insurance coverage that has already expired. Depreciation Expense. The portion of the costs of tangible assets allocated or charged as expense during an accounting period. 1/1/2019 P100,000 Asset = P10,000 per year depreciation 10 years life ( useful life) as of 1/1/2022 accumulated depreciation***(Contra asset Account) 3 years’ x P10,000 = P30,000 (1/1/2019- 12/31/2021) value P100,000 – P30,000*** = P70,000 (Net Value) Uncollectible Accounts Expense (Bad debts) . An amount of receivables estimated to be doubtful of collection and charge as an expense during an accounting period. Interest Expense. An expense related to the use of borrowed funds. Freight Out - refers to transportation expenses of merchandise sold. Supplies Expense - this represents cost of supplies that were used and consumed that bears specific titles as office supplies expense, store supplies expense, shop supplies expense, etc. Repairs and Maintenance - for expenses incurred in repairing or servicing the buildings, machineries, vehicles, equipment, etc., which are owned by the business. Uncollectible Accounts - for the anticipated loss that the business may incur arising from uncollectible accounts. (Bad debts) Depreciation Expense - for the portion of the cost of property and equipment or fixed assets that has expired based on rational and systematic allocation procedure. Taxes and Licenses - for the amount paid for business permits, licenses and other government dues except the Income Tax paid which is not allowable by law as a deduction. Insurance Expense - account title for the expired portion of the insurance premium paid. Miscellaneous Expense- any amount paid for not significant expense to warrant a particular classification.