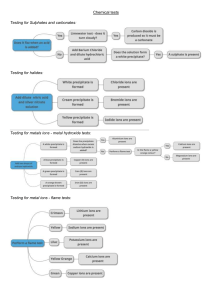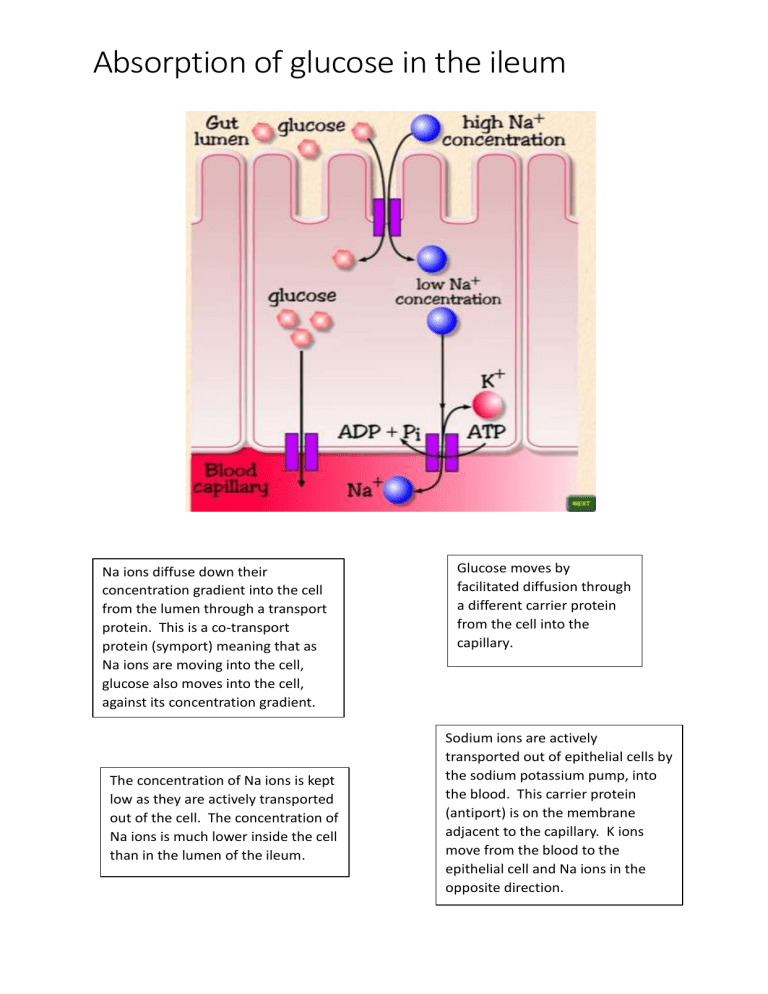
Absorption of glucose in the ileum Na ions diffuse down their concentration gradient into the cell from the lumen through a transport protein. This is a co-transport protein (symport) meaning that as Na ions are moving into the cell, glucose also moves into the cell, against its concentration gradient. The concentration of Na ions is kept low as they are actively transported out of the cell. The concentration of Na ions is much lower inside the cell than in the lumen of the ileum. Glucose moves by facilitated diffusion through a different carrier protein from the cell into the capillary. Sodium ions are actively transported out of epithelial cells by the sodium potassium pump, into the blood. This carrier protein (antiport) is on the membrane adjacent to the capillary. K ions move from the blood to the epithelial cell and Na ions in the opposite direction.