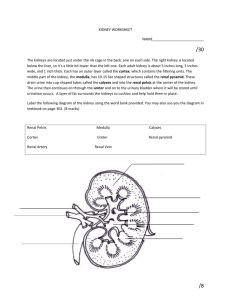
URINARY SYSTEM GENERAL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Learning Objectives 1. Describe the structure of the kidney. 2. List the homeostatic functions of the kidney. 3. Describe the structure of the kidney nephron. 4. Explain the regional functions of the kidney tubule. KIDNEY STRUCTURE Capsule Renal cortex Renal medulla Ureter conducts urine to bladder ORGAN FUNCTIONS: • Fluid balance • Electrolyte balance • Liquid waste removed • Excretion of drugs • Endocrine secretions: erythropoietin renin Vitamin D3 (calcitriol) NEPHRON STRUCTURE Million filtering units cortex medulla Tubule regions include: 1. Bowman’s Capsule (start of tubule) surrounds glomerulus 2. Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) 3. Loop of Henle 4. Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) 5. Collecting Duct (CD) Cortical Nephron is the most common type in humans cortex medulla 2 TYPES OF NEPHRONS Juxtamedullary Nephron maintains hyperosmotic medullary gradient REGIONAL CHANGES IN VOLUME & OSMOLARITY REGIONAL FUNCTIONS Excretion (E) = Amt Filtered (F) - Amt Reabsorbed (R)+ Amt Secreted (S) IMPORTANT TERMS 1. Filtration is the movement of solutes and water from the blood into the lumen of the renal tubule to generate a filtrate. 2. Reabsorption is the movement of solutes and water from the lumen of the renal tubule across the epithelial cells and back into the blood. 3. Secretion is the movement of solutes directly from the blood across the epithelial cells and into the luminal filtrate. 4. Excretion is the removal of solutes and water from the body as urine. GENERAL CONCEPTS 1. The kidneys’ primary functions are to maintain fluid volumes of the body by regulating salt balance and to maintain the osmolarity of the body by regulating water balance. 2. Additional homeostatic functions include removal of wastes and detoxification of drugs. 3. The kidney secretes hormones, including erythropoietin in response to hypoxia, renin in response to low blood pressure, and active Vitamin D3. 4. The kidney contains a million filtration units, called nephrons. Each nephron is fed by a portal system. 5. Filtration occurs across the first capillary bed (glomerulus). Reabsorption and secretion occur along the renal tubule to alter the composition of the filtrate. The final product is urine which leaves the kidney by the ureter.