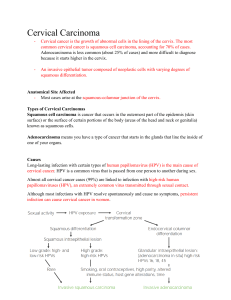
CERVICAL CANCER PRESENTER: Dr ARCHANA K L INTRODUCTION CERVIX is the lower part of womb, it connects uterus and vagina. cervix The cervix is a tubular structure. It is composed of stromal tissue which is lined by squamous epithelium in the vagina (ectocervix) and columnar epithelium within the cervical canal (endocervix). The meeting of the two types of the epithelium is called squamocolumnar junction (SCJ) and this is usually at the ectocervix. The squamocolumnar junction is a dynamic point. In children it lies at the ectocervix that is just at the external os. At puberty and during pregnancy it extends outwards as the cervix enlarges and in adult life it returns to the ectocervix through the process of metaplasia Transformation zone: This region of the cervix where the columnar epithelium has been replaced and/or is being replaced by the new metaplastic squamous epithelium It corresponds to the area of cervix bound by the original squamocolumnar junction at the distal end and proximally by the furthest extent that squamous metaplasia known as new squamocolumnar junction It is formed at puberty. Only in 4% of cases present at birth. The transformation zone TZ is the site where premalignancy and malignancy develop. Phases of Cancer Development Healthy cells dysplasia Carcinoma in situ Distant metasatases Regional lymph node involvement Localized invasive cancer EPIDEMIOLOGY Cervical cancer significant cause of morbidity and mortality among women globally, is the second most common cancer(after breast cancer) 80% of cervical cancer occur in developing countries… where cervical cancer is the 2nd most cancer in women In that 2/3rd of cervical cancer diagnosed at an advanced stage with a poor prognosis for survival. INCEDENCE CURRENT DATA Indicates 50% decrease in both incidence and mortality since 1947(3-4% per year) PERIODIC CANCER SCREENING EARLY DETECTION AND TREATMENT DOWNSTAGING OF THE DISEASE Risk factors for cervical cancer Human papilloma virus infection Being sexually active at a young age Having many sexual partner MULTIPARITY Younge age at the first full term pregnancy Weakened immune system(HIV positive, transplant patient) Smoking cigarettes Exposure of DES in mother’s womb Symptoms of Cervical Cancer Irregular vaginal bleeding(vaginal bleeding during and after intercourse) Foul smelling vaginal discharge Abnormal vaginal discharge Post menopausal bleeding Pain with sexual activity Pelvic pain LACUNAE Lack of organised screening Programme in developing countries.. Accuracy of screening tests in developing countries range in sensitivity and specificity TEST SENSITIVITY SPECIFICITY Cytology 31-78% 91-99% HPV testing 61-90% 62-94% VIA 50-96% 44-97% VILI 44-93% 75-85% IDEAL METHOD OF CERVICAL SCREENING IN LOW RESOURCE SETTINGS TEST SHOULD HAVE o SENSITIVITY o AFFORDABILITY o FEASIBILITY o MAXIMUM COVERAGE VIA –BEST TEST.. Screening protocol for Cervical Cancer Assess likelihood Abnormal vaginal bleeding (i.e post-coital, between menstrual periods, post menopause) Foul-smelling discharge Pain during vaginal intercourse Are the above symptoms associated with abdominal mass, low back or abdominal pain No Ye s Clinical detected cervical growth or ulceration No Follow up Ye s Refer immediately Requirements for VIA TESTING Examination Gloves Speculum Acetic acid Ring lens system Cotton swabs VIA Reporting forms Procedure for testing Woman should lie down on her back with legs folded (lithotomy position not required) Insert speculum gently and expose the cervix Note any abnormal discharge, bleeding or growth in the cervix Apply adequate amount of acetic acid to the cervix using cotton swabs Wait for 1 minute to note the changes Identify the squamocolumnar junction as the line joining the pink smooth squamous epithelium with red velvet like columnar epithelium Look for aceto-white patches All the aceto-white patches are not considered positive If there are no acetowhite patches in the ectocervix, then the test is negative If there is a aceto-white patch, its density, margin and relationship to the SCJ should be noted Procedure should be explained to woman CERVIX-NORMAL & ACETO WHITENING INTERPRETATION 0F VIA RESULT VIA Negative or Normal VIA Positive Supicious of invasive cancer VIA NEGATIVE OR NORMAL Diagnosis of cin: I. Cytologic screening Originally the “Pap” smear was introduced by Papanicolou, where cell removed from the cervix using a wooden spatula and placed on glass slide and fixed. This was then examined by a cytologist for the immature squamous cells sheds from the area of the CIN. Now Pap smear is superseded by liquid based cytology. Cervical smear is taken using plastic spatula, then it is rinsed in a liquid media. Cells are separated by centrifugation, thin layer smear are made. It avoids the risk of false postive, false negatie or unsatisfactory smear. Normal cervical cell has small nuclei that is flattened and pyknotic but abnormal cell has large nuclei, cytological atypia and high N/C Colposcopy: Colposcopy is the outpatient examination of the magnified cervix using a light source. It is used for both diagnosis and treatment. After inserting a speculum the cervix is examined using Binocular operative microscope under magnification (5-20 time). Colposcopy 5% acetic acid is applied, as it causes nucleoproteins within the cells to coagulate. Therefore areas of increased cell turnover, for example CIN will appear white. An abnormal smear can show cells in different degree of maturity (dyskaryosis) and is divided into: Mild dyskaryosis and borderline changes (low grade) Moderate and severe dyskaryosis (high grade) Abnormal smears act as a mean of referring the patient to the colposcopic clinic for further assessment. colposcopy Schiller’s test: by application of iodine, areas of CIN lack the presence of intracellular glycogen and therefore are stain yellow as opposed to normal which stain brown when iodine is applied. colposcopy Abnormal vascular pattern like punctuate or mosiasim. Biopsy is taken from the most abnormal site. Colposcopy is deemed unsatisfactory if TZ is not viewed adequately. HPV DNA testing: As HPV is the main causative factor of CIN and cervical cancer, recently detection of HPV DNA in serum has been introduced to screening program. HPV TRIAGE strategy includes i. Pap smear test(LBC) ii. HPV Testing iii. Colposcopy The sensitivity of cervical smear in picking up women with CIN is around 70 percent, however, as there is slow progression for most women with CIN to cancer, if a lesion is missed then this should be picked up on subsequent smear. The specifity is 90% . If the test is negative the patient is re-placed on routine recall. HPV VACCINES Recently HPV vaccines have been developed to prevent primary infection with certain oncogenic HPV types (16,18,31,33) from the capsid coat of the virus. Bivalent vaccines(cervarix)against HPV types 16,18 Quadrivalent vaccineL(gardasil) against types 6,11,16,18 Route of adminstration – intramuscular Dose - 0.5ml DOSAGE SCHEDULE – 0,1,6 OR 0,2,6