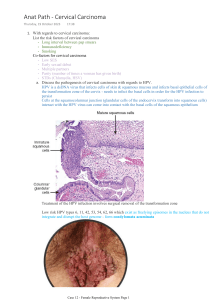
Cervical Carcinoma - Cervical cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the cervix. The most common cervical cancer is squamous cell carcinoma, accounting for 70% of cases. Adenocarcinoma is less common (about 25% of cases) and more difficult to diagnose because it starts higher in the cervix. - An invasive epithelial tumor composed of neoplastic cells with varying degrees of squamous differentiation. Anatomical Site Affected - Most cases arise at the squamous-columnar junction of the cervix. Types of Cervical Carcinomas Squamous cell carcinoma is cancer that occurs in the outermost part of the epidermis (skin surface) or the surface of certain portions of the body (areas of the head and neck or genitalia) known as squamous cells. Adenocarcinoma means you have a type of cancer that starts in the glands that line the inside of one of your organs. Causes Long-lasting infection with certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV) is the main cause of cervical cancer. HPV is a common virus that is passed from one person to another during sex. Almost all cervical cancer cases (99%) are linked to infection with high-risk human papillomaviruses (HPV), an extremely common virus transmitted through sexual contact. Although most infections with HPV resolve spontaneously and cause no symptoms, persistent infection can cause cervical cancer in women. Clinical Features • Abnormal cervical cytology in asymptomatic patients • Cervical mass • Vaginal bleeding or discharge • Pain, urinary symptoms (ureteral obstruction leading to anuria or uremia, hematuria, frequency, vesicovaginal fistula), gastrointestinal symptoms (tenesmus, rectovaginal fistula), lymphedema in the lower extremities in advanced tumors Diagnosis • Histologic examination of biopsy or excisional material List of Medications to Treat Cervical Cancer • Bevacizumab- It is a monoclonal antibody that works by blocking the growth of blood vessels that are needed to support tumor growth. • Bleomycin Sulfate - It stops or slows the growth of cancer cells and other rapidly growing cells by damaging their DNA. • Topotecan Hydrochloride - damages the DNA of cancer cells and other rapidly growing cells, causing them to die. • Pembrolizumab - It works by keeping cancer cells from suppressing the immune system. This allows the immune system to attack and kill the cancer cells. • Tisotumab Vedotin-tftv- It is made of a monoclonal antibody chemically linked to a cancer-killing drug. The monoclonal antibody binds to a protein on the surface of some cancer cells. The linked drug enters these cancer cells and kills them. Tisotumab vedotin may also stimulate the immune system to kill cancer cells. Treatments - Surgery - Chemotherapy - Radiation Therapy