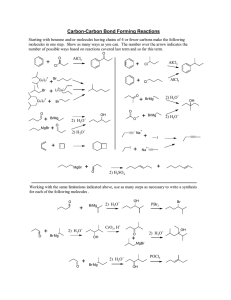
* * *Oxidation increase in oxidation number addition of oxygen removal of hydrogen *Reduction decrease in oxidation number addition of hydrogen removal of oxygen * *Hydrolysis - reaction in the presence of water, acid, base or enzyme. *Tautomerism - interconversion of aldehyde/ketone to alcohol. *Condensation - reaction of two or more substances with the removal of water from the molecules. *CH3CH2OH + O2 → CH3CHO + H2O *(CH3)2CHOH + O2 → (CH3)2C=O + H2O *CH3CHO + H2 → CH3CH2OH * (CH3)2C=O + H2 → (CH3)2CHOH *NADH + H+ → NAD + 2H+ *NAD + 2H+ → NADH + H+ *FAD + 2H+ → FADH2 *FADH2 → FAD + 2H+ * *CH3COOCH3 + H2O → CH3COOH + CH3OH *CH3COOH + CH3OH → CH3COOCH3 + H2O * *pH = -log [H+] *[H+] = inv. log –pH *pH = pKw – pOH *pH = 14 – pOH *[H+] = Kw/[OH-] *[H+] = 1 x 10-14/ [OH-] pOH = - log [OH-] [OH-] = inv. log – pOH pOH = pKw – pH pOH = 14 – pH [OH-] = Kw/[H+] [OH-] = 1x10-14/[H+] Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation: pH = pKa + log A-/HA * * •From the reaction of two water molecules, the following equilibrium constant expression can be written: K = [H3O+][−OH] [H2O]2 •Multiplying both sides by [H2O]2 yields Kw, the ion-product constant for water. Kw = ion-product constant [H3O+][−OH] 7 * •Experimentally it can be shown that [H3O+] = [−OH] = 1.0 x 10−7 M at 25 oC Kw = [H3O+] [−OH] Kw = (1.0 x 10−7) x (1.0 x 10−7) Kw = 1.0 x 10−14 •Kw is a constant, 1.0 x 10−14, for all aqueous solutions at 25 oC. 8 * To calculate [−OH] when [H3O+] is known: To calculate [H3O+] when [−OH] is known: Kw = [H3O+][−OH] [−OH] = Kw = [H3O+][−OH] Kw [H3O+] = [H3O+] −14 1 x 10 [−OH] = [H3O+] Kw [−OH] −14 1 x 10 [H3O+] = [−OH] 9 * If the [H3O+] in a cup of coffee is 1.0 x 10−5 M, then the [−OH] can be calculated as follows: [−OH] = Kw [H3O+] = 1 x 10−14 1 x 10−5 = 1.0 x 10−9 M In this cup of coffee, therefore, [H3O+] > [–OH], and the solution is acidic overall. 10 * 11 * pH = −log [H3O+] The lower the pH, the higher the concentration of H3O+. •Acidic solution: pH < 7 [H3O+] > 1 x 10−7 •Neutral solution: pH = 7 [H3O+] = 1 x 10−7 •Basic solution: pH > 7 [H3O+] < 1 x 10−7 12 * •If [H3O+] = 1.2 x 10–5 M for a solution, what is its pH? pH = –log [H3O+] = –log (1.2 x 10–5) = –(–4.92) = 4.92 •The solution is acidic because the pH < 7. 13 * •If the pH of a solution is 8.50, what is the [H3O+]? pH = −log [H3O+] 8.50 = −log [H3O+] −8.50 = log [H3O+] antilog (−8.50 ) = [H3O+] [H3O+] = 3.2 x 10−9 M •The solution is basic because [H3O+] > 1 x 10–7 M. 14 * 15 * 16 *Refer to the lab workbook. * *Chemical reactions in the cell *Ionization of water *Computations of pH and buffers *pH of body fluids *