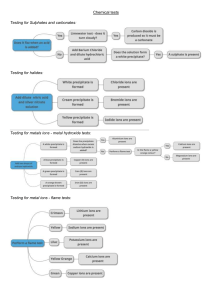
* Metals Experimental techniques Non-metals ·Measurement Time -> always cations, are always arious Atoms, o -> - -> Elements & Physical clock Temperature Mass are Mass Compounds Chemical & change conserved is ↳apparentchange Hermometer scaly one Volume->burettes, pipetty, measuring cylinders ~ all chemical mass usually in in ofthe products energy change:released identify -> relection -> ·Structure whatan unknown liquid factor:distance substance distance -> solventwill always is made of travel Separation -> -> & solution impure Salute solids:use Solms filtration evaporation surroundings -> warmer colder means left non-metato ↓ low melting conductors point, brittle, dull, conductors poor Ions (mass number Tonic and bonds - ·Formation number) latomic number -nucleotnumber & physical & point -proton & surroundings Atomic theory purification & melting good further by middle, & ↓ high · · metals right gas a - matter separated - solvatmoved a mixture: - moved of because occurs is reactants or absorbed ·Paper Chromatography reactions of ions compounds:metal Lionic of non-metal [notmolecules, butions] -formed by -> impure liquids: use differentboiling gain loss or ofelections points · Metals transfer can than more one election a to non-metal distitation oxidation:loses - => - · reduction: gains high melting electrostatic - => electrons Properties - fractional electrons forces hard cystals & boiling between ions pointbecause ionic = of bonding latice structure & high mp => distillation strong attraction between oppositely charged - - - dissobes insulator in when water-> water solid conductor when =3 forces forms strong electrostatic force preventfrom moving liquid= > Forces broken down, so ions with ions able to move. Molecules . Formation: - - - · election sharing metals (group 8 group or between non-metals I, I,#) do O because don't covalentbands form not unreactive Properties: -low - · and Covalent bonds mp &bp=> weal intermolecular forces doesn'tconductelectricity:) Strong bard, Ioniz vs. non-volatile volatility (high my &bp) volatie insoluble soluble solubility conductivity only form le fre carry to in water law=non-electrolyres when dissolved or motte charge) I do can'tc arry Simple strong ious, notcontain an Hydrogen some do Hydrogn form ins dissolved) wher wrabt) learn (all ious) to oxic:OH So electric currents Stoichometry % Radicals easily covalent ioi2 intermolecular can'tm ove Covalent property electrical elections so Sulfate:SOY HCO,"Phosphate:POY carbonate: Vitrale.Noe Copper Sulfate: CuSOn Potassium nitrate:KNOS Carbonate:20? Calcium hydroxide: (a(OH)2 weat I Electricity Chemistr and ·Electrolytes non-electrolytes and thatc a n conductelectricity ↳electrolytes: compounds Li will light - in ifsolution electric L ciruit: used to by elections moving) lions moving circuits of and wire electrolytes between distinguish and electrolytes non Conditions: electrode L so inert is to negative free thata re ions (molten move to dissolved) or electrolyte itwon'treactwith positive anode connected L terminal, white cathode to terminal Process: I · bulb electrolyse=complete an caused currents I contains · is up electrodes · beater in neg ions to move Le travel Le reaching through - the the anode eathode Motten Lead(II) and anode give up circuit -> cathode - by taken are e positive up ions (4b Brz) Bromide neg electrode -> lead cathode, moves to -"bromide moves to anode -electrodes - Products: - usually made silvery lead deposits - brown bromide -Anode:Pb - · Cathode:2 Sodium ofCarbon Brite) (1) - vapour inert of dish anode near 2e --> ->Brz(g) 4b(e); half equation 2e- + Chloride solution: disassociation:reversible form Laqueous HY and or because ions molecules can break vice versa always include OH discharged, a code: chlorine solutions cathode:Sodium altealing a reaction water up to - bottom at + Cathode:lydoga molecule, - -> up (Nat, H), only Nat because remains the loss surplus ofhydroxide Ht ions are ian, butsolution ofhydrogen ions ious turns leaves 2nd anode:Chlorid (C) and - OH), discharged depending either solution on way of measuring ando/exo: ↳ be could ious If concentration. dilute bubbling - or effervescence products ofelectrolysis is hydrogen are and oxygen ~ colorless ae ifdilute, hydroxide solution / or chlorine colorless gas ↓ becomes increasingly alkaline pale green gas sodium as formed. is OIL RIG - and ↓ L - electrode, ateach seem oxidation => loss is of reduction e, is gain Enthalpy by o Dilute · energy Cathode->reductions - Sulfuric Anode-> - - · Ions sulfuric H*, SO, 2 OH mode: -> H & 0 gas - SO, OH, acid: discharged -= discharged, O gas cathode at vions discharge e) activation es tions (Ky/mol) equation product exo:reactant - (DH) AH and profiles an reactions en product es H = is -ve DH is = the ofenergy required mim amount = formed:9OH=2H20+0z the 2xotemic erdotomic ↓ & non-metal & of -endo:reactanten 2H +2e He gas formed: H chemical in end atthe electrolysis products: metal - - - dilute shown - ·Energy cathode:It Predicting - in Oxidation Acid -effervesence:Product:colorless - Change -heat electrons form acceptelectrons molecules & ↓ atanode form (It2, Bril metallic atoms (C, Al) or Igas. Chemical · energetics Energy changes - - exothermic: is chemical reactions ↑ temp & energy transfered surroundings Lex: combustion, respiration, neutralization) to energy absorbed:(2x: edottormic: 1st way of measuring e n photosynthesis & Hermal decompositions Where exo/ende: - does en come erdotremia from? et0 - Overall - - because exo nor energy released - than absorbed " Alkane: Methane I C Hu => => C2As Propane =S C3 H8 Petane Hexane % absorbed to brate bonds Len form absorbed Ethane Butane Exo:e n Endo:e r bonds to if notused bonds) absorbed break to (in up excess WhatCan · to break bonds released es Rare thatexact quantities used, ifused up:limiting are Rate Change (of -concentration reactant, ) ofReaction solution) a Cy Ho => C5 H12 => 26 => Hin Rate ofreaction: · Collision theory: energy chemical involved bonds Leffective reacting ~the activation bigger the reaction Lif be will acten => ·Monitoring the rate of low is less collisions ata break bonds to energy the stower the energy, particular temperature -> more otherwise, - another one collision:enough to particles the the break enough justbounce off will particles in be must effective collision, if - act e r is hgh - temperature ·4 Kinetic effective reaction: · 2. Efforescence plunger 2. 3. starts Measure Show flass in ocurs C0219) as poduced is T collision/s = of product size moving. gas volume change reaction syringe every with time on in 10s - in amount same particle a- e shorter time a (surface area) catalyst. a graph erzyme- · biologicalcate X collision treory: -> sufficientenergy to overcome activation RedoxReactions ·Oxydation, Reduction / 1. Measure as soon mass↓ Draw 2. 3. as as of flash mass inserted plug CO2 (y) escapes graph Reaction rate to show as ↓ & adding O2 contents an 10 ses, every t removing -() changes - overtime dependentvariable:volume -control between variable:(not allowed of CO2 changel to marble & hydrochloric proceeds acid (time) (charged by independentvariable) trup + ↓ reducede Oxidation ↳ how independentvariable:reaction adding elementor molecule results · - t both removing by flash. from the reaction Redox and ↓ W in · · · a iron I Oz ! -EOC) +weee States many electrons an atom loses or gains when it's chemical bond (II) iron oxide (Fe0) => oxidation (III) orde (Feg0z) Oxygen has oxidation stale - => of state 11 - -2 of th 11 + 3 take i - of no & charge on it, reverse of ion so 3-has oxidation. What Acids, Bases and solution Salts dissolved any substance - Acid in were neine Lindicators: litinus X universal neutral:↑ range pH = ·Whatare ↳ ↳ by typical Ca2 (concentration of Hions) acids substance reactions scate that -water replaceable Hatoms contain chemical in reactions:Acid + Acid metal => Carbonate + Acid base + AA, salt +A(g) => -> saff salt CO2 + + sulfates shape ↓ - I + with Alkali alkali-liquid base Salt+H Salt-HeOr Salt+Heo A -> that - reacts I z metals carbonate bases Acids #20 base substance * AC, I+M AB, Neutralization - Cropper GeSOy crystalization:responsible for contain water:anhydrous. Salt+H20 · Acid formul SOG = Heir ↓ +H20 = + + soluble salts: alkali H20 salt anion + not Making · metal atoms do - Phosphate (4On- > = cation - Suffule (SOn2 => H3PO, (NOz- Nitrate => H2SOn indicator:-In (C1-) Chloride -> HNOz acidic/altaline/neutral ↳ atoas Salts Hil water I thatreplace =metal atoms -3 oAqueous Safts: are 202 describes of alkalis Atkalis + water reactions = -H(ag), but bases and PH- = HCE lag) HNOz He SOn · H POy Making 1. · Acidityin if - - two soil: acidic -> by quickline - 2. + quicktimet CaO(s) - He (e) -> CaCOH)2 pH of stakedstine soil tested by:soil + distilted to pHfound = in + chart. zino Oxide + carbonate + - 11 - not 9) copper(I) b) carbonatet-11 copper) /D oxide dilute + react warmed -1.--> to rea beaut hydrochoic - - Identification ofions indicatorse) Paper Identifying -solids Metal Ions flame = and acid series a "feated - IsS * quickline - Zinc acid sufferic + a) CaCOs(s) -> (a0(s) Welg) limestone Zinc dilute b) neutralize Salls gases (Cations) from: tests Inichrome wire dipped solid compound, acid, then blue Bunsen flame. The into flame identifies into concentrated metal ion color in and is the hydrochloric then seen a into in compound the Lit - Nat x 0 orange = + bilac = G= - I brightred = green blue solutions:dissolve (B /(2) royal pale in water & hydroxide/ammonia with Cu21aq) 201 -TagPPP, anCOHS2 insoluble + CW (Ca2t) remains IW (In2+) dissolved IG (Feat) inscluble IR (Fest) mix Ca(ag) 20H-lag) + insoluble [Fe3+ag) blue a -> solution I Culor(s) 30H -lag) -> + FeCOH," blue alkaline = red Identifying Anions:(solids and acidic = solutions) A Only applies to carbonates I W2 calcium carbonate. cloudiness calcium - Diture 1. hydrochloric gass produced is mithy, the Acid 2HCe is solid acid contains Na,CO2 (s) + CACe(aq) 2nC037s) + the solid, added passed through a to limewater. If solid carbonate water Salt Carbonate (aq) is carbon diaide 2NaCe(aq) H20(2) +CO2 (g) In <ty(aq) He0 (e) +002(g) -> -> + + - The limewater with cloudiness Ife dissapears:2a (0, is continues (s) is caused by insoluble pass though, to changed to soluble hydrogen carbonate, (a(H(03)2 (aq) Chlorine:the Ammonia:the gaz only is basic Periodic Table. acidic, gas butalso a bleaching agent Group Air Imetals: /Oxyge burn => · easily Li- red, 2 metal float => Na &R heat of Orange, of gay produced & carbon monoxide lilac forms · it so given off & which suffer Complands contain rapidly around combustion incomplete of hydrocarbors -> suffer dioxide-burning fossil fuel · the metal, melts reaction sphere, bubbly a At = surface, moving on -> · 2 metals P 02 + => Water viguously Nat ofair flames colored & Pollutants of nitrogen-burning fesil fuel oxides metal dissapers K hydrogen -> got solution resulting => => Chlorine easily burning metals form white solid, a 2 metal Group Cl2 + => the metal halogens bleach chloride. 2 mefalct(s) -> dissolve & Metalz H20 (1 ↳ Metals => -> Hmetal (ag) yellow, Br=Sorange, Jodie haloges fo 2 Metal 3C2 -> => > form - Cl2 a solution of 2 Na Metal + => (ag) a -> <Metal C1, (s) 1. 2. testfor Ifliquid blue 2 NaCl Metal z + as *anhyotruos hydrated [CuSOa(s) 3 Also be used copper using (11) (II) sulfate sulfate He0 (2) anhycos CoCl2 (s) 6He0 + copper -> from whiteto forms. -> CuSO cobalt 4. 5 HeO (11) Chloride CoCly. 6He0 mixed stainly & reaching other with oiling/greesing ion: metaly to produce allage seach s steel Fuels Cracking the cil atkes solid water, powder will turn 5 + alloying: loxygen from iron is I Proper water contains 2. as · add testfor water preventwater salt & Water Chemical 1. acid marble chips form of in Methods of preventing rusting brown salts + Displacement I metal O + hydrochloric dilute of calcium carbonate => + Reaction 1 forming water reactwith solutions => · to oElements: Water=> Air (g) + the in react He chlorire (aq) 2 metal OH => + => aflatore is 2 metal 2 H20 burns fractions belongs -> ICracking much I to more a family of tydocurbar reactive than decame (alkanes called saturated - by drocarbons linked by only that contain -> single covalent bender carbon and hyotoga unsaturated atoms contain Alhane's& Athenes ↑ doesn'treactwith bromine - one or more carbarts-carbon hydrocarbon e double bads -> reactwith bomire and bromine loses colos & E ** / = - u r . - I - M - - = ↑ ⑧ i - - . - = a - - = - I n - E 3 - wi &0 ~ I Ex E 3 3 . == - = I ↑ - I > - - ↑ e = ~ - 1 : W oi & & e - i ↑ M -- - - ↑ = · - m n n / ~ - ↑ ↑-↑ - ↑ ·↓ ↑ - " ↑ P- M - ↑ f - & & & war Ifmry j ↑ M > - > ↑ - M X - > - ↑ n > ↑ = E - E I M - - - - · D - to Q - i . · i f - - ⑬ - i = . S - - u 8 E ⑳ - - ↳ - - ⑳ E = ~↑ ↑ ↑ A - -E - = ~ 1 ↑ o = " - E I · ! A · s I M is u / E = I E8 o M - - I ** - - ↑ - d i I ↑ ~ II ↑ · S - & · - = - E E-⑧ - mi i - 5 - = W - A ~ d~ - = = - we I r =· f -r & A E oo -> - E s ↳ · : ⑦ I I - i - =>19/40(D) 62145/20 temperature ~improving for hychogen powder aqueous ·magnesium ↳ time to rise variables o o o to resistance "resistance it is as more Try solution. Catalase measuring cylinder for 3 2. surface: to (What results to anomalous is wear goggles size ofdisk & result.] hydrogen provide of shorter = - intruder gloves safety length" testthatby comparing has a ratio oflength density greater several taking more water, saltsample into ruter to testtube depth measure thin ensure ruter of and then into testt ube in the results is me & repeate rinsed testtube nextt o find to concentration solution with next plotgraph table wire table results with all solutions Sulfuric Hy SOG Acid Nitric Heid NHO3 Hydrochloric Acid HC1 Acids: compounds & Conclusion & depth en cylinder · measuring cylinder water in the test? any thatc a n fitinside measuring results Record & take readings record use differentlengths of at for differentvalues resistance to than readings · Pour Processing 1. ↑ concentration reach dist -Accuracy: 2. magnesium powder solution: time concentration, to process resultsby 2. Use 1. the reactive Method: 1. - solidtoms on p.d/current "saltsolution - solution, = proportional ↳ · to constant:temperature, keep any spotanomalous repeated be may investigating hydrogen peroxide hazard · and pops blue-colorless = copper controlled more surface the experiments · hydrogen peroxide between to displaces acids result positive a it is as cylinder solution:hydrogen peoside for measuring relationship which to sulfate apper + change:magnesium ·aparatus · lighted splint, is of measuring itdoesn'treactwith acid, because coppert instead by using pipette measurement test a · hydrochloric when doesn'tchange · ofX atoms thataortain hydrogen 62/M5/20 12/40(G) => properly count age o cutting · reduce o riste cuto n stain stops exactly surface, away from fingers solid burette -> studentknows calculate dilute acid & aqueous block toppler ·"distance Apparatus limits of experimental o · Accuracy: to the distance starting & enter Conclusion: o · · position of ball ball along travelled suitable ·repeate each range when <& by & of heights releasing ang straight line though is itis > for measuring & constant origin same ball the horizontal height and ramp beach-what I to suitable puti n graph/table ball plotgraph of heights of slope distance = each experimentbecause in to each other chloride solution insoluble vary heightoftop of slope force applied no closestvolumes heightoframp pop"- plan & ball Measurements: + the accuracy method: -ramp constant:o of sodium silver nitrate not 3 aster over) travelled proportional & itchanger choose reaction identical are (tips ~ Variables complete when for complete for the angle Whatis is reaction average nitric results · clarify a constant where not may => -> ·to · stain + just2mm to pippette ofcetery type of type & range of heights againstdistance travelled difficult white precipitate find to %o I the exactpointatwhich the 61/M5/20 changes cube · · safety · · hydrochloric dilute an of acid is acid gloves Wear for complete the notneutral were others white sodium aqueous + hydroxide because less used precipitate powder neutralization = itis diffuser acid as goggles & because reactions concentrated more of lightreflection ~improve results o => acidic to as chloride they don't go endpoint orange at = chloride sodium = the reaction in # & o acid volumes pHchanges because red color to hazard ·choose (E) 1/40 > = improve accuracy of "Water Method value => will travel waves diff filt 0 Variables: same. method - I a Results:travel time of Conclusion:1 ofwave for look 2. pattern back around & darkroom & bright light to find forth smallest of incidence where no (20cm, find depth to stop watch aug producing of speed (range depth water depthof a use & environment source waves graph & wave values repeate &arg, diff depths ofwater" in with He0 tak of water minimum speeds repeats o by refraction lightsource carefully more at Apparatus: & & of 15cm (20) and water & time A speed in ↑ depth as 63/45/2) 19/40(D) = · o o o when predicting ifacids stirring · some o pH o time measuring for time are allow gas value indicator solutions because:range, innaturate ↓ thoroughly of mass on amounts ofNato Measuerrate:tenp decrease, Constant:volume Processing:avg ·any & & rep masses concentration of graph + & similar temps (the increases same) mixed some with whole #, only NaS2 nitric + escape before distinguishing bung is placed between colors as corrosive acid. pulistyrene up Apparatus:thermometer, measuring cylinder, D &4:diff between-e-, same the stays acidic more coftected because be not temp depends pH, because -> be to ↓, solution:between >↓ produced may consider:time patterns, to acid & of repeate NaCHup 20 to x5 g acid pattern improvementofcalculating efficiency in temp as t in tump- mass insulated beaker. & goggles in is conical difficult. flash lighti s refracted and mL of in gas Li R Na Y B a L zW rol CG gas LiR IG IR Chloride:dilate Suffare: Nitrate: dfte NOH Nacid/Sn -> All acid/BC sol acid /At He lighted Of glaring splint lnewal CO2 Niy sole splint liking => precipitate /gas/litmus) pop relights flame + + : roty a i -> powder precipitate smell Metals & ble positive, are Non-metals are Electrolig ((Br) Lead Browide Sodium Diet X A(Pb) Chloride Sulfuric - I Acid 2 (Na) aon negative Lik NaY he Ch